How Do I Know How Long I Have Left To Live
You might want to know how long you have left to live. This can help you prepare and plan the time you have left. There might be things you want to do or people you want to see. But some men dont want to know how long they have left. Everyone is different.
You can ask your doctor how long you have left to live. They wont be able to give you an exact answer. This can be frustrating and it may feel like your doctor is trying to avoid your questions. But no-one can know for certain how long you have left because everyone’s body and everyone’s cancer is different. However, your doctor will be able to give you some idea based on where the cancer has spread to, how you are responding to treatment, how quickly the cancer has spread, and what problems it is causing.
It can be helpful to talk with your family about this. You may not want to upset them but they might have similar questions and thoughts to you.
If you have months or maybe years left to live, it can be difficult for your doctor to say exactly how long you have left. This is because they dont know how you will respond to different treatments. If your treatment stops working so well, there may be other treatments available. Some men may not respond well to one treatment, but may respond better to another. Read more about treatments for advanced prostate cancer.
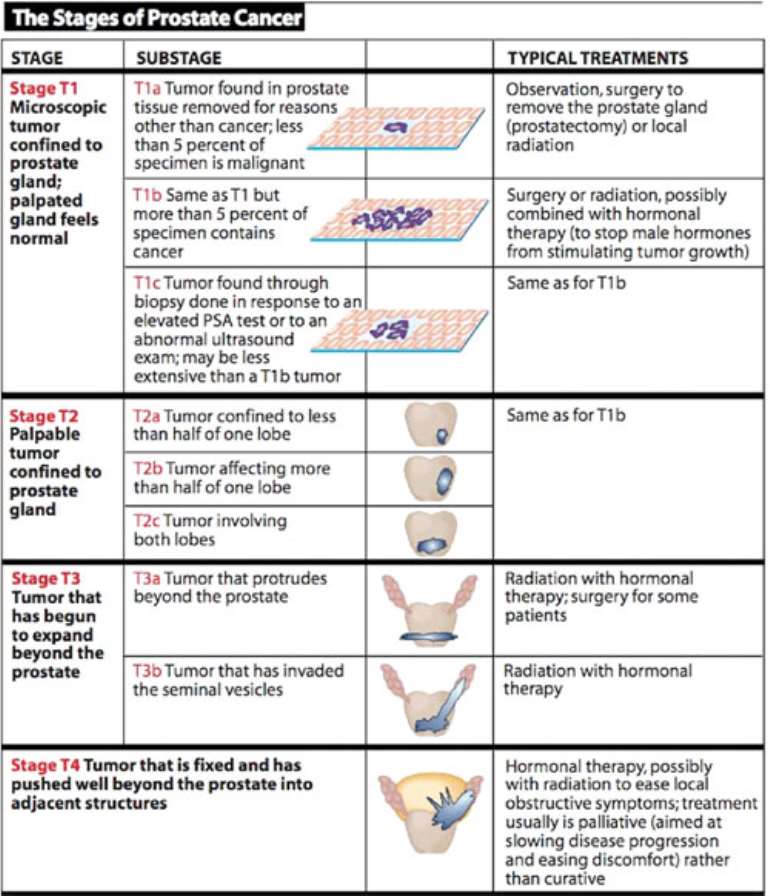
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
There are four stages to prostate cancer. Depending on the stage, doctors will need to formulate different treatment plans to effectively treat the cancer.
Do note that this is a summary of the four stages of cancer to help you understand how it changes and affects you or your loved one.
- Stage I: This is when the cancer is considered to be in its early stages. Patients may not be able to detect symptoms as the tumour cannot be felt. The cancer cells are well-differentiated and are indistinguishable from normal, healthy cells.
- Stage II: At this point, the cancer is growing slowly and can only be found in the prostate. The tumour may be small, but there is still a risk of growing and spreading outside of the prostate gland.
- Stage III: The tumour is growing rapidly and is likely to grow, spread, and develop in other parts of your body.
- Stage IV: At this stage, the cancer cells have spread beyond the prostate and into other parts of the body this is also known as advanced, or metastatic, prostate cancer.
There is also the possibility of the cancer recurring after treatment, either in the prostate gland or affecting another part of the body.
