Chances Prostate Cancer Will Recur
Overall, a man who has undergone prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer has a 10 to 30 percent chance of experiencing prostate cancer recurrence during his lifetime. Among these cases of recurrence, about half happen during the first three years after prostatectomy, another 30 percent occur from years 3 to 5 post-prostatectomy, and about 19 percent happen after year 5. Some experts say the figure of recurrence is even higher.
What To Do When Radiation And Hormone Therapy Fail
For some men, radiation and hormone therapy do not put the brakes on prostate cancer that recurs after prostatectomy, and the disease continues to spread. In such cases, one treatment option may include chemotherapy with docetaxel , which may extend survival and effectively treat cancer pain. Another option is the immunotherapy sipuleucel-T , which for now is limited to men with metastatic prostate cancer who have no symptoms or whose cancer pain does not require use of narcotics and who have not responded to hormone therapy.
Two other choices for men who have not responded to traditional hormone therapy are abiraterone , a form of hormone therapy that has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for advanced cancer that has resisted previous hormone therapy and enzalutamide , which is approved for men whose prostate cancer has spread and not responded to both hormone therapy and chemotherapy .
For the majority of men who undergo prostatectomy for localized prostate cancer, the disease does not recur. However, for those men who do experience prostate cancer recurrence, there are treatment options, and patients should discuss the risks and benefits of all the alternatives with their healthcare providers and loved ones before making a decision.
How Effective Is Modern Radiation Treatment Of Prostate Cancer
Radiation therapy can give more radiation dose directly to the prostate than to surrounding healthy tissues, given the improvements in technology and imaging techniques. Physicians use various imaging techniques to see the prostate and surrounding tissues in three dimensions, so that the radiation beams can be tailored more precisely to the individual patient’s unique needs. Physicians can estimate and minimize the dose of radiation that will be received near the rectum, small bowel, bladder and hips during the course of radiation treatment to reduce the risk of side effects and complications. The goal is to safely provide a higher dose of radiation than even five years ago, which helps to improve the chances of cure. For similar stage and prostate cancer types, radiation therapy is as effective as surgery but with a different treatment process and different side effects.
Read Also: Recurrent Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Why Do Prostate Cancer Treatments Cause Urinary Incontinence
It helps to know a bit about how the bladder holds urine. When urine is emptied into the bladder from the kidneys, it is stored inside the bladder until you have the urge to urinate. The bladder is a hollow, muscular, balloon-shaped organ. Urine flows out of the bladder, and leaves the body through a tube called the urethra. Urination happens when the muscles in the wall of the bladder contract, forcing urine out of the bladder. At the same time, muscles that surround the urethra relax and allow the flow of urine. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra. Because an enlarged prostate gland can obstruct the urethra, it can cause urination retention or other problems with urination.
Removing the prostate through surgery or destroying it through radiation can disrupt the way the bladder holds urine and can result in urine leakage. Radiation can decrease the capacity of the bladder and cause spasms that force urine out. Surgery can, at times, damage the nerves that help control bladder function.
Treatment By Stage Of Prostate Cancer
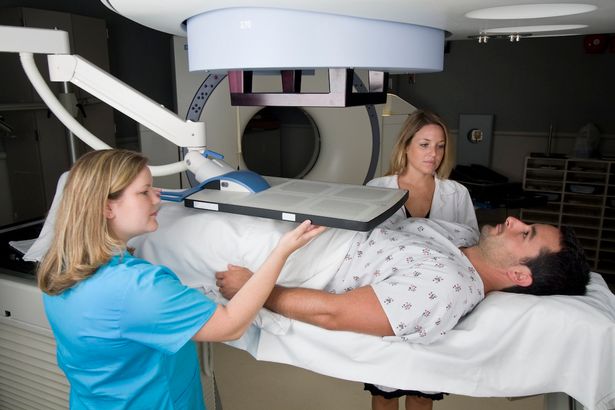
Different treatments may be recommended for each stage of prostate cancer. Your doctor will recommend a specific treatment plan for you based on the cancers stage and other factors. Detailed descriptions of each type of treatment are provided earlier on this same page. Clinical trials may also be a treatment option for each stage.
Early-stage prostate cancer
Early-stage prostate cancer usually grows very slowly and may take years to cause any symptoms or other health problems, if it ever does at all. As a result, active surveillance or watchful waiting may be recommended. Radiation therapy or surgery may also be suggested, as well as treatment in clinical trials. For those with a higher Gleason score, the cancer may be faster growing, so radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy are often recommended. Your doctor will consider your age and general health before recommending a treatment plan.
ASCO, the American Urological Association, American Society of Radiation Oncology, and the Society of Urologic Oncology recommend that patients with high-risk early-stage prostate cancer that has not spread to other areas of the body should receive radical prostatectomy or radiation therapy with hormonal therapy as standard treatment options.
Locally advanced prostate cancer
Watchful waiting may be considered for older adults who are not expected to live for a long time and whose cancer is not causing symptoms or for those who have another, more serious illness.
Recommended Reading: Ideal Prostate Plus Side Effects
How Prostate Cancer Staging And Risk Stratification Affect Treatment Options
Your treatment choices are determined by several factors, including your cancers stage, aggressiveness and assigned risk stratification . Your age and current general health condition may also affect your choices.
Prostate cancer staging
Prostate cancer staging determines whether the cancer is confined to the prostate gland or whether theres evidence of metastasis, meaning its spread to other areas of the body.
Tools and methods to determine staging may include the prostate-specific antigen test, the digital rectal examination , the Gleason score and the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system, which provides information on the tumor, lymph node involvement and metastasis of a cancer. Imaging tests, such as a PET/CT scan, may also help determine your cancers stage.
The four stages of prostate cancer are subdivided into more precise categories, but we generally refer to three groups that indicate how far the cancer has spread:
Localized, meaning theres no indication that the cancer has spread beyond the prostate
Regional, meaning theres evidence of cancer cells in nearby lymph nodes or tissue
Distant, meaning theres evidence the cancer has spread to other organs or body parts farther from the prostate
Almost 90 percent of prostate cancers are diagnosed at the localized or regional stage. The five-year relative survival rate for men diagnosed with prostate cancer at these stages is nearly 100 percent.
Prostate cancer risk assessment
An Increased Psa Level
A biochemical relapse is when your PSA level rises after having treatment that aims to cure your cancer.
You might not need to start treatment straight away. Your doctor will continue to monitor your PSA levels regularly to see if your PSA rises quickly or stabilises. You might have a scan if your PSA rises quickly.
The choice about whether to have treatment and what treatment to have will depend on:
- the treatment you have already had
- your general health
Also Check: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
Can You Get Erections After Prostate Cancer Treatment
If you have ever wondered whether you’ll be able to have an erection after prostate cancer treatment, you are not alone. Many men who are facing a prostate cancer diagnosis, or who have undergone prostate cancer treatment, are worried about whether or not they will be able to have an erection after prostate cancer.
What Type Of Follow
If prostate cancer recurs, follow-up treatment depends on what treatment you have already had, the extent of your cancer, the site of recurrence, other illnesses, your age, and other aspects of your medical situation.
One possible treatment might include hormone therapy. Researchers are working on new drugs to block the effects of male hormones, which can cause prostate cancer to grow, and drugs to prevent prostate cancer growth.
Radiation therapy, ultrasound, extreme cold, electrical current, or medicines may be used to relieve symptoms of bone pain. Chemotherapy or other treatments being medically researched are also options.
Now in clinical trials are several types of vaccines for boosting the body’s immune system against prostate cancer cells. Sipuleucel-T is the only vaccine available on the market for prostate cancer.
Read Also: Zinc And Prostate
Fertility After Prostate Cancer Treatment
It is nearly impossible for a man to retain his ability to father children through sexual intercourse after initial treatment. During prostatectomy, both the prostate and the nearby seminal vesicles are removed. Seminal vesicles and the prostate provide semen that carries the sperm down the urethra and out the penis during ejaculation. The loss of semen following surgery makes ejaculation impossible, so the sperm cannot physically leave the body. Radiation therapy nearly always impairs fertility. Radiated prostate cells and seminal vesicles tend to produce semen that cannot transport the sperm well. Sperm can also be damaged, though this occurs far less frequently with more accurate dose planning.
Brachytherapy For Prostate Cancer
Brachytherapy is a form of internal radiation therapy. With this type of therapy, radiation is delivered to the prostate tumor inside the body via a catheter or another implantable device.
High-dose rate brachytherapy uses radioactive Iridium-192 to deliver high doses of radiation to the prostate tumor. Treatments are short, sometimes requiring as few as five sessions. Brachytherapy radiation more tightly surrounds the tissues were targeting, which may help spare normal tissues.
Read Also: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Enlarged Prostate
What Happens To Your Psa Levels After Radiation Therapy
After radiation therapy Radiation therapy doesnt kill all of the cells in the prostate gland, so its not expected to cause the PSA to drop to an undetectable level. The remaining normal prostate cells will still make some PSA. The pattern of the drop in PSA after radiation therapy is also different from after surgery.
What Happens Between Appointments
Contact your doctor or nurse if you have any concerns or get any new symptoms or side effects between your follow-up appointments.
Its important to speak to them if youre concerned about anything dont worry about them being too busy.
You can get support or advice over the telephone, or they might bring forward the date of your nextfollow-up appointment.
You May Like: How Does Cialis Work For Bph
Msks Approach To Radical Prostatectomy
Our prostate surgery team includes experts in several techniques, including robot-assisted surgery, open surgery, and laparoscopic surgery. Regardless of which surgical approach you choose, our goal is to remove your cancer completely and preserve normal urinary and sexual function.
With all surgical approaches, weve developed and use innovative techniques to preserve the tiny nerves and blood vessels attached to the prostate that help control erections. These and other advances have made some of the complications of prostate cancer surgery less common and more manageable and can spare nerves from damage. Well work closely with you and your medical team to manage any short- or long-term side effects you may experience.
Ultimately, youll help determine which approach your surgeon takes.
How Long Will My Follow
You will have follow-up appointments for some time after your treatment. Exactly how long will depend on your cancer, any side effects of treatment and the services in your area. You will usually have appointments for several years.
After your follow-up appointments finish, you may continue to have PSA tests. Speak to your GP if you have any problems or concerns they can refer you back to the hospital. Make sure you remind them about your prostate cancer, especially if its been a while since you had treatment or a PSA test.
Also Check: What Is The Definition Of Prostate Gland
What To Expect After Radiationtreatment For Prostate Cancer
Afterreceiving brachytherapy, if you receive pellets that give off radiation overthe span of a couple months, you will need a doctors note to travel,as some detection systems will be alerted. It is also recommended to avoiddirect contact with pregnant women and small children, even though theradiation does not travel far from the prostate.
Somepatients treated with EBRT can experience lymphedema when a buildup of fluidover time in the legs or genital region causes pain and swelling. Some casesmay not go away over time, but most are treated with physical therapy. Theradiation causes damage to the lymph nodes, blocking fluid from returning tothe heart.
Both typesof radiation have several shared side effects associated with the treatmentincluding:
- Urinary frequency
- Irritated urethra in the weeks following treatment
- Burning/bleeding during urination
Adjuvant And Salvage Post
Sometimes, intensity modulated radiation therapy is given after a patient has had a prostatectomy. There are two situations where this treatment done. In the first situation, it may be known before the surgery or discovered after the surgery, that the cancer was more extensive than expected. The cancer may have penetrated the capsule which surrounds the prostate or extended into the seminal vesicles or extend to the edge of the surgical margin. In this case, your physicians may determine in consultation that a course of IMRT to the prostate bed and surrounding tissue is needed to reduce the risk of a recurrence and kill any microscopic prostate cancer cells that may be present. The goal of adjuvant post-prostatectomy radiation therapy is to reduce the risk or eliminate a recurrence of cancer in the prostate bed.
In the second situation where IMRT is given after a prostatectomy, usually months or years have passed since the surgery before evidence of a recurrence in the prostate bed develops. This is usually discovered by a rising PSA after surgery. In this situation, treatment called salvage post-prostatectomy IMRT is given to the prostate bed and surrounding tissue to kill the recurrent prostate cancer cells. The goal of this treatment is to eradicate the prostate cancer and lower the PSA.
Daily CT scans or Calypso beacons for daily localization and tracking is used with both adjuvant salvage post-prostatectomy radiation therapy.
Don’t Miss: Carboplatin Prostate Cancer
Are There New Techniques That Reduce The Chance Of Becoming Incontinent
When removingthe prostate, surgeons try to save as much of the area around the bladder and the sphincter muscles around the urethra as possible, thus limiting damage to the sphincter. Doctors have also fine-tuned the process of placing radioactive seed implants, using sophisticated computer projections that allow the seeds to destroy the prostate while limiting damage to the bladder.
Still, at this point, any man who is undergoing radiation or surgery to treat prostate cancer should expect to develop some problems with urinary control. With newer techniques, some men will have only temporary problems controlling their urine, and many will regain full control of their bladder in time.
Continued
Chemotherapy Drugs For Prostate Cancer
- Docetaxel
- Mitoxantrone
- Estramustine
The drugs listed above are only a sample of what is available and is used to illustrate a truth. Because of the range and variety of drugs used in both these treatments the impact on sexual function can range from sever to insignificant.
Hormone replacement therapy for prostate cancer, for example, can often impact sex drive rather that create erectile dysfunction. It is important to work with your physician to explore all available treatment options. How to keep a healthy erection?
Read Also: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
How Is A Recurrence Detected
After prostate cancer treatment, you will go for medical check-ups every few months as determined by your doctor. At each follow-up appointment, your doctor will order a blood test to measure PSA levels. This test helps your doctor detect a cancer recurrence. You will also be examined. New symptoms should be reported to the doctor, as these may prompt other testing.
When PSA test results suggest that the cancer has come back or continued to spread, X-rays or other imaging tests may be done, depending on your situation and symptoms. Your doctor may use a radioactive tracer called Axumin with a PET scan to help detect and localize any recurrent cancer so that it could be biopsied or treated.
Your doctor may also use a new drug called Ga 68 PSMA-11 in the scan which binds to PSMA-positive prostate cancer lesions in the tissues of the body so they can be targeted for treatment.
How Your Doctor Monitors You After Treatment
After treatment you have follow up appointments, which usually include regular blood tests to check the levels of a protein called prostate specific antigen . They check to see if your PSA level rises. And they also look at how quickly it rises.
An increase in PSA can mean there are prostate cancer cells in your body. The cells might be in or around the prostate. Or they might have spread to other parts of your body. You might need treatment if it rises.
Prostate cancer that comes back after treatment is called recurrent prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: No Ejaculate Flomax
About Dr Dan Sperling
Dan Sperling, MD, DABR, is a board certified radiologist who is globally recognized as a leader in multiparametric MRI for the detection and diagnosis of a range of disease conditions. As Medical Director of the Sperling Prostate Center, Sperling Medical Group and Sperling Neurosurgery Associates, he and his team are on the leading edge of significant change in medical practice. He is the co-author of the new patient book Redefining Prostate Cancer, and is a contributing author on over 25 published studies. For more information, contact the Sperling Prostate Center.
Search the spc blog
What Is Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer develops in the prostatea small gland that makes seminal fluid. It is the second most common type of cancer in men. Prostate cancer usually grows over time and in the beginning stays within the prostate gland, where it may not cause serious harm. While some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly.
Prostate cancer that is caught early has a better chance of successful treatment.
Recommended Reading: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
