Positron Emission Tomography Scan
A PET scan is similar to a bone scan, in that a slightly radioactive substance is injected into the blood, which can then be detected with a special camera. But PET scans use different tracers that collect mainly in cancer cells. The most common tracer for standard PET scans is FDG, which is a type of sugar. Unfortunately, this type of PET scan isnt very useful in finding prostate cancer cells in the body.
However, newer tracers, such as fluciclovine F18, sodium fluoride F18, and choline C11, have been found to be better at detecting prostate cancer cells.
Other newer tracers, such as Ga 68 PSMA-11 and 18F-DCFPyl , attach to prostate-specific membrane antigen , a protein that is often found in large amounts on prostate cancer cells. Tests using these types of tracers are sometimes referred to as PSMA PET scans.
These newer types of PET scans are most often used if its not clear if prostate cancer has spread. For example, one of these tests might be done if the results of a bone scan arent clear, or if a man has a rising PSA level after initial treatment but its not clear where the cancer is in the body.
The pictures from a PET scan arent as detailed as MRI or CT scan images, but they can often show areas of cancer anywhere in the body. Some machines can do a PET scan and either an MRI or a CT scan at the same time, which can give more detail about areas that show up on the PET scan.
How Long Does It Take To Recover From A Prostate Biopsy
A patient may take about four to six weeks or even more recover after a prostate biopsy. The recovery process after biopsy usually depends on the patient’s health and age. Doctors may recommend only light activities for 24-48 hours after a prostate biopsy. The doctor prescribes painkillers, vitamins, and antibiotics for a few days to speed up the healing process.
After the biopsy, it is normal to experience the following sensations or symptoms:
- Burning urination: It may start within 24 hours after the biopsy and may continue until three to seven days. This burning sensation is a side effect of the procedure and usually considered normal.
- Frequent urination: It may gradually improve over the first 24-36 hours.
- Blood in the urine: It is considered normal to have slightly red-tinged urine or urine that resembles the color of a rose or red wine. This may last from 12 hours to 3 weeks after the biopsy.
- Blood in stool: A patient may notice red stains on the toilet tissue or see some bloody streaks in the stool. This may last for up to five days.
- Blood in the semen: This may persist for up to six weeks after the biopsy.
- Tiredness: A patient may feel tired for a month or two. It usually takes 30-45 days to regain full normal strength after the procedure hence, sufficient rest is usually advised by the doctor.
Post-biopsy restrictions and instructions:
How Do You Prepare For A Prostate Biopsy
Your doctor will get you tested for urinary tract infections . If UTI is detected, the biopsy will be postponed till the infection clears with antibiotics.
You need to stop taking blood-thinning medications such as aspirin and warfarin and any other medications as advised by your doctor several days before the surgery.
Your doctor or nurse may instruct you to take an enema before the procedure. This helps to keep the bowels clean during the surgery.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Osteoblastic Or Osteolytic
How Does The Procedure Work
Ultrasound procedure:
Ultrasound imaging uses the same principles as the sonar that bats, ships, and fishermen use. When a sound wave strikes an object, it bounces back or echoes. By measuring these echo waves, it is possible to determine how far away the object is as well as its size, shape, and consistency. This includes whether the object is solid or filled with fluid.
Doctors use ultrasound to detect changes in the appearance of organs, tissues, and vessels and to detect abnormal masses, such as tumors.
In an ultrasound exam, a transducer both sends the sound waves and records the echoing waves. When the transducer is pressed against the skin, it sends small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body. As the sound waves bounce off internal organs, fluids and tissues, the sensitive receiver in the transducer records tiny changes in the sound’s pitch and direction. A computer instantly measures these signature waves and displays them as real-time pictures on a monitor. The technologist typically captures one or more frames of the moving pictures as still images. They may also save short video loops of the images.
MRI procedure:
A computer processes the signals and creates a series of images, each of which shows a thin slice of the body. The radiologist can study these images from different angles.
MRI is often able to tell the difference between diseased tissue and normal tissue better than x-ray, CT, and ultrasound.