How Can Prostate Cancer Be Treated
Prostate cancer can be treated in a number of different ways depending on factors such as the severity of cancer and the rate at which it is growing.
Maslow explains, In my 20 years of oncology experience, I have seen many changes on the front of prostate cancer. All treatment forms depend on the aggressiveness of the disease and the patients current health status. Radiation often plays a big part in treatment of prostate cancer. This comes in many formsexternal beam radiation, prostate seed implants, proton therapy, high intensity focused ultrasound, and chemotherapy. In some cases for advanced disease, radioactive isotopes can be administered to make the patient more comfortable.
Low-grade prostate cancer may not require treatment, especially if you arent experiencing any symptoms. In these instances, a doctor may recommend active surveillance, which involves closely monitoring symptoms and undergoing regular blood testing, rectal exams, and prostate biopsies.
Other treatments for prostate cancer include hormone therapy, freezing or heating the prostate tissue, surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted drug therapy. Your doctor can recommend the best prostate cancer treatment for you based on your unique condition.
You May Like: Can A Ct Scan Detect Prostate Cancer
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Metastasis To Bone Life Expectancy
Talking To Your Doctor About Parp Inhibitors
Only about one-quarter of men with prostate cancer have the gene mutation that qualifies them to take a PARP inhibitor. New medicines that are now in clinical trials might one day expand the number of men who could benefit from this treatment.
If you have late-stage prostate cancer that isn’t responding to chemotherapy or hormone therapy, you can ask your doctor about PARP inhibitors.
Show Sources
Bladder And Urinary Troubles

A prostate tumor that has grown significantly in size may start to press on your bladder and urethra. The urethra is the passage the carries urine from your bladder out of your body. If the tumor is pressing on your urethra, you might have trouble passing urine.
One of the common areas for prostate cancer to spread to is the bladder, because the two organs are close. This can cause additional problems with urination and bladder function.
Some symptoms your bladder and urethra are being affected by cancer include:
- urinating more frequently
- getting up in the middle of the night to pee
- feeling like you have to urinate often and not actually passing anything
Don’t Miss: Does Benadryl Affect The Prostate
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
Doctors describe the growth and spread of prostate cancer in stages. Doctors use these stages as guides when choosing treatment options or offering prognoses to their patients.
Prostate cancer staging is based on a number of different factors, including prostate cancer screening tests such as a digital rectal exam or prostate-specific antigen test and imaging studies like bones scans, MRIs, CT scans, and trans-rectal ultrasounds.
You May Like: Triumph Nutritionals Preferred Prostate Plus
Gleason Score For Grading Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is also given a grade called a Gleason score. This score is based on how much the cancer looks like healthy tissue when viewed under a microscope. Less aggressive tumors generally look more like healthy tissue. Tumors that are more aggressive are likely to grow and spread to other parts of the body. They look less like healthy tissue.
The Gleason scoring system is the most common prostate cancer grading system used. The pathologist looks at how the cancer cells are arranged in the prostate and assigns a score on a scale of 3 to 5 from 2 different locations. Cancer cells that look similar to healthy cells receive a low score. Cancer cells that look less like healthy cells or look more aggressive receive a higher score. To assign the numbers, the pathologist determines the main pattern of cell growth, which is the area where the cancer is most obvious, and then looks for another area of growth. The doctor then gives each area a score from 3 to 5. The scores are added together to come up with an overall score between 6 and 10.
Gleason scores of 5 or lower are not used. The lowest Gleason score is 6, which is a low-grade cancer. A Gleason score of 7 is a medium-grade cancer, and a score of 8, 9, or 10 is a high-grade cancer. A lower-grade cancer grows more slowly and is less likely to spread than a high-grade cancer.
Recommended Reading: Erectile Problems After Prostate Surgery
Read Also: Hemp Oil For Enlarged Prostate
General Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
According to the American Cancer Society:
- The relative 5-year survival rate is nearly 100%
- The relative 10-year survival rate is 98%
- The 15-year relative survival rate is 91%
Note: Relative survival rate means the percentage of patients who live amount of years after their initial diagnosis.
Keep in mind, however, that because the compiled list figures are of cancers diagnosed up to 15 years ago, you may have an even greater chance of survival than these indicate due to advances in prostate cancer treatment technology
Is Stage 1 Prostate Cancer Serious
Stage 1 is the least advanced form of prostate cancer. Cancer in this stage is small and hasnt spread past the prostate gland. Its characterized by a PSA of less than 10 ng/mL, a grade group score of 1, and a Gleason score of 6. Stage 1 prostate cancer has a 5-year survival rate of nearly 100 percent .
What is the life expectancy after prostate removal?
Based on the natural history of localized prostate cancer, the life expectancy of men treated with either radical prostatectomy or definitive external-beam radiotherapy should exceed 10 years.
Can you survive stage 4 prostate?
Treatments may slow or shrink an advanced prostate cancer, but for most men, stage 4 prostate cancer isnt curable. Still, treatments can extend your life and reduce the signs and symptoms of cancer.
You May Like: How Do They Surgically Remove The Prostate
Table 1 Why A Low Psa Does Not Mean You Are Cancer
The Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial included a provision that men randomized to receive placebo undergo a prostate biopsy at the end of the study, even if they had normal PSA levels and digital rectal exams. To their surprise, investigators found that many of these men had prostate cancer in some cases, high-grade prostate cancer.
PSA level 13 *Note: A PSA level over 4.0 ng/ml traditionally triggers a biopsy. Adapted with permission from I.M. Thompson, et al. Prevalence of Prostate Cancer Among Men with a Prostate-Specific Antigen Level 4.0 ng per Milliliter. New England Journal of Medicine, May 27, 2004, Table 2.
This study inadvertently provided evidence not only that prostate cancer occurs more often than once believed, but also that PSA levels may not be a reliable indicator of which cancers are most aggressive. Both findings add weight to the growing consensus that many prostate tumors currently being detected may not need to have been diagnosed or treated in the first place.
Donât Miss: What Is Good To Take For Prostate Health
How Prostate Cancer Is Diagnosed And Staged
Cancer staging helps you and your doctor understand how advanced your cancer is and how much it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Knowing your cancer stage also helps your doctor determine the best treatment options for you and estimate your chance of survival.
The most widely used staging system for cancer is the TNM system that classifies cancer from stage 1 to stage 4.
TNM stands for:
- Tumor: the size and extent of the tumor
- Nodes: the number or extent of nearby lymph node involvement
- Metastasis: whether cancer has spread to distant sites in the body
The TNM scale is used for many types of cancer. When a doctor uses it to determine your prostate cancer stage, theyll consider several other factors as well, including:
You May Like: Can Enlarged Prostate Cause Bleeding
How Prostate Cancer Staging Is Done
Initial staging is based on the results of PSA blood tests, biopsies, and imaging tests. This is also called clinical staging.
PSA refers to a protein made by the prostate measured by a lab test.
- A higher level of PSA can indicate a more advanced cancer.
- The doctors will also look at how fast the PSA levels have been increasing from test to test. A faster increase could show a more aggressive tumor.
A prostate biopsy is done in your doctor’s office. The results can indicate:
- How much of the prostate is involved.
- The Gleason score. A number from 2 to 10 that shows how closely the cancer cells look like normal cells when viewed under a microscope. Scores 6 or less suggest the cancer is slow growing and not aggressive. Higher numbers indicate a faster growing cancer that is more likely to spread.
Tnm Staging System The Most Widely Used Staging System For Prostate Cancer Isthe Ajcc Tnm System For Prostate Cancerthere Are 4 Stages Often The Stages 1 To 4 Are Written As The Roman Numeralsi Ii Iii And Iv Generally The Higher The Stage Number The More The Cancerhas Spread The Stages Can Be Further Divided Into A B Or C An Earlier Lettermeans A Lower Stage Talk To Your Doctor If You Have Questions About Staging Tnm Staging Is Based On The Following: T Describes Thetumour And Whether Doctors Can Feel It Or See It On Imaging Tests It Alsodescribes Whether The Tumour Has Grown Outside Of The Prostate To Thesurrounding Tissues T Is Usually Given As A Number From 1 To 4 A Highernumber Means That The Tumour Takes Up More Of The Prostate Or That The Tumourhas Grown Outside Of The Prostate Into Nearby Tissues Some Stages Are Alsodivided Further Into A B Or C An Earlier Letter Means A Lower Stage The Clinical T Is Your Doctor’s Best Estimate Of Theextent Of The Cancer Based On A Physical Exam A Digital Rectal Exam A Prostatebiopsy And Imaging Tests If You Have Surgery To Remove Your Prostate Apathological T Will Be Given Pt Is More Accurate Than Ct T The Tumour Has Grown Outside The Prostate And Into The Seminal Vesicles T4 The Tumour Has Grown Outside The Prostate And Into Nearby Structures Suchas The Bladder Rectum Pelvic Muscles And Pelvic Wall
N describeswhether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the prostate. N0 means that thecancer hasn’t spread to any nearby lymph nodes. N1 means that it has spread tonearby lymph nodes.
M describeswhether the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. M0 means that the cancerhas not spread to other parts of the body. M1 means that it has spread to otherparts of the body.
PSA level describes the amount of the prostate-specificantigen in the blood.
Grade Group is a measureof how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
Don’t Miss: How To Effectively Stimulate Prostate
When To See Cleveland Urology
Note your symptoms and take action. If you are between the ages of 59 and 69, are African American, and/or have a family history of prostate cancer, see your doctor as soon as possible.
Typically, a screening test for prostate cancer will be performed, which includes digital rectal exam and a PSA test.
Do You Know The Five Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
Posted on by Cleveland Urologyin News
Do you know that prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in American men next to skin cancer? Do you know that the prostate is a vital part of a mans reproductive system? Do you know men can have both benign and cancerous growths in the prostate gland? Most importantly, do you know the five warning signs of prostate cancer? Every man should know when to take action.
Also Check: Can You Check For Prostate Cancer Yourself
Gleason Prostate Cancer Score
1960s as a way to measure how aggressive your prostate cancer may be.
A pathologist determines your Gleason score by looking at a biopsy of your prostate tissue under a microscope. They grade the cells in the biopsy on a scale of 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are healthy prostate, whereas grade 5 cells are highly mutated and dont resemble healthy cells at all.
The pathologist will calculate your Gleason score by adding together the number of the most prevalent type of cell in the sample and the second most prevalent type of cell.
For example, if the most common cell grade in your sample is 4 and the second most common is 4, you would have a score of 8.
A Gleason score of 6 is considered low-grade cancer, 7 is intermediate, and 8 to 10 is high-grade cancer.
A Biopsy Is Done To Diagnose Prostate Cancer And Find Out The Grade Of The Cancer
A transrectal biopsy is used to diagnose prostate cancer. A transrectal biopsy is the removal of tissue from the prostate by inserting a thin needle through the rectum and into the prostate. This procedure may be done using transrectal ultrasound or transrectal MRI to help guide where samples of tissue are taken from. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells.
Sometimes a biopsy is done using a sample of tissue that was removed during a transurethral resection of the prostate to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia.
If cancer is found, the pathologist will give the cancer a grade. The grade of the cancer describes how abnormal the cancer cells look under a microscope and how quickly the cancer is likely to grow and spread. The grade of the cancer is called the Gleason score.
To give the cancer a grade, the pathologist checks the prostate tissue samples to see how much the tumor tissue is like the normal prostate tissue and to find the two main cell patterns. The primary pattern describes the most common tissue pattern, and the secondary pattern describes the next most common pattern. Each pattern is given a grade from 3 to 5, with grade 3 looking the most like normal prostate tissue and grade 5 looking the most abnormal. The two grades are then added to get a Gleason score.
Read Also: What Doctor Does Prostate Exams
Tnm Staging: More Precise And More Complicated
A more involved but precise staging method is endorsed by the American Joint Committee on Cancer. The precision of this system helps doctors select patients for research and treatment on the basis of the biology of the cancer.
TNM stages categorize
- The size of the tumor
- The involvement of lymph nodes
- Metastasis and cancer grade.
The system is a bit complicated and is thoroughly described in public information provided by the ACS.
Good Prostate Cancer Care
Your MDT will be able to recommend what they feel are the best treatment options, but ultimately the decision is yours.
You should be able to talk with a named specialist nurse about treatment options and possible side effects to help you make a decision.
You should also be told about any clinical trials you may be eligible for.
If you have side effects from treatment, you should be referred to specialist services to help stop or ease these side effects.
Also Check: How To Self Prostate Massage
