Stage 4 Prostate Cancer: Symptoms And Treatment
Prostate cancer is a common ailment in older adults. It is currently the most commonly diagnosed cancer type in males. It is also the second cause of cancer-related death in males.
But not all types of prostate cancer are dangerous, and only aggressive cancer leads to advanced disease.
Every step in the clinical management of prostate cancer is complex and highly variable. From screening to watchful waiting and advanced prostate cancer management, almost everything related to this disease is currently not carved in stone. New advances and statistics contribute to advancing our understanding of the disease. Thus, management guidelines are always subject to change.
In this article, were reviewing the state-of-art in advanced prostate cancer management. Stage 4 prostate cancer causes a variety of health problems and complications. Thus, it is essential to identify and understand the disease to prevent late-stage cancer in high-risk patients.
In this article, were reviewing the state-of-art in advanced prostate cancer management. Stage 4 prostate cancer causes a variety of health problems and complications. Thus, it is essential to identify and understand the disease to prevent late-stage cancer in high-risk patients.
What Is My Outlook
If youre diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may want to know how well your treatment is likely to control your cancer and for how long it will control it. This is sometimes called your outlook or prognosis. But not all men will want to know this.
While it isnt possible to cure advanced prostate cancer, treatments can help keep it under control, often for several years. Treatments will also help manage any symptoms, such as pain.
No one can tell you exactly what your outlook will be, as it will depend on many things such as where the cancer has spread to, how quickly it has spread, and how well you respond to treatment. Some men may not respond well to one treatment, but may respond better to another. And when your first treatment stops working, there are other treatments available to help keep the cancer under control for longer. Speak to your doctor about your own situation and any questions or concerns you have.
How Will My Cancer Be Monitored
Your doctor will talk to you about how often you should have check-ups. At some hospitals, you may not have many appointments at the hospital itself. Instead, you may talk to your doctor or nurse over the telephone. You might hear this called self-management.
You will have regular PSA tests. This is often a useful way to check how well your treatment is working. Youll also have regular blood tests to see whether your cancer is affecting other parts of your body, such as your liver, kidneys or bones.
You might have more scans to see how your cancer is responding to treatment and whether your cancer is spreading.
Your doctor or nurse will also ask you how youre feeling and if you have any symptoms, such as pain or tiredness. This will help them understand how youre responding to treatment and how to manage any symptoms. Let them know if you have any side effects from your treatment. There are usually ways to manage these.
Also Check: What Does Prostate Cancer Mean
Read Also: How Often Should You Check For Prostate Cancer
What If You Have Metastatic Castration
This means you have a type of metastatic prostate cancer thatâs able to grow and spread after you had hormone therapy to lower your testosterone levels.
Still, most people with mCRPC stay on androgen deprivation therapy because it might still be effective against some prostate cancer cells.
Your doctor may recommend adding other treatments like:
- Treatments to ease symptoms like pain
You could also find out if a clinical trial might be right for you.
Some people with mCRPC simply choose to try active surveillance or watchful waiting.
The Role Of Biochemical Markers
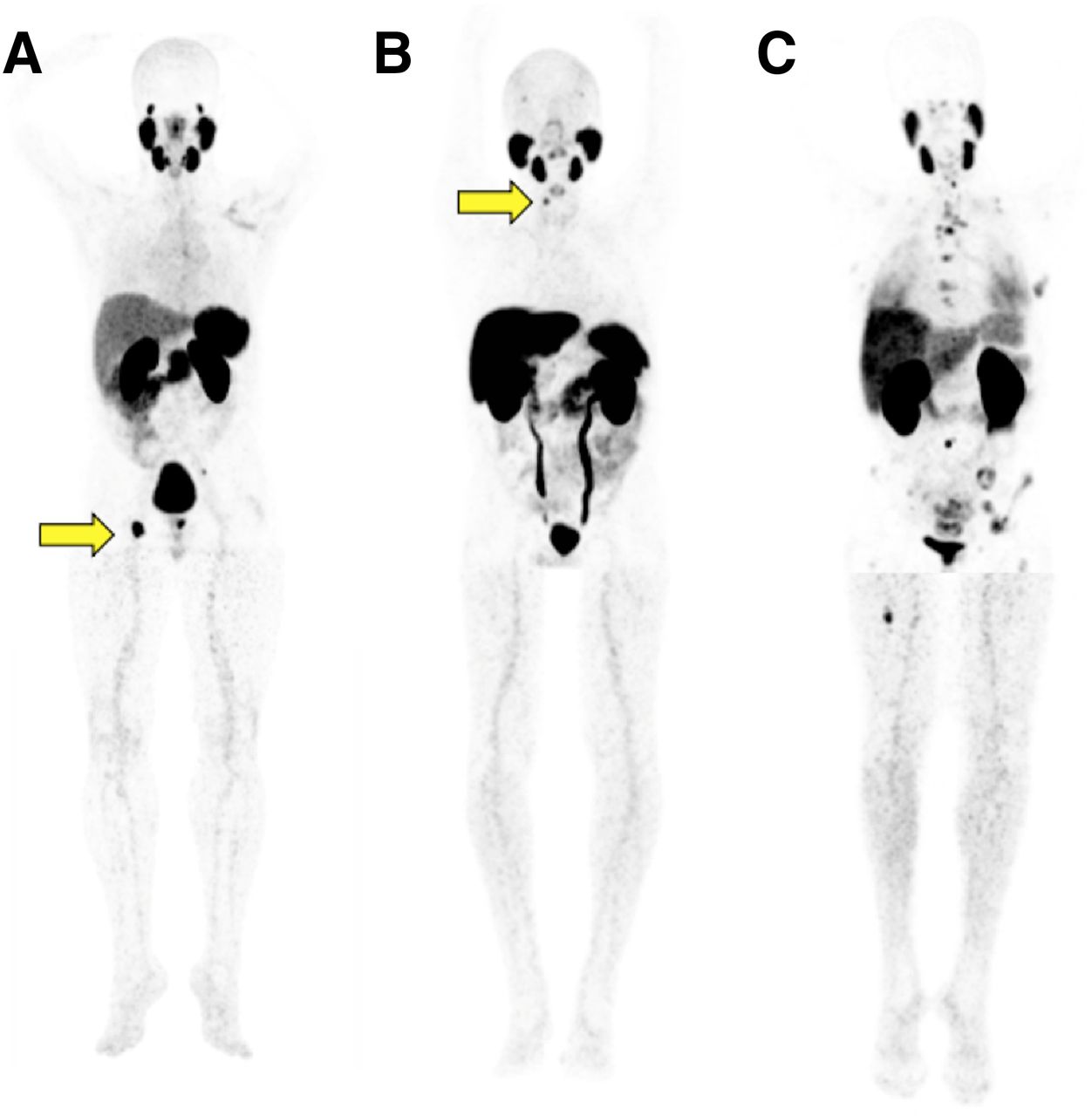
Urokinase, a member of serine proteases that also function as a growth factor to osteoblastic cells, is believed to play a catalytic role in the metastasis of prostate cancer to the skeleton and extraskeletal sites. In a model of urokinase overexpression, Copenhagen rats inoculated with MatLyLu rat prostate carcinoma cells transfected with plasmids encoding overexpression of urokinase were investigated for the pattern of metastasis . The study outcomes revealed significantly earlier and more widespread development of bone metastasis in the ribs, scapula, and femora of rats inoculated with pYN-ruPA as compared to the control that manifested metastasis only in the lumbar vertebrae at 2021 days post inoculation. Biochemical assay and histological evaluation revealed an accompanying progressive increase in serum ALP level and osteoblastic activity compared to the control animals .
Also Check: What Is The Success Rate Of Prostate Surgery
What Are My Treatment Options With Advanced Prostate Cancer
The treatments your doctor recommends will depend on factors specific to you, from your overall health to how advanced your cancer was when it was first diagnosed.
Many men receive ADT, a type of hormone therapy, which deprives the body of the male hormones that the cancer needs to keep growing.
For most men, however, hormone therapy stops working at some point. Alternatives to hormone therapy were approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2018, and Tagawa often starts men on these therapies as soon as theyre diagnosed with bone metastases. Other treatment options may be available through clinical trials.
In addition, chemotherapy, surgery, and immunotherapy as well as radiation treatments, like external beam radiation, which directly target bone problems may be considered. Major cancer centers, such as Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City and MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, have teams of prostate cancer specialists, as well as sophisticated radiation and other treatment equipment consolidated in one place, which can help with the coordination of care.
Donât Miss: What Is The Treatment For Prostate Cancer That Has Spread
Multivariate Regression Logistic Analysis
In the multivariate analyses, the BGS, cTx, tPSA, and ALP were the only independent predictors of BM . Model A combined the BGS , cTx , tPSA, and ALP and presented an AUC of 0.899 . Model B combined the BGS , cTx , tPSA, and ALP and presented an AUC of 0.870 . Model C combined the BGS , cTx , tPSA, and ALP and presented an AUC of 0.902 . Model D combined the BGS , cTx , tPSA, and ALP and presented an AUC of 0.877 . The AUC of model C was larger than that of models A, B and D. Based on model C, the optimized model combined the BGS , cTx , tPSA, and ALP and presented an AUC of 0.910 , which was the largest AUC obtained from the five models . The NRI was 9.64% compared with model C . In the logistic regression prediction analysis, model E remained independently associated with a significantly increased risk of BGS , cTx , tPSA , and ALP . A nomogram was generated to directly calculate the probability of bone metastasis , and the calibration curve showed the degree of height fitting of the nomogram-predicted probability with the actual probability .
Table 3
The multivariate logistic regression analysis results were summarized using the following equation:
Logit = -2.572 + 0.723GS + 2.418T + 0.003tPSA + 3.093ALP
Figure 4
ROC curves of the multivariate regression logistic analysis models. Comparison of ROC curves for models A-E. Model A, AUC: 0.899 , model B, AUC: 0.870 , model C, AUC: 0.902 , model D, AUC: 0.877 , model E, AUC: 0.910 .
Also Check: How Does Prostate Cancer Treatment Affect The Reproductive System
How Long Does It Take For Prostate Cancer To Metastasize To Bone
prostate cancerspreadspread to bonesbones
The cancer cells spread to the bones by breaking away from the prostate gland and escaping attack from your immune system as they travel to your bones. These cancer cells then grow new tumors in your bones. Cancer can spread to any bone in the body, but the spine is most often affected.
Also, what is the treatment for prostate cancer that has spread to the bones? Men with prostate cancer that has spread to the bones may consider treatment that infuses a radioactive substance into a vein. Strontium-89 , samarium-153 and radium-223 are medications that target fast-growing cancer cells in the bones, and may help relieve bone pain.
One may also ask, how do you know if prostate cancer has spread?
Prostate cancer that has spread to the liver, intestines, or bones of the abdomen and pelvis can usually be found with a CT scan. Cancer which has spread to the lymph nodes can sometimes be detected if the lymph nodes have become enlarged.
What is the prognosis for prostate cancer that has spread to the bones?
There is currently no cure for advanced prostate cancer, but advances in treatments are extending life expectancy and improving quality of life. The ACS state that the 5-year relative survival rate for individuals with prostate cancer that has spread to distant lymph nodes, organs, or the bones is 29 percent.
You May Like: Va Disability Rating For Bph
What Happens If My Cancer Starts To Grow Again
Your first treatment may help keep your cancer under control. But over time, the cancer may change and it may start to grow again.
You will usually stay on your first type of hormone therapy, even if its not working so well. This is because it will still help to keep the amount of testosterone in your body low. But there are other treatments that you can have alongside your usual treatment, to help control the cancer and manage any symptoms. Other treatments include:
Which treatments are suitable for me?
Which treatments are suitable for you will depend on many things, including your general health, how your cancer responds to treatment, and which treatments youve already had. Talk to your doctor or nurse about your own situation, or speak to our Specialist Nurses.
Read Also: What Does An Enlarged Prostate Look Like
Analysis Of The Prediction Model Discriminant Equation
A discriminative PSA level was calculated when this cut-off together with other independent risk factors was substituted into the regression model. Table 5 shows the comparison between the discriminant equation and the bone scan results. The following four cases should be highly suspected of BM: cTl-cT2, BGS 7, ALP > 120 U/L and tPSA > 90.64 ng/ml cTl-cT2, BGS 8, and ALP > 120 U/L cT3-cT4, BGS 7, and ALP > 120 U/L and cT3-cT4 and BGS 8.
Figure 5
The nomogram and calibration curve developed for model E. Nomogram. To estimate the risk of BM, the points for each variable were calculated by drawing a straight line from a patient’s variable value to the axis labelled Points. The score sum is converted to a probability in the lowest axis. Calibration curve. The nomogram-predicted probability is plotted on the x-axis, and the actual probability is plotted on the y-axis. Mean absolute error=0.03.
Treatments For Prostate Cancer Spread To Bones
If prostate cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it nearly always goes to the bones first. Bone metastasis can be painful and can cause other problems, such as fractures , spinal cord compression , or high blood calcium levels, which can be dangerous or even life threatening.
If the cancer has grown outside the prostate, preventing or slowing the spread of the cancer to the bones is a major goal of treatment. If the cancer has already reached the bones, controlling or relieving pain and other complications is also a very important part of treatment.
Treatments such as hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and vaccines may help with this, but other treatments specifically target bone metastasis and the problems it may cause.
Also Check: How Long Do You Have Incontinence After Prostate Surgery
Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
As the data used was extracted from SEER dataset , Ethics approval and Consent to participate could be checked in SEER. We were permitted to have Internet access after our signed data-use agreement was approved by the SEER administration . The date collected from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine was approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhejiang University .
Where Do These Numbers Come From
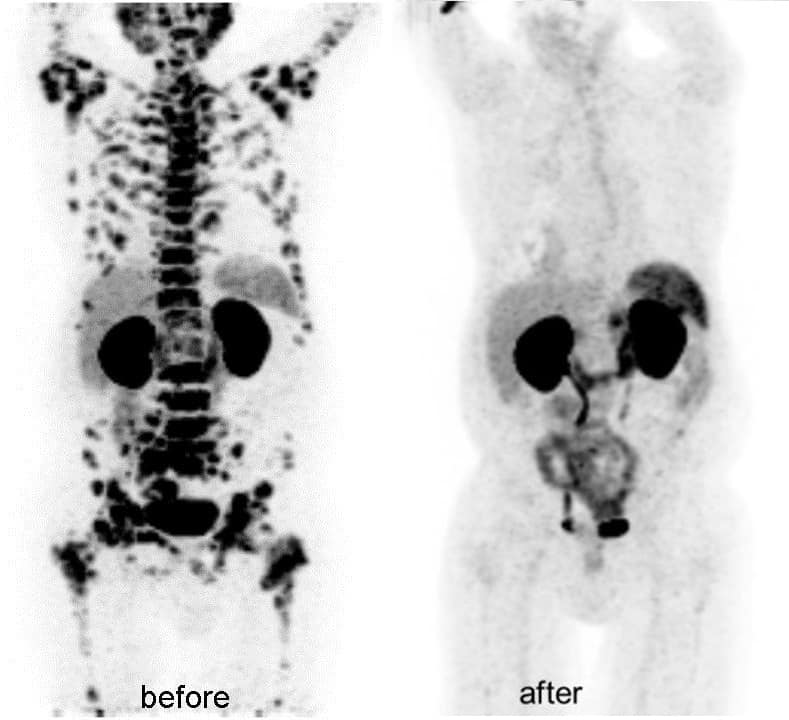
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for prostate cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside the prostate.
- Regional: The cancer has spread outside the prostate to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to parts of the body farther from the prostate, such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
Recommended Reading: Why Do Men Have A Prostate
Diagnosing Bone Mets In Prostate Cancer
Jorge Garcia, MD:We have prostate cancer screening in North America. Although it is a controversial topic right now in the field, I think most men in the United States do walk with what we call localized or locally advanced disease. These are patients who have no evidence of metastases, which means that it allows youas a consumer, as a patientto be able to achieve cure with either surgery or radiation therapy, or the combination of those 2, for that matter.
However, there is a small pocket of patients who are walking in the office with de novo disease, which means they have their primary prostate in place, and they just simply presented like this patient with symptomatic disease. They have back pain, theyre a man older in age, and they have symptoms that will raise the suspicion of, Well, maybe they have prostate cancer. So in this particular case, the patient presented with back pain. That prompted the medical team to actually do a work-up that included a PSA , which was found to be quite elevatedaround 79 or so. And that prompted them to actually have the patient undergo imaging scans, traditionally including a bone scan and a CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvic region. And those scans for this patient, unfortunately, were able to show that the patient had developed prostate cancer metastases in bony structures.
Transcript edited for clarity.
Case: Met HSPCa Progressing to mCRPC
The Role Of Inflammation
Acute inflammation is a biological response triggered by harmful stimuli such as infection, trauma, and tissue injury to eliminate the source of damage . The tumor microenvironment is unequivocally linked with inflammation, whether the infiltration of immune cells engages with tumor cells causing inflammation or chronic inflammation promotes the malignant transformation of cells and carcinogenesis .
In an experiment performed by Morrissey et al., it was found that IL-6 was highly expressed in prostate cancer bone metastases. PC-3 cells inhibited osteoblast activity and induced osteoblast to produce IL-6 that promoted osteoclastogenesis . In addition, a recent study by Roca et al. observed that macrophage-driven efferocytosis induced the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 5 by activating the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and the nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells signaling. CXCL5-deficient mice had reduced tumor progression. These findings suggested that the myeloid phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cancer cells accelerated CXCL5-mediated inflammation and tumor growth in bone . In summary, findings from available evidence suggest the alleviation of chronic inflammation as a potential therapeutic approach for prostate cancer bone metastases.
Don’t Miss: How To Check For Enlarged Prostate
Treatments To Help Manage Symptoms
Advanced prostate cancer can cause symptoms, such as bone pain. Speak to your doctor or nurse if you have symptoms there are treatments available to help manage them. The treatments above may help to delay or relieve some symptoms. There are also specific treatments to help manage symptoms you may hear these called palliative treatments. They include:
This is the team of health professionals involved in your care. It is likely to include:
- a specialist nurse
Read Also: What Is The Best Over The Counter Prostate Medicine
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
Advanced prostate cancer is cancer that has spread from the prostate to other parts of the body. It develops when prostate cancer cells move through the blood stream or lymphatic system.
Watch our video about advanced prostate cancer.
You might hear cancer that has spread described as metastatic prostate cancer, secondary prostate cancer, secondaries, metastases or mets. It is still prostate cancer, wherever it is in the body.
Prostate cancer can spread to any part of the body, but most commonly to the bones and lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are part of your lymphatic system, which is part of the bodys immune system. Lymph nodes are found throughout the body including in the pelvic area, near the prostate.
Advanced prostate cancer can cause symptoms, such as fatigue , bone pain, and problems urinating.
The symptoms you have will depend on where the cancer has spread to. Speak to your doctor or nurse if you have any symptoms. There are treatments available to help manage them.
Its not possible to cure advanced prostate cancer. But treatments can help keep it under control and manage any symptoms.
Read Also: Will Blood Test Show Prostate Cancer
What Are The Chances Of Getting Metastatic Prostate Cancer
About 50% of men diagnosed with local prostate cancer will get metastatic cancer during their lifetime. Finding cancer early and treating it can lower that rate.
A small percentage of men aren’t diagnosed with prostate cancer until it has become metastatic. Doctors can find out if it’s metastatic cancer when they take a small sample of the tissue and study the cells.
