Questions To Ask Your Doctor Or Nurse
- What type of hormone therapy are you offering me and why?
- Are there other treatments I can have?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of my treatment?
- What treatments and support are available to help manage side effects?
- Are there any lifestyle changes that might help me manage my cancer, symptoms, or side effects?
- How often will I have check-ups and what will this involve?
- How will we know if my cancer starts to grow again?
- What other treatments are available if that happens?
- Can I join any clinical trials?
- If I have any questions or get any new symptoms, who should I contact?
What Is The Difference Between Prostate Cancer And Advanced Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland begin to grow out of control. In the early stages of prostate cancer, the cancer cells are only present in the prostate and have not spread to nearby tissues.
Advanced prostate cancer, also known as stage 4 prostate cancer, occurs when cancer cells have spread to other areas of the body.
Are Older Men Undertreated
Schwartz and colleagues44 reviewed the treatment decisions and factors influencing them in a cohort of men with localized prostate cancer. Age, comorbidity, and Gleason score were found to be independent predictors of suboptimal treatment. It was concluded that most men older than 70 years with moderately or poorly differentiated tumors and no to mild comorbidity were given suboptimal treatment. Most of these men were undertreated, receiving watchful waiting therapy when potentially curative therapy could have been applied. With optimal treatment, clinical outcomes could have been improved.
Thompson and colleagues46 investigated otherwise healthy octogenarians diagnosed with prostate cancer who underwent radical prostatectomy. At the last follow-up visit, 10 patients had survived more than a decade after surgery, and 3 patients had died within 10 years of surgery. The remaining 6 patients were alive at less than 10 years of follow-up. Seventy-four percent of patients were continent. No patient had died of prostate cancer, and the 10-year, all-cause survival rate was similar to that observed in healthy patients 60 to 79 years old undergoing radical prostatectomy. These findings indicate that careful selection of patients even older than 80 years can achieve satisfactory oncologic and functional outcomes after surgery. It is important to note, however, that the rate of urinary incontinence after surgery exceeds that of younger counterparts.
Read Also: Lupron Treatment For Prostate Cancer
Radiation A Contributing Cause
Aksnessæther believes the increased risk of bladder cancer may have several causes.
Radiation to this area of the body is definitely a contributing cause. But we also know that patients who get radiation live longer and the increased life expectancy itself gives them a greater likelihood that they will develop another type of cancer, Aksnessæther says.
Patients who received both radiation and hormone therapy lived an average of 15.3 years after treatment, while those who received hormone therapy only lived for 12.8 years after treatment. The patients were 67 years on average when they were included in the study.
Some of the patients who had initially been given only hormone treatment were offered the opportunity to receive radiation therapy afterwards as it became clear that this resulted in better survival.
This group, which received so-called salvage radiation treatment, actually had the best survival of all, and the lowest risk of secondary cancer, says the researcher.
The researchers believe there are two reasons for this.
It took about seven years before these patients received radiation treatment, which means that we dont have such a long follow-up time after the radiation. In addition, this was probably a select group, meaning a resourceful and healthy group of men, since they were offered new treatment. Thus, they are basically more likely to live longer than the others, she says.