How Should I Prepare
Prior to a prostate biopsy, tell your doctor about all the medications you take, including herbal supplements. List any allergies , recent illnesses, and other medical conditions.
You may need to stop taking blood thinners for seven to 10 days before the procedure. This will help prevent excessive bleeding during and after the biopsy. The doctor may check your blood clotting on the day of the procedure. Ask your doctor and the hospital radiology clinic or department for more information.
You may need to take oral antibiotics a day before and the morning of the biopsy. This will help prevent infection.
If you are having an MRI-guided biopsy, you will need to wear metal-free clothing and remove any metallic objects, such as jewelry, watches, and hearing aids.
A technologist will walk through an MR imaging safety checklist with you. Tell your technologist about prior surgeries and metal implants, such as pacemakers, aneurysm clips, and joint replacements.
An MRI-guided procedure may use an injection of gadolinium contrast material. Because gadolinium does not contain iodine, it can be used safely in patients with contrast allergies.
Your MRI procedure may use an endorectal coil. This is a thin wire covered with a latex balloon. The doctor will lubricate this assembly and gently insert it into your rectum. Tell the doctor if you are allergic to latex so they may cover the coil with a latex-free balloon.
Read Also: How Are Fiducial Markers Placed In The Prostate
How We Approach Prostate Biopsies And Prostate Cancer Diagnosis At Ctca
When you come to CTCA for a prostate biopsy or a second opinion, youll have access to tests that may help increase the accuracy of each biopsy. Our team has expertise with these tests and procedures, allowing us to work quickly and efficiently.
If youre diagnosed with prostate cancer, a multidisciplinary team of genitourinary experts, which may include a urologist, a urologic oncologist, a radiation oncologist and a medical oncologist, will review your case and develop a personalized plan based on your specific circumstances and needs.
We only treat cancer at CTCA, which means our cancer experts are skilled at assessing risk associated with each persons circumstances. We give you the pros and cons of the treatment options available to you, allowing you time to talk with your team of doctors and other experts about those options.
Our cancer experts are also vigilant about what patients need and when they need it. We know that when men are told they have slow-growing prostate cancer, some of them wont keep up with the necessary follow-ups, so we help keep them on track.
If you choose to receive treatment with us, you may benefit from our integrative approach to cancer treatment. Our multidisciplinary team works together to help prevent and manage the side effects of cancer and its treatment, providing supportive care services, such as:
What Happens In A Prostate Biopsy
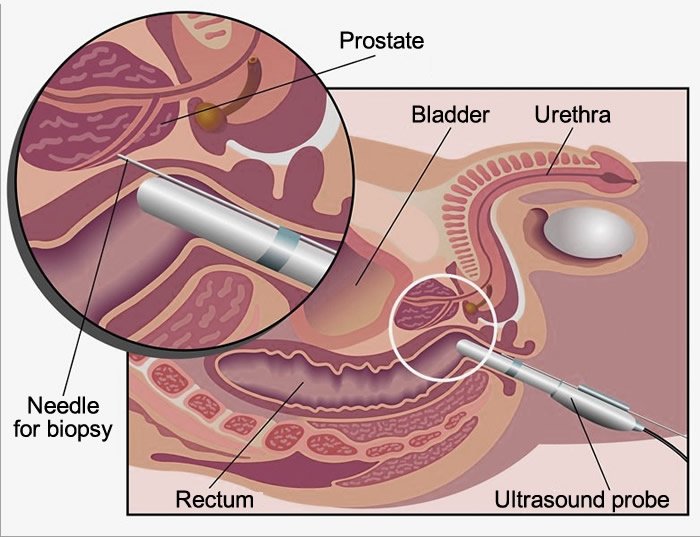
You will need to lie down on your side. Then you will be asked to bring your knees up to your chest. Next, the doctor will apply gel and gently insert a thin probe into your rectum.
Transrectal ultrasonography uses sound waves to take pictures of your prostate. Your doctor will use these pictures to know where they need to give you an injection, which will make it less painful when they take the tissue sample. They also use images to guide the needle into place.
