Staging Spread And Survival Rates
As with all cancers, doctors use the term stage to describe the characteristics of the primary tumor itself, such as its size and how far prostate cancer has spread when it is found.
Staging systems are complicated. The staging system for most cancers, including prostate cancer, uses three different aspects of tumor growth and spread. It’s called the TNM system, for tumor, nodes, and metastasis:
- T, for tumor describes the size of the main area of prostate cancer.
- N, for nodes, describes whether prostate cancer has spread to any lymph nodes, and how many and in what locations.
- M, for metastasis, means distant spread of prostate cancer, for example, to the bones or liver.
Using the TNM system, each man’s prostate cancer can be described in detail and compared to other men’s prostate cancer. Doctors use this information for studies and to decide on treatments.
As far as survival rates for prostate cancer go, however, the staging system is pretty simple. As we’ve mentioned, in terms of survival rates, men with prostate cancer can be divided into two groups:
Is Prostate Cancer Curable
Prostate cancer is the most common type of cancer among men, second only to skin cancer. Learning that one has any type of cancer isnt easy, but the first question on most patients minds after diagnosis is, is prostate cancer curable?
The short answer is yes, prostate cancer can be cured, when detected and treated early. The vast majority of prostate cancer cases are discovered in the early stages, making the tumors more likely to respond to treatment. Treatment doesnt always have to mean surgery or chemotherapy, either. Non-invasive radiation therapy can effectively treat prostate cancer in the case of Pasadena CyberKnife, radiosurgery treatment generally takes less than a week, and you can typically resume your normal activities the same day you receive treatment.
Survival Rates In Prostate Cancer: The Facts
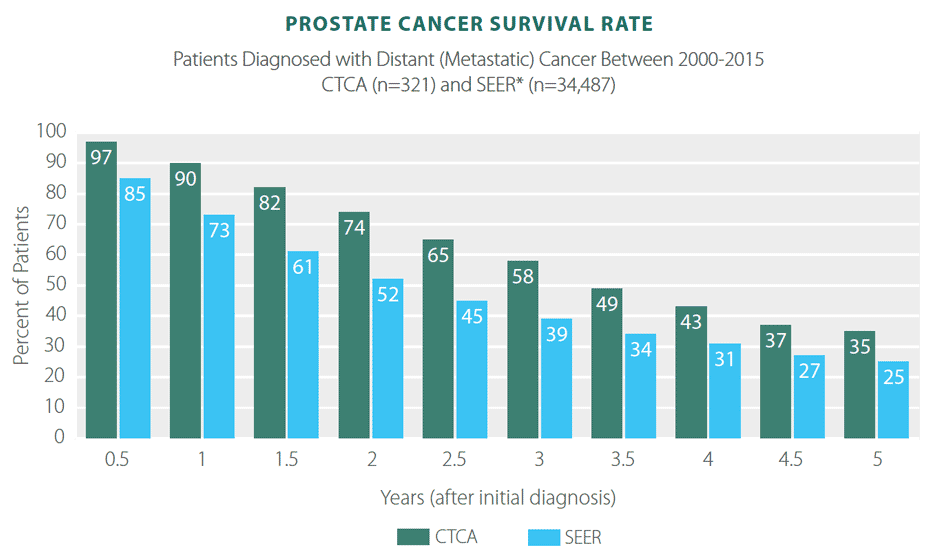
For you as a patient, the disease-specific survival rate is the decisive aspect: what are the chances of surviving prostate cancer? 98 % of our patients who underwent radical prostatectomy, and in whom the tumor was confined to the prostate gland , were still alive 10 years after their operation. Even in patients with an advanced stage tumor , the survival rates are between 72 and 95 %.
Disease-speciic survival rates of our patients after 10 years in percent
The table on the page Results shows the disease-specific survival rate of our patients following surgery, according to the stage of the tumor.
- If the tumor was confined to the protstate or had “only” spread to the periphery of the prostate, the 10-year survival rate was more than 98%.
- If cancer cells had already spread to the seminal vesicle or to the area surrounding the prostate, the rate was between 87% and 77% respectively.
- If the lymph nodes were affected , 81% of our patients survived.
- If the preoperative PSA value was > 20 ng/mL , the disease-specific survival rate was 93%.
- If the preoperative Gleason Score was 8 or higher, 70% of the patients survived.
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Be Careful With Saturated Fat
This is essential dietary advice if we want to counter inflammation. Saturated fat converts into inflammatory cytokines in the body. Thats why high-fat diets link with more aggressive diseases. We recommend consuming low-fat dairy, avoiding red meat fat, and healthier cooking methods different from frying.
Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
All observational studies stated the survival rate of localized prostate cancer in Asian countries were included in the study. Articles of other cancers reported survival in people who reported regional, metastatic, as well as review and meta-analysis studies were excluded. It should be noted that studies that did not report the sample size or confidence interval of survival rates were not included in the meta-analysis.
Recommended Reading: Cialis For Bph Dosage
What Is The Survival Rate For Prostate Cancer
The average five-year survival rate for prostate cancer is very optimistic: 98%. This means it is relatively unlikely that a man diagnosed with prostate cancer will die from the disease.
This high survival rate is largely attributable to the fact that most prostate cancers are detected before the prostate cancer spreads to other organsin other words, when it is localized. Prostate cancer is detected at these earlier stages with regular screenings, which is why its so important for men to begin screening for prostate cancer at age 50.
That being said, there are aggressive prostate cancers that may decrease the chance of survival. The chances of survival dramatically decrease if the cancer has the opportunity to spread to further areas of the body.
Understanding Prostate Cancers Progression
To determine the appropriate treatment, doctors need to know how far the cancer has progressed, or its stage. A pathologist, the doctor trained in analyzing cells taken during a prostate biopsy, will provide two starting pointsthe cancers grade and Gleason score.
- Cancer grade: When the pathologist looks at prostate cancer cells, the most common type of cells will get a grade of 3 to 5. The area of cancer cells in the prostate will also be graded. The higher the grade, the more abnormal the cells.
- Gleason score: The two grades will be added together to get a Gleason score. This score tells doctors how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
After a biopsy confirms prostate cancer, the patient may undergo additional tests to see whether it has spread through the blood or lymph nodes to other parts of the body. These tests are usually imaging studies and may include a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or computed tomography scan.
You May Like: Prostate Gland Zones
Outlook For Men With Localised Prostate Cancer
Most localised prostate cancer is slow-growing and may not need treatment or shorten a mans life. For many men who have treatment for localised prostate cancer, the treatment will get rid of the cancer. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment.
Gleason Score Vs Grade Groups
The International Society of Urological Pathology released a revised prostate cancer grading system in 2014. The grade group system seeks to simplify Gleason scores and give a more accurate diagnosis.
One of the major problems with the Gleason score is that some scores can be made up in different ways. For example, a score of 7 can mean:
- 3 + 4. The 3 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 4 is the second most common. This pattern is considered favorable intermediate risk.
- 4 + 3. The 4 pattern is the most common in the biopsy and 3 is the second most common. This pattern is considered unfavorable and may mean local or metastatic spread.
So, although both situations give a Gleason score of 7, they actually have very different prognoses.
Heres an overview of how the two grading systems compare:
| Cancer grade | |
|---|---|
| grade group 5 | 910 |
Not all hospitals have switched to the grade group system. Many hospitals give both grade group and Gleason scores to avoid confusion until grade groups become more widely used.
You May Like: Urinozinc Prostate Plus
What Is Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer that affects the prostate gland in men. Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer deaths for men in the US.
The prostate lies below the bladder and in front of the rectum. In men, the size of the prostate increases with increasing age. In younger men, it is about the size of a walnut. Its primary function is to make fluid to nourish the semen.
Growth in the prostate can be of two types
Prostate cancer starts in the prostate gland and may spread to the nearby areas: lymph nodes, organs, or bones in other parts of the body.
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of prostate cancer is 90%, it means that men who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as men who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Read Also: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Does Overdiagnosis Lead To Overtreatment Of Older Men
The widespread use of PSA screening has led to an increase in the diagnosis and treatment of early localized prostate cancer. Data from the US Cancer of the Prostate Strategic Urological Research Endeavor database suggest a significant decrease in risk in the last 2 decades in the United States, with more patients being identified with low-risk disease at diagnosis, but the role of active treatment of low- and intermediate-risk disease in elderly men remains controversial.
The median time from diagnosis to death from prostate cancer for men with nonpalpable disease is approximately 17 years., Considering that the US male life expectancy at the age of 65 years is 16 years, aggressive therapy will hardly extend life expectancy of older men with no palpable prostate cancer at the time of diagnosis. Twenty to 30% of prostate cancers detected by PSA screening programs show Gleason scores of 6 or lower and, thus, are not poorly differentiated and have volumes smaller than 0.5 cm3.
Histologic evaluation of radical prostatectomy specimens demonstrated that about 20% to 30% of cancers are small volume, show low Gleason scores, and are consequently clinically harmless., Many of these cancers pose little threat to life, especially for older men. Has PSA screening resulted in prostate cancer overdiagnosis?
Stage Iv Cancer Life Expectancy
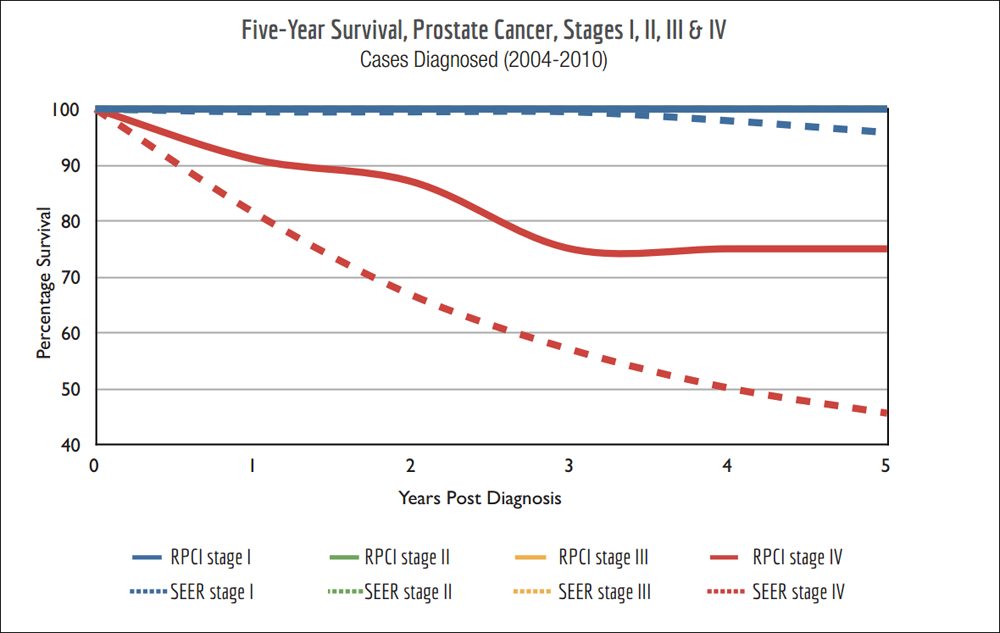
The five-year relative survival rate for prostate cancer that has spread to distant organs is 28%. This means about 28% of the patients with stage 4 prostate cancer will live for five years.
According to certain studies, about 98% men with low or intermediate grade prostate cancer will live for more than five years. However, only 67% men with end stage prostate cancer will live for more than five years.
End stage prostate cancer life expectancy is normally less than five years. It may vary according to the age and overall health of the patient, the type of treatment, and the extent and location of metastases , etc.
Studies show that the five-year survival rate for prostate cancer without bone metastasis is 56%. For prostate cancer with bone metastasis, it is only 3%.
The five-year survival rate for prostate cancer with bone metastasis and skeletal involvement is unfortunately less than 1%.
Usually, at stage IV, doctors assure life only for three years. The life expectancy not only depends on the treatment, but also on the physical and mental health of the patient. Patients who are loved and cared by their family members can fight the disease courageously. Those with strong will power live longer. There are examples of patients who have lived for eight years, or even further. Some recent studies show that a prostatectomy, even in late stage prostate cancer, can double or triple the life expectancy of a patient . But more studies are required to prove this fact.
Recommended Reading: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
Outlook For Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer
Many men with locally advanced prostate cancer have treatment that aims to get rid of their cancer. For some men, this treatment can be very successful and they may live for many years without their cancer coming back or causing them any problems. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment. Read more about the risk of your cancer coming back.
Some men with locally advanced prostate cancer will have treatment that aims to help keep their cancer under control rather than get rid of it completely. For example, if you have hormone therapy on its own, it can help to keep the cancer under control, usually for several years. And there are other treatments available if your hormone therapy stops working.
Survival For All Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Generally for men with prostate cancer in England:
- more than 95 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 1 year or more
- more than 85 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 5 years or more
- almost 80 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 10 years or more
Survival for prostate cancer is also reported in Scotland and Northern Ireland. But it is difficult to compare survival between these countries because of differences in the way the information is collected.
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account the background mortality that they would have experienced if they had not had cancer.
