Treatments May Have Side Effects
The treatment options for early-stage prostate cancer fall into three broad categories: surgery, radiation therapy, and active surveillance. Your doctor will make a treatment recommendation based on your numbers as well as a mathematical tool known as a nomogram, which can help you and your doctor better assess how extensive your cancer is likely to be and whether it is likely to become active in the future.
Yet clinical studies have not provided any evidence that one treatment is better than another or that any treatment at all actually prolongs life: The average 5-, 10-, and 15-year survival rates are virtually the same for all treatment options in early-stage prostate cancer, including active surveillance. Its also important to understand that no mathematical model is foolproof, and some men diagnosed with early-stage, locally confined disease will later find out that their cancer was more extensive than originally believed.
If you are diagnosed with early-stage prostate cancer, you have a number of treatments to choose from. A brief comparison is listed in Table 2.
Figure 1 Location Of The Prostate Gland
The prostate gland, about the size of a walnut, produces fluid that forms part of the semen that is ejaculated during sexual activity. The prostate is located adjacent to the rectum and just below the bladder, and wraps around the upper part of the urethra, which carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
This location creates challenges in both diagnosis and treatment. During a digital rectal exam, for example, a doctor is able to feel only the back portion of the prostate. If cancer has developed in the apex, base, or deep inside the prostate, it may not be palpable.
Surgeons and radiation oncologists also face challenges in eradicating a tumor without causing lasting damage to surrounding organs and structures. When removing a tumor from the breast or colon, a surgeon is able to remove enough surrounding tissue to ensure clean margins, meaning that all the cancer has been removed. But when treating prostate cancer, a comparable amount of tissue cannot be removed surgically or targeted. It takes a skilled surgeon and radiation oncologist to eradicate diseased tissue without harming portions of the rectum, bladder, and penis, thereby minimizing the likelihood of complications.
Its also important to understand the limits of current medical knowledge about prostate cancer.
What Is My Outlook
If youre diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may want to know how well your treatment is likely to control your cancer and for how long it will control it. This is sometimes called your outlook or prognosis. But not all men will want to know this.
While it isnt possible to cure advanced prostate cancer, treatments can help keep it under control, often for several years. Treatments will also help manage any symptoms, such as pain.
No one can tell you exactly what your outlook will be, as it will depend on many things such as where the cancer has spread to, how quickly it has spread, and how well you respond to treatment. Some men may not respond well to one treatment, but may respond better to another. And when your first treatment stops working, there are other treatments available to help keep the cancer under control for longer. Speak to your doctor about your own situation and any questions or concerns you have.
Recommended Reading: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Prostate Cancer: Stages Grades And Treatment
Cancer stage refers to the size of the tumor and whether or not it has spread to other parts of the body prostate cancer is staged using the TNM system. Cancer grade refers to how quickly the cancer cells will grow and spread prostate cancer is graded using the Gleason score. Treatment of prostate cancer is based on a combination of age, life expectancy, and personal preferences, in addition to cancer grade and stage. In general, the higher the grade or stage, the more likely it is that the cancer will spread.
What Does It Mean If In Addition To Cancer My Biopsy Report Also Mentions Acute Inflammation Or Chronic Inflammation

Inflammation of the prostate is called prostatitis. Most cases of prostatitis reported on biopsy are not caused by infection and do not need to be treated. In some cases, inflammation may increase your PSA level, but it is not linked to prostate cancer. The finding of prostatitis on a biopsy of someone with prostate cancer does not affect their prognosis or the way the cancer is treated.
Recommended Reading: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate Infection
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Treatments And Prognosis
Stage 4 prostate cancer is the most advanced stage of the disease. It means that cancer has spread beyond the prostate to distant areas of the body. Learn more about this stae, what treatments are available, and the prognosis.
Brianna Gilmartin / Verywell
Table 1 Why A Low Psa Does Not Mean You Are Cancer
The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial included a provision that men randomized to receive placebo undergo a prostate biopsy at the end of the study, even if they had normal PSA levels and digital rectal exams. To their surprise, investigators found that many of these men had prostate cancer in some cases, high-grade prostate cancer.
PSA level 13 *Note: A PSA level over 4.0 ng/ml traditionally triggers a biopsy. Adapted with permission from I.M. Thompson, et al. Prevalence of Prostate Cancer Among Men with a Prostate-Specific Antigen Level 4.0 ng per Milliliter. New England Journal of Medicine, May 27, 2004, Table 2.
This study inadvertently provided evidence not only that prostate cancer occurs more often than once believed, but also that PSA levels may not be a reliable indicator of which cancers are most aggressive. Both findings add weight to the growing consensus that many prostate tumors currently being detected may not need to have been diagnosed or treated in the first place.
Recommended Reading: Chemo Pills For Prostate Cancer
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
To help understand the progression of prostate cancer, discuss these questions with your doctors:
- What is my Gleason score?
- Has the cancer spread outside my prostate?
- Whats my prostate cancer stage?
- Are other tests needed to determine my cancer stage?
- What are the treatment options for my stage of cancer?
- Can I avoid treatment right now and go on active surveillance?
How Prostate Cancer Is Diagnosed And Staged
Cancer staging helps you and your doctor understand how advanced your cancer is and how much it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Knowing your cancer stage also helps your doctor determine the best treatment options for you and estimate your chance of survival.
The most widely used staging system for cancer is the American Joint Committee on Cancers TNM system that classifies cancer from stage 1 to stage 4.
TNM stands for:
- Tumor: the size and extent of the tumor
- Nodes: the number or extent of nearby lymph node involvement
- Metastasis: whether cancer has spread to distant sites in the body
The TNM scale is used for many types of cancer. When a doctor uses it to determine your prostate cancer stage, theyll consider several other factors as well, including:
- grade groups
You May Like: How To Treat Prostate Cancer That Has Spread To Bones
How Do Prostate Cancer Stages & Grades Affect Survival Rates
Overall, the prostate cancer survival rate is 97.5%most men will not die of prostate cancer, even if they have it until the end of life. However, if you look at survival rates by stage, it has been shown that the more advanced forms of prostate cancer have a lower survival rate .
The National Cancer Institutes Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program , which is the database that compiles the incidence and survival rates, sorts prostate cancer into localized, regional, and distant rather than using the TNM system :
- LocalizedCancer has not spread outside of the prostate
- RegionalCancer has spread outside of the prostate to adjacent structures and lymph nodes
- DistantCancer has spread to remote parts of the body, such as bones, liver, or lungs
Here are the 5-year relative survival rates for men with prostate cancer based on the SEER database information :
Being diagnosed with cancer can be difficult for both you and your loved ones. There is a great deal of information available about staging, survival rates, treatments, etc. Talking to your healthcare providers about your cancer can help you translate the alphabet soup into an actionable plan.
It is important to remember that cancer affects each person differently doctors have guidelines to follow, but no single treatment plan works best for everyone. Work as a team with your healthcare provider to come up with the best strategy for you to manage your prostate cancer.
Extent Your Cancer Has Spread
If your cancer has spread outside of your prostate , there are two category measures to consider. These two measurements are commonly combined with your T-stage to form one TMN score.
N-Category: Determines if and how far the cancer has spread to your lymph nodes.M-Category: Determines if and how far the cancer has metastasized or spread to other organs.
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
|
Any T, any N, M1 Any Grade Group Any PSA |
The cancer might or might not be growing into tissues near the prostate and might or might not have spread to nearby lymph nodes . It has spread to other parts of the body, such as distant lymph nodes, bones, or other organs . The Grade Group can be any value, and the PSA can be any value. |
Prostate cancer staging can be complex. If you have any questions about your stage, please ask someone on your cancer care team to explain it to you in a way you understand.
While the stage of a prostate cancer can help give an idea of how serious the cancer is likely to be, doctors are now looking for other ways to tell how likely a prostate cancer is to grow and spread, which might also help determine a mans best treatment options.
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Treatment
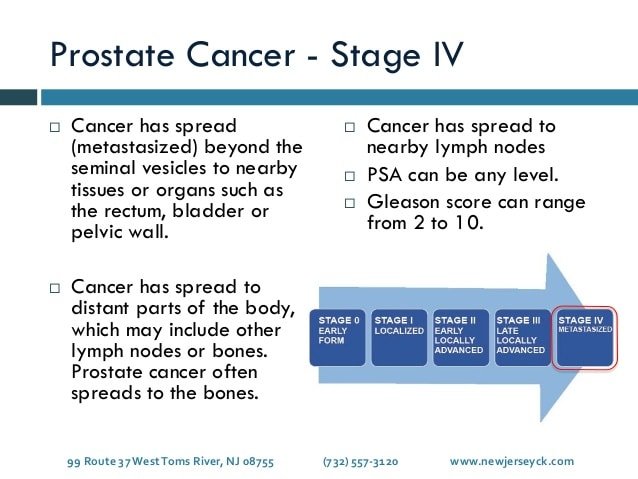
This is the last stage of prostate cancer and describes a tumor that has spread beyond the seminal vesicles to nearby tissues or organs, such as the bladder, rectum, lymph nodes or bones. At this point, treatment of the whole body with hormonal therapy or systemic therapy is the mainstay of stage 4 prostate cancer treatment. Local therapy with surgery or radiation therapy may be needed to help control symptoms. Proton radiation treatment may be used for advanced or late-stage prostate cancer to shrink tumors or control pain. While treatment can only cure a small percentage of T4 tumors, treatment may still be recommended to prolong or improve quality of life. For these distant stage cancers, the 5-year survival rate is 29%.
Don’t Miss: Perineural Invasion Prostate
What Does Your Tnm Prostate Cancer Stage Mean
The TNM system for describing prostate cancer uses the letters T, N, and M, which stand for tumor, nodes, and metastasis.
Specifically, stage 3 prostate cancer has extended through the capsule that surrounds the prostate but has not spread to distant sites in the body.
There are two sub-stages of stage 3 prostate cancer.
- T3a: The tumor has only gone through the capsule without invading the seminal vesicles.
- T3b: The tumor has invaded the seminal vesicles.
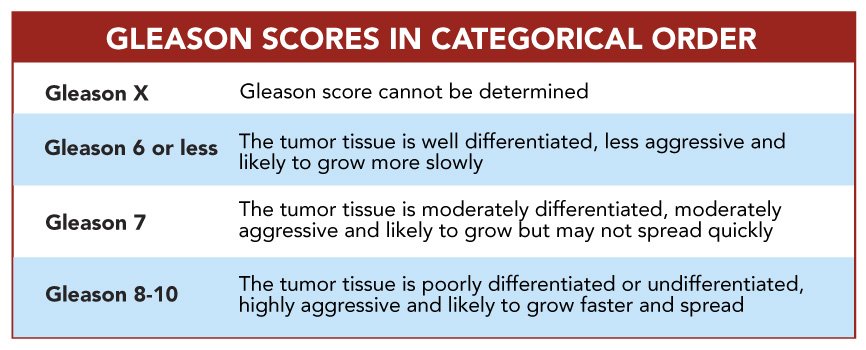
What Does It Mean To Have A Gleason Score Of 6 7 8 Or 9
Because grades 1 and 2 are not often used for biopsies, the lowest Gleason score of a cancer found on a prostate biopsy is 6. These cancers may be called well differentiated or low-grade and are likely to be less aggressive that is, they tend to grow and spread slowly.
Cancers with Gleason scores of 8 to 10 may be called poorly differentiated or high-grade. These cancers are likely to grow and spread more quickly, although a cancer with a Gleason score of 9-10 is twice as likely to grow and spread quickly as a cancer with a Gleason score of 8.
Cancers with a Gleason score of 7 can either be Gleason score 3+4=7 or Gleason score 4+3=7:
- Gleason score 3+4=7 tumors still have a good prognosis , although not as good as a Gleason score 6 tumor.
- A Gleason score 4+3=7 tumor is more likely to grow and spread than a 3+4=7 tumor, yet not as likely as a Gleason score 8 tumor.
Recommended Reading: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
How Important Is The Gleason Score
The Gleason Score is very useful for predicting the behavior of a prostate cancer. However, other factors also contribute to determining the stage of prostate cancer, including:
- The PSA level
- Findings from a rectal exam
- The number of biopsy core samples that contain cancer
- The percentage of cancer making up each biopsy core sample
- If cancer is found in one or both sides of the prostate
- If the cancer has spread outside the prostate
How Prostate Cancer Spreads
- The cells escape into the bloodstream, initially by invading small blood vessels around the tumor, then traveling to larger blood vessels that enable the cells to circulate around the body .
- The cells are filtered through the bodys lymph system although some are captured in lymph nodes, others may travel elsewhere in the body.
- The cells migrate along the length of a nerve, escaping from the prostate into adjacent soft tissue .
Recommended Reading: Flomax Dry Ejaculation
What Are The Potential Complications
Prostate cancer and treatment can lead to problems with urination as well as erectile dysfunction.
If stage 2 prostate cancer spreads outside the prostate, it can reach nearby tissues, the lymph system, or bloodstream. From there, it can metastasize to distant sites. Later-stage prostate cancer is difficult to treat and can be life-threatening.
More Detail On Staging
The standardized Tumor, Node, and Metastasis system is used to stage prostate cancer. The T category is based on the extent of the tumor itself. The N category is based on whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. The M category is based on whether the cancer has spread beyond nearby lymph nodes.
Also Check: Is Zinc Good For The Prostate
The Number Staging System
There are a few different systems used for staging prostate cancer. A simplified number staging system is described below.
- Stage 1 The tumour is contained in the prostate. The tumour is too small to be felt when a doctor does a rectal examination or to be seen on a scan.
- Stage 2 The tumour is still contained in the prostate, but your doctor can feel it when they do a rectal examination.
- Stage 3 The tumour has started to break through the outer capsule of the prostate and may be in the nearby tubes that produce semen .
- Stage 4 The tumour has spread outside the prostate. It may have spread to areas such as the bladder or back passage . Or it may have spread further, for example to the bones.
Using the numbered staging system described above:
- stage 4 is known as advanced prostate cancer.
See also
The grade of a cancer gives an idea of how quickly the cancer might grow or spread. A doctor decides the grade of the cancer by how the cancer cells look under the microscope.
Doctors look at the grade of the cancer to help them plan your treatment.
Gleason is the most commonly used grading system for prostate cancer.
Pathological Stage: A Look At The Actual Cancer Cells And Their Distribution Within The Pelvic Area
This system assesses how pervasive the cancer cells are within and around the prostate. These stages begin at T2.
T2: The tumor is located in the prostate only.T3: The tumor has breached the prostate border on 1 or more sides.T3b: The tumor has begun to grow in the seminal vesicles.T4: The tumor has grown into other neighboring structures, like the bladder, the rectum, or the pelvic wall.
Also Check: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
How Is Stage 2 Prostate Cancer Treated
Your doctor will recommend treatment based on several factors, including your age, overall health, and whether or not youre having symptoms.
Your doctor might consider active surveillance if you have a slow-growing cancer and no symptoms. That means you wont actually be treating the cancer, but you will be monitoring it carefully with your doctor. This might involve visiting your doctor every six months, which would include a digital rectal exam and PSA testing. You might also need an annual prostate biopsy.
Active surveillance is only an option if you can commit to following up as advised by your doctor. Treatment will be considered if there are any changes.
Treatment may involve a combination of therapies, some of which are:
What Does It Mean To Have A Gleason Score Of 6 Or 7 Or 8
The lowest Gleason Score of a cancer found on a prostate biopsy is 6. These cancers may be called well-differentiated or low-grade and are likely to be less aggressive – they tend to grow and spread slowly.
Cancers with Gleason Scores of 8 to 10 may be called poorly differentiated or high grade. These cancers tend to be aggressive, meaning they are likely to grow and spread more quickly.
Cancers with a Gleason Score of 7 may be called moderately differentiated or intermediate grade. The rate at which they grow and spread tends to be in between the other 2.
Also Check: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Diagnosis With The Whitmore
The Whitmore-Jewett System is an older system. It differs from the TNM system in that the stage and sub-stage is determined by whether the tumor can be felt by a physical examination* and by the PSA score.*a digital rectal examination
- Stage B – a tumor is not detected but PSA levels are very high.
- Stage B1 – a tumor can be felt. It is confined to one lobe.
- Stage B2 – a tumor can be felt. It is found in both lobes.
The TNM system when used in conjunction with PSA and Gleason scores is generally favored over the Whitmore-Jewett system it is thought to give a more accurate diagnosis.