Once the area is numbed, there will be a device. There are lots of needles on it. The doctor will put them in your skin. It can make you feel uncomfortable for a second, but it is over quickly.
Your doctor might take a sample from your prostate to see what it is. Then, they will use an instrument called a biopsy gun to take the samples. It should only take about 20 minutes.
After a prostate biopsy, your doctor will tell you only to do light activities for 24 to 48 hours. After that, your doctor might recommend taking antibiotics for a few days.
- Fever
- Worsening pain
Recommended Reading: Is Cialis Good For Bph
To 7 Days Before Your Procedure
You may need to stop taking some of your usual medications before your surgery. Examples include anticoagulants, aspirin, medications that contain aspirin, and vitamin E. Follow your healthcare providers instructions.
You can read about medications that contain aspirin and vitamin E in the resource Common Medications Containing Aspirin, Other Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs , or Vitamin E.
Other Types Of Prostate Biopsies
While the transrectal prostate biopsy is the most common, there are other types of biopsies that your urologist may perform.
Transperineal biopsy
Done under local or general anesthesia, this biopsy takes prostate samples by inserting a needle through the skin of the perineum . As this procedure allows a larger area of tissue to be examined than a transrectal biopsy, your urologist may order one if they think you have cancer despite a negative transrectal biopsy.
Transurethral biopsy
Done under local or general anesthesia, this biopsy goes through the urethra to collect the prostate samples. To do this, the urologist inserts a thin tube with a camera attached into the penis. A surgical tube is then passed through the cystoscope to collect the samples.
Recommended Reading: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
When Is A Prostate Biopsy Done
Physicians may order a prostate biopsy in a few situations:
- Abnormalities in a rectal examination: General practicioners perform these physical prostate exams–during which they use a gloved, lubricated finger inserted into the rectum to look for unusual tissue growth–as part of a man’s annual check-up. When doctor feel a lump or something else abnormal during a rectal exam, they typically order a prostate biopsy.
- Elevated blood levels of prostate-specific antigen : PSA is a protein produced by the prostate. Historically, physicians believed that high PSA levels may indicate the presence of prostate cancer and ordered it as a routine screening test. However, a growing body of research has shown that high levels of PSA may be associated with other conditions, such as prostatitis. If elevated PSA is accompanied by other symptoms, a biopsy can determine whether prostate cancer is present.
What Can You Expect During A Prostate Ultrasound And Biopsy
The procedure is short and generally only takes about 10 minutes. Your urologist, a doctor specializing in mens genital and urinary problems, will perform the procedure.
- Upon arrival in the examination room, you will be given antibiotics to prevent infection.
- You will be asked to lie on your side and bring your knees to your chest.
- The area being tested may be numbed to help reduce any discomfort.
- A lubricated probe is inserted into the rectum to generate the ultrasound.
- A small needle is inserted through the probe to take several tiny tissue samples from the prostate. Some men may feel mild pressure or discomfort during the procedure.
- After tissue samples are taken, they are sent to a lab for an analysis.
Read Also: Chemo Pills For Prostate Cancer
Biopsy During Surgery To Treat Prostate Cancer
If there is more than a very small chance that the cancer might have spread , the surgeon may remove lymph nodes in the pelvis during the same operation as the removal of the prostate, which is known as a radical prostatectomy .
The lymph nodes and the prostate are then sent to the lab to be looked at. The lab results are usually available several days after surgery.
Coping With Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is a common side effect of prostate cancer treatments. Generally, erectile function improves within two years after surgery. Improvement may be better for younger men than for those over age 70. You also may benefit from ED medications. Other treatments, such as injection therapy and vacuum devices, may help.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Female Version Of A Prostate
Controversies And Misconceptions Surrounding Prostate Biopsies
The PSA test measures the levels of PSA proteins in the body, and when it was first developed, it was quickly implemented by many physicians as a screening test for prostate cancer. The thought was that since PSA proteins are only produced by the prostate, elevated levels could be an indication of prostate cancer. As a result, most men with an abnormal PSA test underwent a prostate biopsy.
