Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer
In the 1980s, patients with locally advanced prostate cancer were treated definitively with radiation therapy. However, the risk of locoregional failures after radiation therapy was known to increase with higher initial disease burden . With the success of ADT in the metastatic setting, the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group initiated a series of trials to evaluate the potential benefits of cytoreductive ADT delivered in combination with definitive radiation therapy in an effort to improve disease control.
In 1983, RTOG launched a phase II clinical trial, RTOG 83-07, to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and potential toxicity of diethylstilbestrol , a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen, versus megestrol, a steroidal progestin, in prostate cancer patients with organ-confined disease or extension beyond the prostate . DES proved to more toxic than megestrol with comparable rates of local failure .
The authors of RTOG 85-19 noted that the mechanism of interaction between radiation therapy and androgen deprivation in carcinoma of the prostate remain largely unknown. They suggested that in addition to reducing tumor volume, when offered concurrently with radiation therapy, ADT may interact with radiation on a cellular level. .
Together, RTOG 92-02 and EORTC 22863 demonstrated a clinically meaningful benefit of long-term ADT delivered concurrently with definitive radiation therapy for patients with locally advanced, high-risk disease, which remains the standard of care .
When Adt Fails To Successfully Treat Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer recurs within 12 months of ADT in around 20 per cent of men. Other treatment options then include:
- radiotherapy precisely targeted x-rays are used to control the symptoms of secondary cancers in other parts of the body
- other forms of ADT using types of ADT other than gonadotrophin-releasing-hormone agonists may slow cancer growth for a limited time
- chemotherapy recent evidence indicates some men respond to chemotherapy. The chemotherapy medicines docetaxel or cabazitaxel can improve survival and quality of life
- corticosteroids shrink the cancer and help manage pain
- pain-relieving medication includes morphine
- lifestyle changes improved diet, regular exercise and stress management have been shown to improve quality of life and even prolong survival of men on ADT
- palliative care is used to manage pain and discomfort, including treatments to prevent bone fracture and bone pain.
Adt: What You Really Need To Know
The only people who really like androgen deprivation therapy are the drug companies that make billions of dollars a year selling the drugs. Doctors dont like it, and men dont like being on these drugs.
So why do it?
There are very few specific situations when ADT therapy is the right thing to do. These are the most common:
* Intermediate-risk men who are given six months of ADT plus external-beam radiation
* High-risk men who are getting radiation therapy. This is a finite course of ADT, and this combination two or three years of ADT plus external-beam radiation has been proven to cure cancer in many men.
* Men with metastatic prostate cancer. ADT can make a big difference in these men, in relieving their symptoms and dramatically improving their quality of life. It can also extend life some men have been on ADT for 20 years and are still going strong.
Recommended Reading: Prostate 5xl
Testosterone Suppression Target Of Less Than 20ng/dl
Setting goals for successful suppression of T during ADT for PCa should be based on evidence, measurement technologies, and relevance to patient outcomes. Although all forms of ADT aim to suppress T to castration levels, there has been disparity regarding the target. Recent advancements in assay technologies have enabled quantification of T levels down to extremely low levels and helped establish that T levels in surgically castrated men are substantially lower than originally reported . Based on these results, the European Association of Urology updated its PCa guidelines in 2014 to define the target for T during ADT as < 20ng/dL . Despite this, and a similar recommendation for a 20ng/dL threshold from the Bethesda consensus , the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and American Urological Association have not yet changed their recommendations. Furthermore, the FDA has not amended its regulatory target of > 90% of patients achieving and maintaining T< 50ng/dL for new drug approvals. Studies have also found that patients with T levels below 2032ng/dL benefited from a delay to CRPC and significantly lower risk of death compared to those with higher T levels . Given the weight of this evidence, it may now be appropriate to require ADT drugs to achieve and maintain T levels of < 20ng/dL, and for all clinical treatment guidelines to reflect this lower target .
What Are The Side Effects Of Hormone Therapy For Prostate Cancer
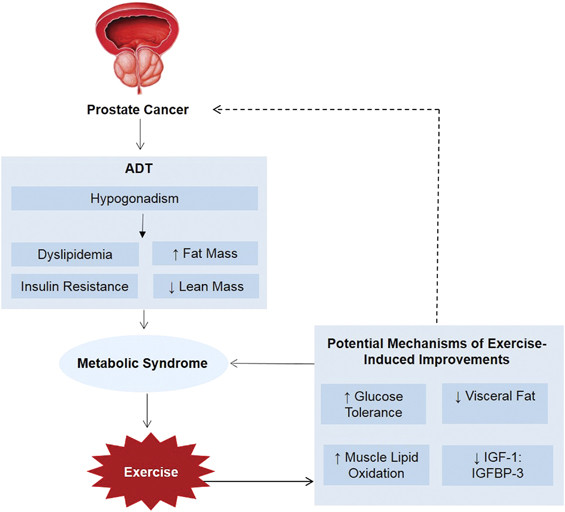
Because androgens affect many other organs besides the prostate, ADT can have a wide range of side effects , including:
- loss of interest in sex
Studer UE, Whelan P, Albrecht W, et al. Immediate or deferred androgen deprivation for patients with prostate cancer not suitable for local treatment with curative intent: European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Trial 30891. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006 24:18681876.
Zelefsky MJ, Eastham JA, Sartor AO. Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. In: Vincent T. DeVita J, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA, eds. DeVita, Hellman, and Rosenberg’s Cancer: Principles & Practice of Oncology, 9e. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2011.
Smith MR, Saad F, Chowdhury S, et al. Apalutamide and overall survival in prostate cancer. European Urology 2021 79:150158.
Also Check: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate
Laboratory Evaluations In The Management Of Prostate Cancer
PCa is an almost unique therapeutic area in that regulatory approvals of drugs such as LHRH agonists and antagonists are based on achievement of endpoints for a defined biochemical surrogate as opposed to clinical outcomes. A similar example would be the approval of statins based on reductions in LDL cholesterol before CV clinical endpoints had been achieved. This concept supports the use of laboratory measurements during PCa treatment as being appropriate to assess response to therapy, tumor microenvironment, state of disease progression and prognosis. Serum PSA levels are routinely evaluated as a biomarker of PCa diagnosis and progression . However, T may also be associated with clinical significance, including nadir levels, microsurges, and escapes during ADT additionally, measurement of FSH may also be relevant .
Cellular Mechanism Of Action
While ADT was being developed clinically for use in patients with prostate cancer, others were investigating the mechanism by which suppression of androgens improves disease control. There was conjecture about the clinical benefit of ADT being a result of cytoreduction or debulking of disease prior to radiation therapy, while others surmised a synergy between ADT and radiation therapy at the cellular level.
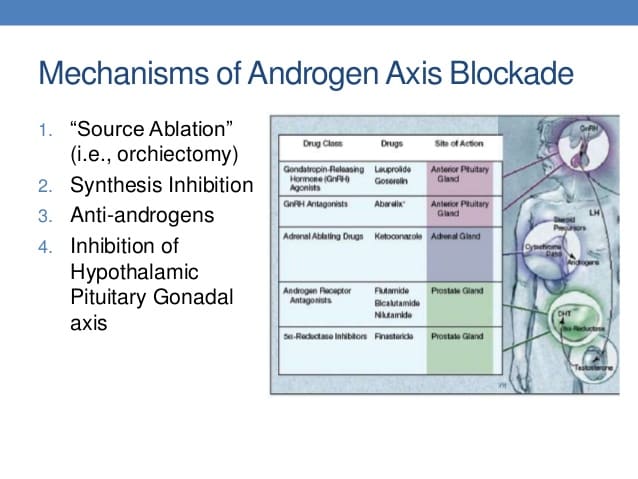
In men, the majority of circulating testosterone is produced by leydig cells in the testes following stimulatory signals produced by the pituitary, LH and FSH. The remainder of testosterone is produced by the adrenal gland, derived from circulating steroid hormone precursors . Once produced, testosterone is transported protein-bound to the target cell where it is metabolized intracellularly by 5-reductase to the super-active metabolite, dihydrotestosterone . DHT binds its cognate receptor, the AR, which subsequently dimerizes and is translocates into the nucleus where it conducts its DNA-directed functions, including transcriptional regulation of target genes .
The critical importance of AR-signaling for prostate cancer growth is further highlighted in the context of castrate resistant prostate cancer, prostate cancer that grows despite androgen levels being suppressed to castrate levels. In these patients, exogenous selection pressure stimulates resistance to ADT through multiple pathways.
You May Like: What Is The Definition Of Prostate Gland
What Is Androgen Deprivation Therapy
Androgen deprivation therapy, also known as androgen suppression therapy or hormone therapy, is a specially designed therapy that aims to lower the levels of androgen hormones in the male body. Why do you ask? There are two types of androgen hormones in the human body testosterone, and dihydrotestosterone. It is because these two androgen hormones are shown to stimulate the growth of the cancer cells and make the spreading of cancer itself a lot easier.
It is believed that as soon as the androgen hormones levels are decreased with the use of androgen deprivation therapy, the process of spreading of cancer slowed down and it is a lot easier to be controlled. There are two types of androgen deprivation therapy operation, during which one or two testicles are removed and medications that lower these levels of androgen hormones. However, hormone therapy is not advised for every stage of cancer.
In most cases, it is the metastatic stage, the advanced stage or usually the last stage of the process that is being treated with the help of androgen deprivation therapy. Androgen deprivation therapy can be used in cases where operation or radiation are not believed to be able to shrink or remove the cancer cells, in cases alongside with radiation, or in cases of the radiation or operation is performed in order to shrink the cancer cells before the team proceeds with the chosen treatment options.
*All individuals are unique. Your results can and will vary.
Testosterone Surges Escapes And Microsurges
Following the first injection of LHRH agonists, a surge in T due to hyperstimulation of the GNRH receptor will occur, followed by downregulation and subsequent inhibition of production of T by the testes. Escapes in T are possible where T levels rise before a subsequent dose. Morote et al. found that T levels above 32ng/dL resulted in a mean PFS of 88 months compared to 137 months for patients who did not experience escapes . Studies have also shown improved survival free of androgen-independent progression when T escapes are minimized .
Microsurges in T may occur following a subsequent dose if suppression of the hypothalamuspituitarygonadal axis has not been effectively maintained in some cases, this can be due to a delay in administration of the next injection . The definition of a microsurge is not standardized it is sometimes defined as an absolute increase in T of 25ng/dL . Additionally, the clinical implications of microsurges remain to be identified .
While the clinical significance of surges in T with the first dose of an LHRH agonist is unknown for most patients , it may be desirable to avoid the consequences of this initial rise and this can be achieved by coadministration of an antiandrogen, or initiation of ADT with an LHRH antagonist.
Recommended Reading: Does Prostate Massage Prevent Prostate Cancer
Side Effects Of Hormone Therapy
As the primary male hormone, testosterone plays an important role in establishing and maintaining the typical male characteristics along with a variety of other processes in the body.
The potential effects of testosterone loss include the following:
-
Hot flashes
-
Osteoporosis, which can lead to bone fractures
-
Fatigue
How Researchers Measure Quality Of Life
How we each define quality of life is, admittedly, rather subjective. But researchers have developed several questionnaires for use in clinical trials to try to assess quality of life. Some of the tools, such as the RAND 36-Item Health Survey, the Functional Assessment of Cancer TherapyGeneral , and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30 questionnaire, pose about 30 to 40 general questions related to physical health and emotional well-being, or ask respondents to indicate the degree to which they agree with various statements. For example:
During the past week, have you had trouble sleeping?
___ Not at all
___ Somewhat worse now than one year ago
___ Much worse now than one year ago
In prostate cancerrelated studies, researchers may ask participants additional questions about their urinary habits, and about their ability to get and maintain an erection, whether they were able to have sexual intercourse, and whether sexual activity during the past month was satisfying. Participants may complete the same survey every few weeks or months, allowing researchers to gauge the response to treatment, on average, of the entire group.
Don’t Miss: Does Prostatitis Go Away On Its Own
Early Versus Delayed Treatment
For men who need hormone therapy, such as men whose PSA levels are rising after surgery or radiation or men with advanced prostate cancer who dont yet have symptoms, its not always clear when it is best to start hormone treatment. Some doctors think that hormone therapy works better if its started as soon as possible, even if a man feels well and is not having any symptoms. Some studies have shown that hormone treatment may slow the disease down and perhaps even help men live longer.
But not all doctors agree with this approach. Some are waiting for more evidence of benefit. They feel that because of the side effects of hormone therapy and the chance that the cancer could become resistant to therapy sooner, treatment shouldnt be started until a man has symptoms from the cancer. This issue is being studied.
Intermittent Versus Continuous Hormone Therapy
Most prostate cancers treated with hormone therapy become resistant to this treatment over a period of months or years. Some doctors believe that constant androgen suppression might not be needed, so they advise intermittent treatment. The hope is that giving men a break from androgen suppression will also give them a break from side effects like decreased energy, sexual problems, and hot flashes.
In one form of intermittent hormone therapy, treatment is stopped once the PSA drops to a very low level. If the PSA level begins to rise, the drugs are started again. Another form of intermittent therapy uses hormone therapy for fixed periods of time for example, 6 months on followed by 6 months off.
At this time, it isnt clear how this approach compares to continuous hormone therapy. Some studies have found that continuous therapy might help men live longer, but other studies have not found such a difference.
Also Check: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
How Does Hormone Therapy Work Against Prostate Cancer
Early in their development, prostate cancers need androgens to grow. Hormone therapies, which are treatments that decrease androgen levels or block androgen action, can inhibit the growth of such prostate cancers, which are therefore called castration sensitive, androgen dependent, or androgen sensitive.
Most prostate cancers eventually stop responding to hormone therapy and become castration resistant. That is, they continue to grow even when androgen levels in the body are extremely low or undetectable. In the past, these tumors were also called hormone resistant, androgen independent, or hormone refractory however, these terms are rarely used now because the tumors are not truly independent of androgens for their growth. In fact, some newer hormone therapies have become available that can be used to treat tumors that have become castration resistant.
Adverse Effects Of Adt
Frequent side effects of ADT that result in poor quality of life include hot flashes, metabolic effects such as gynacomastia as well as an increased body mass index, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome , cardiovascular diseases, and musculoskeletal effects including reduced muscle mass, osteoporosis, and also sexual dysfunction Of these adverse events, metabolic and musculoskeletal effects are the most prevalent and distressing side effects reported by patients .
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Prostate Cancer That Has Spread To Bones
What Are Male Sex Hormones
Hormones are substances that are made by glands in the body. Hormones circulate in the bloodstream and control the actions of certain cells or organs.
Androgens are a class of hormones that control the development and maintenance of male characteristics. The most abundant androgens in men are testosterone and dihydrotestosterone .
Androgens are required for normal growth and function of the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system that helps make semen. Androgens are also necessary for prostate cancers to grow. Androgens promote the growth of both normal and cancerous prostate cells by binding to and activating the androgen receptor, a protein that is expressed in prostate cells . Once activated, the androgen receptor stimulates the expression of specific genes that cause prostate cells to grow .
Almost all testosterone is produced in the testicles a small amount is produced by the adrenal glands. Although prostate cells do not normally make testosterone, some prostate cancer cells acquire the ability to do so .
Localized Intermediate Risk Prostate Cancer
Proven effective for metastatic and high-risk, locally advanced prostate cancer, the use of ADT in combination with definitive radiation therapy was extended to patients with intermediate risk disease. Because survival in these patients is years to decades, short-term ADT was evaluated in these patients, rather than long-term ADT, in order to optimize the risk-benefit ratio by minimizing unwanted acute and chronic toxicities.
The role of ADT combined with definitive radiation therapy for intermediate risk prostate cancer was evaluated in three landmark clinical trials. RTOG 94-08 demonstrated that for patients with low- and intermediate-risk prostate cancer, short term ADT improved outcomes at 10 years, with the largest benefit in the intermediate risk group . While TROG 96.01 confirmed that 6 months of ADT was superior to 3 months of ADT for patients with intermediate and high-risk prostate cancer . Focusing on the unfavorable intermediate risk group , DAmico demonstrated that 6 months of ADT improved overall survival, prostate cancer-specific mortality and all-cause mortality . However, the 15-year follow-up suggested that in the subset of patients with moderate-to-severe comorbidities, the addition of ADT significantly increased overall mortality and cardiac mortality .
You May Like: What Are The Symptoms Of Perineural Invasion
Combining Nadt And Chemotherapy
Pan et al conducted a retrospective review of 3 different therapies in patients with very-high-risk localized prostate cancer: neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy , in 60 men neoadjuvant hormonal therapy , in 73 men and immediate RP without neoadjuvant therapy , in 44 men. The NCHT group had better biochemical progression-free survival time after surgery compared with the NHT and No-NT groups . After RP, 81% of patients in NCHT group, 73% of patients in NHT group, and 48% of patients in No-NT group achieved an undetectable PSA , despite patients in the NCHT having significantly poorer prognostic factors. Randomized controlled investigations are needed to validate these results, and further follow-up is required.
Multiple phase I/II trials have also been performed to investigate the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone prior to RP, however no patients in these trials achieved a complete pathologic response . As there is currently no evidence demonstrating improved clinical outcomes with the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone or neoadjuvant androgen deprivation therapy alone, future research will likely focus on combined neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy.
Although no data have yet emerged that definitively support the routine use of neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy, its safety has been evidenced by several phase I/II clinical trials. Most of the trials on neoadjuvant chemohormonal therapy have investigated docetaxel. These are summarized in Table 4 below.