Read Also: Most Common Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Causes Of Advanced Prostate Cancer
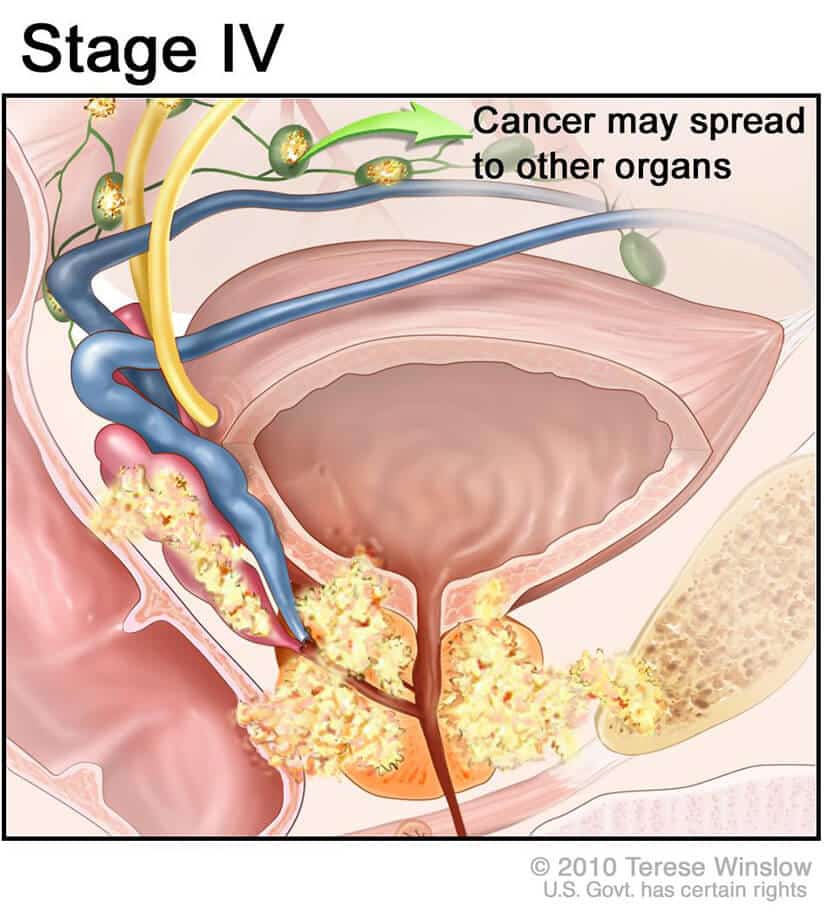
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men in the UK. It is more common over the age 65. Although it can happen at a younger age it is uncommon under 50. People who have a prostate include men, transwomen and people assigned male at birth. If you are a trans woman and have had genital gender affirming surgery as part of your transition, you still have a prostate. Trans men do not have a prostate. It is important to talk to your GP or nurse if you are worried about prostate cancer or have symptoms.
We have more information about the risk factors of prostate cancer.
Also Check: Cold Medicine For Enlarged Prostate
When Is Prostate Cancer Advanced
Once the prostate cancer has moved outside of the prostate gland, it is considered advanced. It could spread to the lymph nodes, nearby tissues, other parts of the body and even the bones. It becomes metastatic prostate cancer once it has gone beyond the tissues that are adjacent to the prostate gland.
Even though this type of cancer can metastasize anywhere in the body around 80 percent of the time it moves to the spine, hips, and pelvis. The cells grow very fast and because they started out in the prostate, it is still considered prostate cancer.
Factors That Increase Risk Of Recurrence
There are many different factors that can help you determine what your risk of recurrence is. Your doctor will go over these during the initial course of treatment, therefore stressing the importance of follow up appointments.
One factor is the involvement of your lymph nodes. If your cancer has metastasized to your lymph nodes, recurrence is more likely. Similarly, the larger the tumor, the more likely that you are to experience complications and rates of recurrence. If the tumor is intertwined or growing into other areas of your body, this also increases risk. The Gleason score is a system of grading your prostate cancer based on severity and localization. The higher the grade, the more likely youll experience recurrence. Finally, the stage of prostate cancer affects recurrence rates. When caught early, recurrence is not as likely as cancers that are in stage three or four.
Cancer can be extremely aggressive and will change your life forever. Make sure that youre doing everything you can to avoid potential problems. Eat well, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. Strengthening your immune system is a great way to reduce your risk of recurrence.
Read Also: Natural Remedies For Dog Prostate Problems
Treating Stage Iii Colon Cancer
Stage III colon cancers have spread to nearby lymph nodes, but they have not yet spread to other parts of the body.
Surgery to remove the section of the colon with the cancer along with nearby lymph nodes, followed by adjuvant chemo is the standard treatment for this stage.
For chemo, either the FOLFOX or CapeOx regimens are used most often, but some patients may get 5-FU with leucovorin or capecitabine alone based on their age and health needs.
For some advanced colon cancers that cannot be removed completely by surgery, neoadjuvant chemotherapy given along with radiation might be recommended to shrink the cancer so it can be removed later with surgery. For some advanced cancers that have been removed by surgery, but were found to be attached to a nearby organ or have positive margins , adjuvant radiation might be recommended. Radiation therapy and/or chemo may be options for people who arent healthy enough for surgery.
> > > This Simple Morning Test Will Fix Your Prostate
Another type of prostate issue is chronic prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This condition causes pain in the lower back and groin area, and may cause urinary retention. Symptoms include leaking and discomfort. In severe cases, a catheter may be required to relieve the symptoms. If the problem is unresponsive to other treatments, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure. If these do not work, your symptoms could progress and become chronic.
An acute bacterial infection can cause a burning sensation. Inflammation of the prostate can affect the bladder and result in discomfort and other symptoms. This is the most common urinary tract problem in men under 50, and the third most common in men over 65. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of CPPS. Patients may experience a fever or chills as a result of the infection.
Also Check: Removal Of Prostate And Side Effects
Your Cancer Care Team
People with cancer should be cared for by a multidisciplinary team . This is a team of specialists who work together to provide the best care and treatment.
The team often consists of specialist cancer surgeons, oncologists , radiologists, pathologists, radiographers and specialist nurses.
Other members may include physiotherapists, dietitians and occupational therapists. You may also have access to clinical psychology support.
When deciding what treatment is best for you, your doctors will consider:
- the type and size of the cancer
- what grade it is
- whether the cancer has spread to other parts of your body
Staging Of Prostate Cancer
Doctors will use the results of your prostate examination, biopsy and scans to identify the stage of your prostate cancer .
The stage of the cancer will determine which types of treatments will be necessary.
If prostate cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, the chances of survival are generally good.
You May Like: Where Is The Prostate Gland And What Is Its Function
Can People With Advanced Prostate Cancer Enroll In Clinical Trials
Major organizations such as the National Comprehensive Cancer Network recommend this course of action for all cancer patients. Researchers are exploring several new ways of diagnosing, monitoring, and treating prostate cancer. Clinical trials test the safety and effectiveness of these new methods and treatments. There are risks and limitations in every clinical trial. For example, you may be assigned to the control group, and not get the new medicine. In that case, the control medicine is the best therapy already available. Placebo or ineffective treatment is rarely if ever used anymore, and if it will be used in the trial, you would be informed. Keep in mind that the new medicine under investigation in the clinical trial may not work. But clinical trials also offer early access to new treatments.
You can find out more about clinical trials by asking a medical oncologist, inquiring at an academic medical center, or browsing a clinical trials listing service. The National Institutes of Health lists clinical trials at www.clinicaltrials.gov.
Show Sources
Immunotherapy For Prostate Cancer
Immunotherapy is a cure for prostate cancer in the shape of a vaccine. This treatment relies on training the patients white cells into recognizing and fighting prostate cancer cells.
On the other hand, this care plan is not an ideal fit for any stage of prostate cancer. On the contrary, immunotherapy usually works by increasing the survival span in patients with advanced cases where the symptoms are sparse or none at all.
Don’t Miss: What Age Is Prostate Cancer Common
Surgery For Prostate Cancer
This treatment option for prostate cancer is usually made available to otherwise healthy patients. Tumors have to be of negligible dimensions and be attached only to the prostate gland in order to be eligible for removal through a surgical procedure.
A prostatectomy is a primary treatment that can cure prostate cancer by extracting the prostate gland and some tissue adjacent to it, depending on the case. However, even after a successful outcome, cancer can relapse if the PSA levels go back above 4.0.
The side effects of this treatment range from erectile dysfunction to a loss of bladder control. Patients need to talk their options through with their doctors in order to make an informed decision.
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Your healthcare provider uses the Gleason score and Grade Groups to stage prostate cancer based on its projected aggressiveness. To get this information, the pathologist:
- Assigns a grade to each type of cell in your sample. Cells are graded on a scale of three to five . Samples that test in the one to two range are considered normal tissue.
- Adds together the two most common grades to get your Gleason score .
- Uses the Gleason score to place you into a Grade Group ranging from one to five. A Gleason score of six puts you in Grade Group 1 . A score of nine or higher puts you in Grade Group five . Samples with a higher portion of more aggressive cells receive a higher Grade Group.