The increase in biopsies resulted in the number of advanced, untreatable prostate cancers decreasing significantly because more prostate cancers were caught earlier, when the disease is easier to treat. But the problem with many patients being diagnosed sooner was that some patients were being aggressively treated when they should have been monitored instead.
Though many in the field of urology believe it was flawed, a controversial study attempted to assess the benefits of the PSA test as a screening tool for prostate cancer, and its results led to the recommendation that most men shouldn’t get the test because it didnt appear to improve mortality rates from prostate cancer. This, combined with growing awareness that many cases of prostate cancer were being treated unnecessarily or prematurely, led to a reduction in prostate biopsies. This controversy led to a reduction in prostate cancer screening and an increase in the number of diagnoses of advanced prostate cancer.
What Happens After A Prostate Biopsy
Your recovery process will vary depending on the type of anesthesia that isused. If you were given general anesthesia, you will be taken to a recoveryroom for observation. Once your blood pressure, pulse, and breathing arestable and you are alert, you will be taken to your hospital room ordischarged to your home.
If local anesthetic was used, you may go back to your normal activities anddiet unless otherwise instructed. You may feel the urge to urinate or havea bowel movement after the biopsy. This feeling should pass after a fewhours.
There may be blood in your urine or stool for a few days after the biopsy.This is common. Blood, either red or reddish brown, may also be in yourejaculate for a few weeks after the biopsy. This, too, is normal.
The biopsy site may be tender or sore for several days after the biopsy.Take a pain reliever for soreness as recommended by your healthcareprovider. Aspirin or certain other pain medicines may increase the chanceof bleeding, so be sure to take only recommended medicines.
-
Increase in the amount of blood in your urine or stool
-
Belly or pelvic pain
-
Trouble urinating
-
Changes in the way your urine looks or smells or burning with urination
-
Fever and/or chills
Your healthcare provider may give you other instruction, depending on yoursituation.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Definition Of Prostate
Temporary Effects On Your Bowel Movements Urine And Semen
- You might see blood in your bowel movements. You might also have a small amount of bleeding from your rectum. These can happen right after your procedure or for the next few days when you have a bowel movement.
- You might see blood in your urine for 7 to 14 days after your procedure. This bleeding might come and go.
- Your semen might look rust-colored for up to 12 weeks after the biopsy. This is because small amounts of blood might be in it.
Donât Miss: How To Reduce Prostate Swelling Naturally
Painful Prostate Biopsy Heres What You Need To Know
A standout amongst the most famous symptomatic tests performed to recognize Prostate Cancer is Biopsy. If you are experiencing pee issues, erectile brokenness, or any prostate-related indications and would look for medical counsel from a medical expert, the standard suggestion would either be for you to experience the PSA test first then Prostate Biopsy or the last quickly.
Don’t Miss: Fiducial Marker Placement Prostate
How Is The Biopsy Procedure Performed
Ultrasound-guided biopsy procedure:
The ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy is carried out by a radiologist or urologist, assisted by a sonographer and often a nurse who helps look after the patient.
You may have a small enema inserted into your rectum half an hour or so before the procedure to clean out your bowels and clear the rectum of feces so that the prostate may be seen more clearly with the ultrasound and to lower the risk of infection.
The procedure is often carried out after you have been given a light general anesthetic, which means you will be asleep or sedated during the procedure. If the procedure is carried out using an anesthetic, an anesthesiologist will be present.
During the procedure, you will be asked to lie on your left side with your legs bent.
The physician will first carry out a DRE with a gloved finger.
An ultrasound probe will then be inserted into your rectum. The probe is sterilized, covered with condoms to ensure protection from any infection or contamination, and lubricated to help it glide easily into your rectum.
After examination of your prostate with the ultrasound, the physician will perform the biopsy. Pictures or images the physician can see on the ultrasound screen are used to guide a very fine needle, through the wall of your rectum into the prostate and take a sample of tissue. With continuous ultrasound imaging, the physician is able to view the biopsy needle as it advances to the prostate in real time.
MRI-guided biopsy procedure:
