What Happens After A Prostate Ultrasound And Biopsy
When the procedure is finished, you may resume your normal meals and daily activities, unless otherwise instructed. Some urologists may prescribe an antibiotic after the biopsy to prevent any infections, but given antibiotics only prior to the biopsy. Some men may have soreness for a few days after the procedure, which is normal. Your provider will contact you when your results are available
Transrectal Ultrasound Scan And Biopsy For Prostate Cancer
A transrectal ultrasound scan is an examination of the prostate gland using ultrasound. Your doctor might take samples of tissue from the prostate during this test. This is a TRUS guided biopsy. It can help to diagnose prostate cancer.
You usually have an MRI scan before your TRUS guided biopsy. The MRI scan helps your doctor decide whether you need a biopsy and where to take the biopsies from.
Deaths From Prostate Cancer Have Now Overtaken Those From Breast Cancer
The new trial, titled: cancer diagnosis by multiparametric ultrasound of the prostate , used 370 male participants who are at risk of prostate cancer.
Finding out whether they were at risk or not, researchers used initial tests such as a prostate-specific antigen test which is a commonly used blood test to help detect prostate cancer and/or an abnormal digital rectal examination which is a test that examines a persons lower rectum, pelvis, and lower belly.
On separate visits, the men were given both mpUSS and mpMRI scans, followed by biopsies involving the use of thin needles to take small samples of tissue from the prostate to analyse under a microscope to check cancer for around 257 patients who had a positive mpUSS or mpMRI test result.
Comparing the results from the tests, they found that prostate cancer was detected accurately in 133 men, with 83 men diagnosed with clinically significant cancer.
Individually, mpUSS detected 66 cases of clinically significant cancer compared to mpMRI which detected 77 cases.
Although mpUSS detected 4.3% fewer clinically-important prostate cancers compared to mpMRI, this method could lead to 11.1% more patients being biopsied in comparison to original testing methods.
This may be because the mpUSS sometimes shows up abnormal areas even though there was no cancer.
Read Also: Can You Still Have An Erection After Prostate Removal
The Role Of Ultrasound In Prostate Biopsy
Prostate biopsy is usually indicated when one or more of the following factors exist: elevated PSA, rising PSA, abnormal findings on digital rectal examination, and prior biopsies demonstrating atypical small acinar neoplasia. Because of the low sensitivity and specificity of TRUS for the detection of prostate cancer, TRUS-guided targeted biopsy has limited value. However, because of its ability to clearly delineate prostate zonal anatomy, its ease of use, and its real-time capabilities, TRUS is the most commonly used modality for guiding systematic prostate biopsy. In 1989, Hodge et al. introduced the use of TRUS to guide sextant biopsy of the prostate gland, which involves sampling of the parasagittal apex, midzone, and base of the right and left sides of the prostate gland. However, the sextant biopsy strategy has since been superseded by extended 10- to 12-core biopsy protocols, which involve performing the standard sextant biopsy plus additional biopsies of the far lateral and apical zones. Extended 10- to 12-core biopsy protocols increase cancer detection rates up to 30%, increase negative predictive value, have a more accurate tumor grade concordance with radical prostatectomy, and do not increase the likelihood of detecting insignificant cancers . However, increasing the biopsy cores to more than 12 samples has not been shown to significantly increase cancer detection rates or negative predictive value but may increase the detection of insignificant cancers .
How Do I Prepare For A Prostate Ultrasound
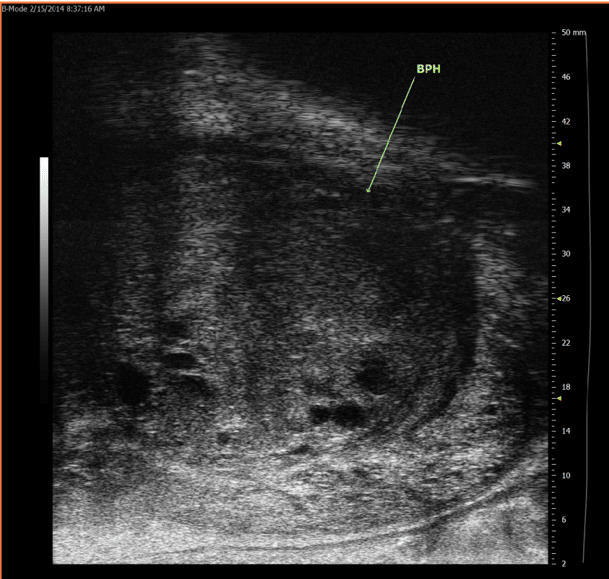
You dont need to do much to prepare for a prostate ultrasound. Its an outpatient procedure that usually takes less than an hour. Your doctor may refer you to a hospital or clinic that has the proper ultrasound equipment for this test. You may also need to sign a consent form before the test.
Some possible instructions that your doctor might give you before the test include:
- Dont eat for a few hours before the test.
- Take a laxative or enema to help clear out your intestines a few hours before the test.
- Stop taking any medications that can thin your blood, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or aspirin, about a week before the procedure. This is usually recommended if your doctor plans to take a biopsy of your prostate.
- Dont wear any jewelry or tight clothes to the clinic on the day of the procedure.
- Take any medications recommended to help you relax during the procedure. Your doctor may recommend a sedative, such as lorazepam .
- Make sure someones available to take you home in case your doctor gives you a sedative.
You May Like: Can A Man Have Sex If His Prostate Is Removed
Getting A Prostate Ultrasound For Prostate Cancer
Rony Kampalath, MD, is board-certified in diagnostic radiology and previously worked as a primary care physician. He is an assistant professor at the University of California at Irvine Medical Center, where he also practices. Within the practice of radiology, he specializes in abdominal imaging.
A prostate ultrasound is often used early as a way of diagnosing prostate cancer. Prostate cancer develops in the prostate, a small gland that makes seminal fluid and is one of the most common types of cancer in men.
Prostate cancer usually grows over time, staying within the prostate gland at first, where it may not cause serious harm. While some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly. The earlier you catch your prostate cancer, the better your chance of successful treatment.
If your healthcare provider suspects you might have prostate cancer they will conduct a number of tests which may include a prostate-specific antigen test, a digital exam of your prostate, and an ultrasound. If your blood work comes back and your PSA is high, your prostate feels abnormal upon exam and the ultrasound show signs of cancer, your practitioner will likely want to do a biopsy.
An Ultrasound Can Diagnose Most Prostate Cancer Cases In Men With Great Accuracy Only Missing 34% Of Severe Cases
As a disease which one in six men will get in their lifetimes prostate cancer is generally detected by magnetic resonance imaging scans.
However, MRI scans are expensive and time-consuming, so researchers looked to ultrasound scans to diagnose the disease finding that there was generally good accuracy in a clinical trial involving 370 men.
The researchers advocated for prostate cancer ultrasound scans to be used as a first test, especially in low- and middle-income countries where access to high quality MRI scans is expensive and difficult. The ideal objective would be to use these methods in combination, to maximise current cancer detection.
The prostate cancer ultrasound scans were a great success, only narrowly missing 4.3% of more clinically important prostate cancer cases which is cancer that is meant to be treated rather than monitored compared to MRI scans which are currently used.
You May Like: Is An Enlarged Prostate Serious
Mr Fusion Biopsy Techniques
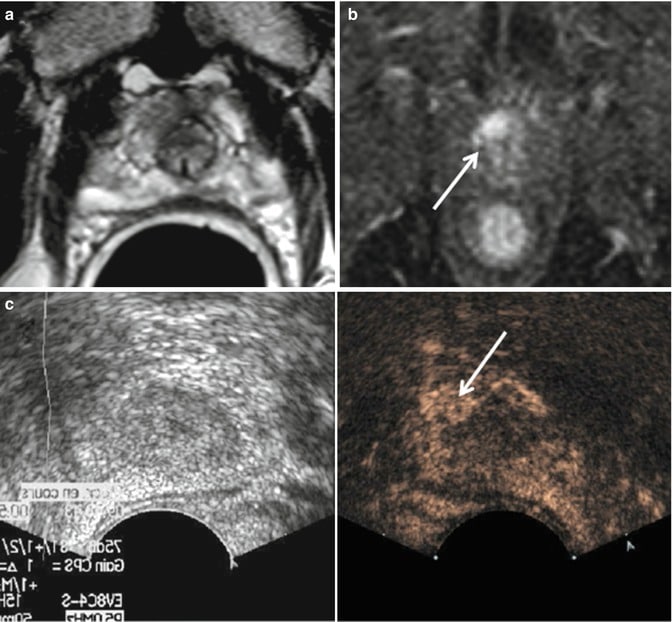
MRI has a moderately high sensitivity and specificity for the detection and staging of prostate cancer. Recently, a new technique has emerged which allows a pre-performed MRI to be coregistered to landmarks so that real-time virtual ultrasound-guided biopsied can be performed . Experience is limited, but this is a very promising development that would overcome the limitation of TRUS in detecting cancer while retaining the flexibility and convenience of TRUS-directed needle biopsy .17). Visualising the needle and tumour simultaneously increases the accuracy of targeted biopsy or ablative therapy.
MR transrectal ultrasound fusion image. Multiparametric axial MR images with functional information identifying a cancer not visible on TRUS . Fused data set, superimposing after coregistration the MR images that identify the tumour based on its reduced diffusion onto the real-time TRUS images. The red bars represent biopsy trajectories. Biopsy directed by the TRUS revealed a Gleason 7 cancer. Courtesy of Dr Erik Rud, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway.
What Happens After A Prostate Ultrasound
Once the test is done, you can take off the gown and put your clothes back on. Your rectum may feel tender for a few days, but you wont need to follow any specific aftercare instructions. Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic to prevent infection.
In some cases, your doctor or technician may ask you to wait in the facility until your results are available. Youll usually need to wait a few days for a radiologist to look at the images and diagnose any conditions, however. Depending on where the test was done, you may wait up to two weeks for results.
Your doctor will schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss your test results. If you have any abnormalities or conditions that are visible on the images, your doctor will point out these areas. Excess tissue, prostate enlargement, or cancerous tumors will appear on the ultrasound images as bright white areas that represent the dense tissue.
Read Also: What Does The Prostate Feel Like
What Happens During A Prostate/rectal Ultrasound
You may have a prostate/rectal ultrasound done as an outpatient or during ahospital stay. The way the test is done may vary depending on yourcondition and your healthcare provider’s practices.
Generally, a prostate/rectal ultrasound follows this process:
You will need to remove any clothing, jewelry, or other objects that may get in the way of the procedure.
If asked to remove clothing, you will be given a gown to wear.
You will lie on an exam table on your left side with your knees bent up to your chest.
The healthcare provider may do a digital rectal exam before the ultrasound.
The provider puts a clear gel on the transducer and puts the probe into the rectum. You may feel a fullness of the rectum at this time.
The provider will turn the transducer slightly several times to see different parts of the prostate gland and other structures.
If blood flow is being looked at, you may hear a whoosh, whoosh sound when the Doppler probe is used.
Once the test is done, the provider will wipe off the gel.
A prostate/rectal ultrasound may be uncomfortable and you will need toremain still during the test. The gel will also feel cool and wet. Thetechnologist will use all possible comfort measures and do the scan asquickly as possible to minimize any discomfort.
What Is Ultrasound Imaging Of The Prostate
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. It is safe and painless. It produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging is also called sonography. It uses a small probe called a transducer and gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves travel from the probe through the gel into the body. The probe collects the sounds that bounce back. A computer uses those sound waves to create an image. Ultrasound exams do not use radiation . Because ultrasound captures images in real-time, it can show the structure and movement of the body’s internal organs. The images can also show blood flowing through blood vessels.
Prostate ultrasound, also called transrectal ultrasound, provides images of a man’s prostate gland and surrounding tissue. The exam typically requires insertion of an ultrasound probe into the rectum of the patient. The probe sends and receives sound waves through the wall of the rectum into the prostate gland which is situated right in front of the rectum.
Don’t Miss: Does Prostate Stimulation Cause Ejaculation
Positive Outlook For Patients
What does this mean for patients? It may mean that instead of the urologist referring a patient out for mpMRI, he can perform a micro-ultrasound scan in the office, which takes approximately 15 minutes. Together with other risk factors and biomarkers, the results will help patients feel more confident in their decision to either proceed with a biopsy or to postpone it.
As with any clinical study, further large-scale investigation is warranted. However, the authors conclude that micro-ultrasound is an appealing alternative to mpMRI for detecting prostate cancer.
Brian Wodlinger, Ph.D., is vice president, engineering and clinical at Exact Imaging. Prior to Exact Imaging, Wodlinger held research positions at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center and Case Western Reserve University. This research won Popular Mechanics Top Breakthroughs of the Year award and has been featured in the popular media on platforms such as CBSs 60 Minutes. He holds eight patents in the medical devices space, has designed and executed more than 13 clinical trials and has authored more than 18 peer-reviewed research articles in prestigious journals such as The Lancet and PLoS ONE.
References:
1. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology V1.2019. . Prostate Cancer Early Detection Recommendations. National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc.
The Challenges With Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed male cancer, yet the standards for diagnosis remain blurry. Based on elevated PSA level or abnormal digital rectal exam, men will typically undergo a standard 10-12 core transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy. Although the idea is to systematically sample the whole prostate, the majority of cores are taken from the peripheral zone. Due to its distance from the rectum, the anterior is rarely sampled, while areas in the midline are undersampled to avoid the urethra. The transrectal route also makes it more difficult to target the apex.1 The TRUS biopsy is considered blind or random because the appearance of cancer is pretty ambiguous on the conventional, low-frequency ultrasound. This often leads to the underdetection of clinically significant cancer and the overdetection of low-grade cancers.2 The high false negative rate and potential for infectious complications make matters even worse for men with suspected low grade cancer. Unfortunately, the current standard of care to monitor low grade prostate cancer relies on repeat TRUS biopsy every 6-24 months. Due to the random nature of systematic biopsies, pathology results can differ significantly, with up to 37%-48% of men with low grade cancer receiving a benign diagnosis on confirmatory biopsy.3 This form of active surveillance repeatedly subjects patients to the potential undergrading of disease, overuse of antibiotics, invasive surgery and risk of sepsis.
You May Like: Hormone Shot Prior To Prostate Radiation
Advanced Genomic Testing For Prostate Cancer
The most common lab test for prostate cancer is advanced genomic testing, which examines a tumor to look for DNA alterations that may be driving the growth of the cancer. By identifying the mutations that occur in a cancer cells genome, doctors may get a clearer picture of the tumors behavior and be able to tailor a patients treatment based on the findings.
Expert cancer care
The Role Of Ultrasound In The Treatment Of Prostate Cancer
Traditional treatment options for clinically localized prostate cancer include radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation, brachytherapy, and active surveillance . Two additional treatment options for clinically localized prostate cancer are cryoablation and high-intensity focused ultrasound .
Cryoablation is a thermoablation technique that achieves cellular destruction by rapid cycles of freezing and thawing, resulting in coagulative necrosis. Under TRUS guidance, argon-based probes are advanced into the prostate gland via a transperineal approach. Pressurized argon gas is used to freeze the probe tip, which can reach temperatures as low as 187°C. The probe tip can then be rapidly thawed by exchanging pressurized helium into the probe, rapidly reheating the tip to 67°C. Achieving complete cell destruction requires temperatures lower than 40°C . In a literature review, Marien et al. reported that focal therapy of prostate cancer with cryoablation had a biopsy-free recurrence rate of 60%94%. Posttreatment complications included erectile dysfunction and incontinence .
The data on cryoablation and HIFU in the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer are promising. More comprehensive research is currently under way to better characterize cryoablation and HIFU as options for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: How Do Know If You Have Prostate Cancer
Color And Power Doppler Ultrasound
The principle behind the use of color Doppler ultrasound and power Doppler ultrasound in the evaluation of prostate cancer is the detection of increased perfusion compared with surrounding prostate tissue related to tumor neovascularity. Three different flow patternsdiffuse flow within, focal flow within, and surrounding flowhave been found to be associated with prostate cancer on CDUS, with diffuse flow being the most common pattern. The combination of CDUS and gray-scale ultrasound has been shown to detect a greater number of prostate cancers than gray-scale ultrasound alone, with higher specificity and positive predictive value . CDUS is especially useful in detecting isoechoic prostate cancers that demonstrate increased vascularity. Despite improved prostate cancer detection, CDUS has limited diagnostic accuracy because a substantial number of cancers are still missed, and it has relatively low specificity because not all tumors are hypervascular and not all hypervascular lesions are malignant .
PDUS is more sensitive than CDUS in detecting flow, especially slow flow . However, PDUS has not been shown to have increased benefit over CDUS for detecting prostate cancer. Studies suggest that on CDUS and PDUS, hypervascular and hypovascular lesions are associated with higher and lower Gleason scores, respectively .
How Does Ultrasound Work
An ultrasound machine has 3 key parts: a control panel, a display screen, and a transducer, which usually looks a lot like a microphone or a computer mouse. The transducer sends out sound waves and picks up the echoes. The doctor or ultrasound technologist moves the transducer over the part of the body being studied. The computer inside the main part of the machine analyzes the signals and puts an image on the display screen.
The shape and intensity of the echoes depend on how dense the tissue is. For example, most of the sound waves pass right through a fluid-filled cyst and send back very few or faint echoes, which makes them look black on the display screen. But the waves will bounce off a solid tumor, creating a pattern of echoes that the computer will show as a lighter-colored image.
Recommended Reading: What Does Your Prostate Control