Also Check: Can You Climax After Prostate Removal
Cancer That Clearly Has Spread
If the cancer has spread outside the prostate, it will most likely go to nearby lymph nodes first, and then to bones. Much less often the cancer will spread to the liver or other organs.
When prostate cancer has spread to other parts of the body , hormone therapy is probably the most effective treatment. But it isnt likely to cure the cancer, and at some point it might stop working. Usually the first treatment is a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonist, LHRH antagonist, or orchiectomy, sometimes along with an anti-androgen drug or abiraterone. Another option might be to get chemotherapy along with the hormone therapy. Other treatments aimed at bone metastases might be used as well.
What Are Male Sex Hormones
Hormones are signaling molecules produced by several glands that flow in the bloodstream and influence the growth and development of cells and organs. Androgen is a male sex hormone that controls the development and regulation of male characteristics. The androgens that are most abundantly found in males are testosterone and dihydrotestosterone . Androgens are crucial for the normal growth and functioning of the prostate gland.
On the other hand, androgens also play a vital role in the growth of prostate cancer. Androgens promote the growth and development of both normal and cancerous cells without any discrimination. They do so by binding and activating the androgen receptors . Once these androgen receptors are activated, they stimulate the expression of genes that promotes the growth of prostate gland cells.
Read Also: Can Prostate Cause Erectile Dysfunction
How To Make The Right Treatment Decision
Current expert guidelines for treatment of localized prostate carcinoma recommend potentially curative therapy for patients whose life expectancy is at least 10 years.12,14 Patients with limited life expectancy are more likely to die from health conditions other than prostate cancer. Men with a life expectancy of more than 10 years are more likely to die from progressive prostate cancer.14 This 10-year rule enjoys broad acceptance among urologists and radiation oncologists.15,16
Conservative management proved to be an acceptable treatment option for men with low-grade Gleason scores, clinically localized disease, and life expectancies of less than 10 years. Increasing age was described as a risk factor for receiving inadequate treatment for prostate cancer.17 Thus, older men have been shown to receive potentially curative therapy less often than younger men.18,19 Radical prostatectomy is preferred treatment in men younger than 70 years, whereas radiation therapy is applied predominantly in patients older than 70 years. Conservative therapy such as watchful waiting or androgen deprivation by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogs is preferentially applied in men older than 80 years. Watchful waiting or hormonal therapy is used to treat 82% of men older than 80 years.
Surgically Removing The Prostate Gland
A radical prostatectomy is the surgical removal of your prostate gland. This treatment is an option for curing prostate cancer that has not spread beyond the prostate or has not spread very far.
Like any operation, this surgery carries some risks, such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
In extremely rare cases, problems arising after surgery can be fatal.
Its possible that prostate cancer can come back again after treatment. Your doctor should be able to explain the risk of your cancer coming back after treatment, based on things like your PSA level and the stage of your cancer.
Studies have shown that radiotherapy after prostate removal surgery may increase the chances of a cure, although research is still being carried out into when it should be used after surgery.
You may want to ask your doctors about storing a sperm sample before the operation so it can be used later for in vitro fertilisation .
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
You May Like: What Does Prostate Stimulation Feel Like
Who Is At Risk For Advanced Prostate Cancer
The exact cause of prostate cancer isnt clear. Your risk of developing this particular cancer increases after you reach age 50.
Certain groups are more likely to develop aggressive forms of prostate cancer, including African-American men and men who carry certain inherited genetic mutations such as BRCA1, BRCA2, and HOXB13.
Most men with prostate cancer dont always have a family history of the disease. But having a father or brother with prostate cancer more than
You probably wont need all of these tests. Your doctor will choose the tests based on your symptoms and physical exam.
If any of the images reveal abnormalities, it doesnt necessarily mean that you have cancer. Additional testing may be necessary. If they find a mass, your doctor will probably order a biopsy.
For a biopsy, your doctor will use a needle to remove samples from the suspicious area. A pathologist will then analyze the removed cells under a microscope to see if theyre cancerous. The pathologist can also determine if you have an aggressive form of prostate cancer.