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Spread To Bone Marrow
The Importance Of Screening
Finally, the promising survival rates of prostate cancer are largely thanks to frequent screening. By screening for prostate cancer through PSA tests and the like, doctors are able to identify prostate cancer when it is localized. This greatly increases a patients chance of survival.
It is important that men 50 and above are screened for prostate cancer every two years. Depending on your circumstances, your doctor may recommend annual screening.
What Can Affect My Outlook
No one can tell you exactly what will happen. How prostate cancer affects you will depend on many things.
- Your stage Whether your cancer is localised, locally advanced, or advanced.
- Your Gleason score or grade group The higher your Gleason score, the more aggressive the cancer, and the more likely it is to spread.
- Your treatment options You may be able to have treatment aimed at getting rid of the cancer. Or you may be able to have treatment to keep the cancer under control. Read more about choosing your treatment.
- Your health If you have other health problems, you may have fewer treatment options. And you may be more likely to die from another condition, such as heart disease.
- Your PSA level After youve been diagnosed, PSA tests are a good way of monitoring your prostate cancer and seeing how youre responding to treatment.
- How successful your treatment is Your treatment may be successful at getting rid of your cancer or keeping it under control. But for some men, treatment may not work as well as expected.
Recommended Reading: Viagra And Bph
How To Understand The Gleason Score
For instance, if the Gleason Score is written 4+3=7, this means 4 is the grade assigned to the most cancerous cells, while 3 is the grade of the next largest section of the tumor. Together they make up the total Gleason Score, in this instance 7.
A Gleason Score of 6 is considered low-grade. It describes cancer cells that resemble the normal cells and, therefore, the cancer is slow-growing.
A Gleason Score of 7 is considered an intermediate grade, with a medium risk of aggressive cancer. In this case, it is very important to know what is the primary grade . If the primary grade is 3 and the secondary grade is 4, the cancer is not that likely to spread so quickly or cause important problems while a Gleason Score of 7, with the primary grade of 4 and the secondary grade of 3 is more likely to be more aggressive and high-risk.
Consider asking about your primary Gleason Grade, especially when your Gleason Score is 7 and the Gleason Grades are not specified.
A Gleason score of 8-10 is considered to be high-risk. Cancers are likely to spread more quickly and be more aggressive.
For a better understanding of your particular situation, do not hesitate to contact a urologist!
How Is Prostate Cancer Staged
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer that develops in men and is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in American men, behind lung cancer and just ahead of colorectal cancer. The prognosis for prostate cancer, as with any cancer, depends on how advanced the cancer has become, according to established stage designations.
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland present only in men, found in the pelvis below the bladder. The prostate gland wraps around the urethra and lies in front of the rectum. The prostate gland secretes part of the liquid portion of the semen, or seminal fluid, which carries sperm made by the testes. The fluid is essential to reproduction.
The term to stage a cancer means to describe the evident extent of the cancer in the body at the time that the cancer is first diagnosed.
- Clinical staging of prostate cancer is based on the pathology results, physical examination, PSA, and if appropriate, radiologic studies.
- The stage of a cancer helps doctors understand the extent of the cancer and plan cancer treatment.
- Knowing the overall results of the different treatments of similarly staged prostate cancers can help the doctor and patient make important decisions about choices of treatment to recommend or to accept.
Also Check: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Cancer staging is first described using what is called a TNM system. The “T” refers to a description of the size or extent of the primary, or original, tumor. “N” describes the presence or absence of, and extent of spread of the cancer to lymph nodes that may be nearby or further from the original tumor. “M” describes the presence or absence of metastases — usually distant areas elsewhere in the body other than regional lymph nodes to which the cancer has spread. Cancers with specific TNM characteristics are then grouped into stages, and the stages are then assigned Roman numerals with the numerals used in increasing order as the extent of the cancer being staged increases or the cancer prognosis worsens. Prognosis is finally reflected by considering the patient’s PSA score at presentation as well as their Gleason score in assigning a final stage designation.
The American Joint Commission on Cancer system for prostate cancer staging is as follows:
Traditionally, advanced prostate cancer was defined as disease that had widely metastasized beyond the prostate, the surrounding tissue, and the pelvic lymph nodes and was incurable. However, a more contemporary definition includes patients with lower grade disease with an increased risk of progression and/or death from prostate cancer in addition to those with widely metastatic disease.
The National Cancer Institute and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines on prostate cancer version 2.2017 indicate the following:
