The Groundbreaking Technology Includes:
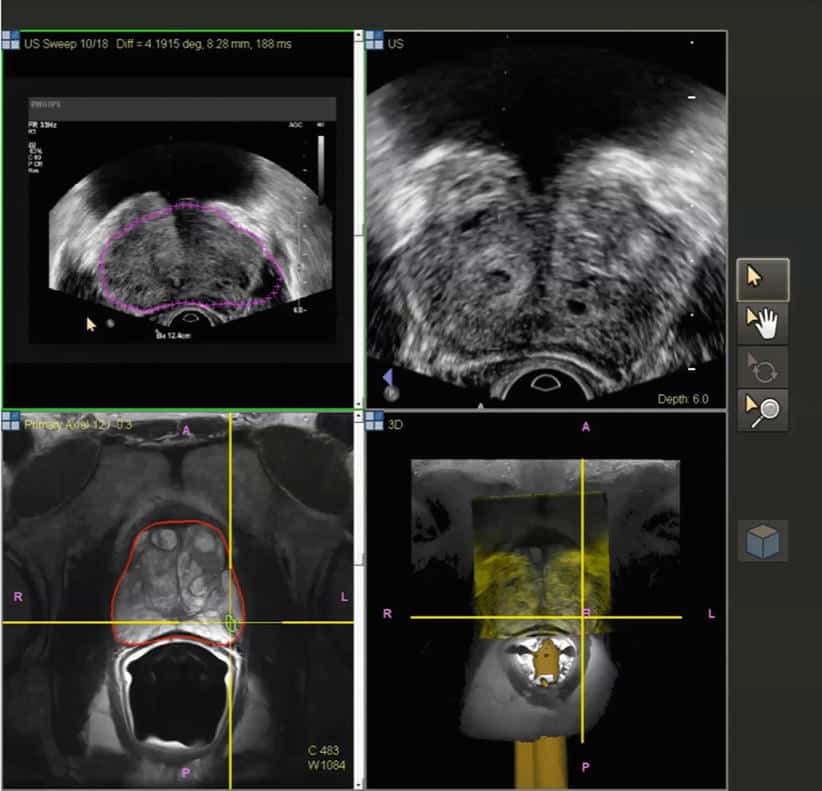
The PROMAP-MR combines 3D ultrasound and MRI to produce an accurate 3D mapping of biopsy samples within multimodal images.
The PROMAP-US combines full 3D ultrasound and automatic organ tracking to create, visualize and memorize a 3D map of target lesions and biopsy samples.
How 3D Ultrasound/MRI Fusion Biopsy Works
- Creates a 3D map of the prostate.
- Identifies suspicious lesions or targets on MRI.
- A specially trained urologist overlays 3D MRI and 3D ultrasound images in order to get a precise picture and location of suspicious areas of the prostate .
- Accurately guides the biopsy needle into the target lesion. Uniform random biopsies of other areas of the prostate may also be performed, depending upon the clinical circumstances.
- The computer creates a record of the exact location of each biopsy, which is then stored and available for future use.
Studies show that computer-assisted 3D Ultrasound/MRI Fusion Biopsy provides a more precise way to identify clinically significant prostate cancers. This allows patients access to unique technology that will significantly improve their clinical outcomes.
Who is a Candidate?
Several groups of patients can take advantage of this diagnostic tool including:
Talk to your doctor about the 3D Ultrasound/MRI Fusion Biopsy to see if you are a candidate for this advanced diagnostic procedure for prostate cancer.
Contact Us
Targeted Prostate Biopsy: What You Should Know
Targeted biopsy is being used at UCLA to diagnose prostate cancer. Targeted biopsy refers to using advanced imaging techniques to identify areas of the prostate suspicious for cancer, and then directly biopsying them. The traditional method of biopsy uses ultrasound imaging, with which tumors are hard to see. With targeted prostate biopsy, systematic sampling of prostate tissue is performed. The new method employs sophisticated MRI technology, developed at UCLA, to visualize prostate cancer, and fusion of the MR images with real-time ultrasound using the specialized biopsy equipment. The result is a 10-20-minute procedure, done in the clinic under local anesthesia, that is much more accurate at finding significant prostate cancer in men.
Benefits Of Mri/us Fusion Guided Biopsy:
- Identifies and locates hidden tumors missed by traditional biopsies
- Enhances visualization of tumors within the prostate, detailing exact size and location of suspicious tissue and tumors
- 3D map of the prostate and tumor allows for targeted biopsies and improved sampling for a more accurate diagnosis.
- Fusion of live 3D Ultrasound and MRI images provide more accurate staging, diagnosis and individualized cancer treatment and management plan
- The system provides the ability to retrieve a record of previous biopsy sites to allow the urologist to go back to the exact area of a previous biopsy site
While MRI and MRI/US Fusion Guided Biopsy may offer benefit in a few scenarios, it is not appropriate for all men. Those who would potentially benefit, generally fall into the following categories:
Prostate MRI and MRI/US Fusion Guided Biopsies are the most advanced techniques available to screen and stage prostate cancer in the appropriate situations. Although a prostate MRI or MRI/US Fusion Guided Biopsy is not appropriate for all men, if you or a loved one are concerned about the risk of developing prostate cancer, we encourage you to talk to your Urologist about these tests to determine if they are right for you.
To learn more about these procedures and about Dayton Physicians Network Urology please call 937-293-1622.
Were here for you, leading with the latest technology.
You May Like: How Is The Prostate Removed
Benefits Of Mri Fusion Biopsy
mpMRI is the cornerstone of fusion biopsy. Because this technology utilizes several image series to obtain both anatomical assessments of the prostate and physiologic assessments that represent potential changes arising from tumor cell proliferation, it not only helps identify prostate cancer but also directs the biopsy to areas of clinically significant disease, said Dr. Stratton.
Also see – Point: Is HIFU for low-risk prostate Ca ready for prime time?
Many reports show that mpMRI fusion biopsy improves biopsy accuracy. For example, in a retrospective study of 135 patients undergoing prostatectomy, Baco et al reported that the index lesion identified on mpMRI fusion biopsy was concordant with findings from prostatectomy pathology in 95% of patients.3
Other research shows the benefits of mpMRI fusion biopsy for maximizing detection of higher risk disease and limiting detection of low-risk disease. For example, in the multicenter PROMIS study that included 576 biopsy-naïve men, patients underwent mpMRI followed by mapping biopsy and TRUS biopsy.4 The study found that including mpMRI would improve the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer by 18% while potentially reducing the detection of clinically insignificant cancer by 5%.
Just as with MRI fusion biopsy, however, there are concerns with cost and utilization of resources accompanying the use of mapping biopsies, Dr. Cookson said.
Next: Ensuring quality
How Does The Procedure Work
Ultrasound procedure:
Ultrasound imaging uses the same principles as the sonar that bats, ships, and fishermen use. When a sound wave strikes an object, it bounces back or echoes. By measuring these echo waves, it is possible to determine how far away the object is as well as its size, shape, and consistency. This includes whether the object is solid or filled with fluid.
Doctors use ultrasound to detect changes in the appearance of organs, tissues, and vessels and to detect abnormal masses, such as tumors.
In an ultrasound exam, a transducer both sends the sound waves and records the echoing waves. When the transducer is pressed against the skin, it sends small pulses of inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body. As the sound waves bounce off internal organs, fluids and tissues, the sensitive receiver in the transducer records tiny changes in the sound’s pitch and direction. A computer instantly measures these signature waves and displays them as real-time pictures on a monitor. The technologist typically captures one or more frames of the moving pictures as still images. They may also save short video loops of the images.
MRI procedure:
A computer processes the signals and creates a series of images, each of which shows a thin slice of the body. The radiologist can study these images from different angles.
MRI is often able to tell the difference between diseased tissue and normal tissue better than x-ray, CT, and ultrasound.
You May Like: Do Guys Have To Get A Prostate Exam
Certain Uses Of Mri In Question
Some urologists are using MRI to clarify the extent of a mans prostate cancer before surgery, while others endorse its use to monitor patients on active surveillance and potentially reduce the number of serial biopsies they require. However, Dr. Klein says evidence supporting MRIs use in these situations is inconclusive and still evolving.
One potential use for MRI thats drawing significant interest is as a triage test to determine whether men at risk of prostate cancer require a first biopsy. In a recent study involving 626 men with no biopsy history, researchers concluded that MRI-guided biopsy, compared with TRUS biopsy, resulted in a similar detection rate of clinically significant prostate cancer but with fewer cases of clinically insignificant cancer. Nearly half the men had negative MRI findings and could forgo biopsy, at the risk of missing clinically significant cancer in 4% of cases, the study authors concluded.
Earlier studies found that, compared with TRUS biopsy, MRI fusion biopsy detected a higher percentage of clinically significant prostate cancers and fewer clinically insignificant tumors, and that using multiparametric MRI as a triage test could reduce unnecessary biopsies by a quarter.
Koelis Technology For Fusion Biopsy
For over a decade KOELIS® has assisted urologists and radiologists from around the world in their routine clinical practice providing the latest technology for personalized prostate cancer.
We propose precise real-time 3D transrectal ultrasound fusion-guided transperinal and transrectal prostate biopsy against conventional and random systematic biopsy to increase sampling quality with KOELIS Trinity®. In a simple process and device, KOELIS Trinity® cartographer is a powerful diagnostic tool to plan, implement, review and control a personalized care solution. It creates a detailed and personalized map of the patients prostate showing accurate core distribution since our image-based cartographer is equipped with the Organ-Based Tracking® technology. Without changing the usual clinical practices, this technique brings an increased quality control over biopsy localizations. A precise, individual prostate biopsy mapping is a value for the accurate diagnosis and the further management of each patient.
Health innovation as a passion
At KOELIS®, we innovate every day in collaboration with world-renowned universities and hospitals to offer physicians new advancements in imaging and a greater field of view in order to bring personalized answers to every patient, in the respect of their quality of life.
Do you have questions about our precision fusion technology? Find the common inquiries or contact us !
Read Also: How To Reach Your Prostate
Recommended Reading: How To Determine Prostate Cancer Stage
What Are The Limitations Of Ultrasound
A biopsy can only show if there is cancer in the tissue samples. It is possible to miss cancer in unsampled areas of the prostate.
For MRI-guided biopsies, you must remain perfectly still to ensure the technologist captures high-quality images. If you are anxious, confused, or in severe pain, it may be hard to lie still. If so, the images may not be of high enough quality to be useful.
Likewise, the presence of an implant or other metallic object sometimes makes it difficult to obtain clear MR images. A person who is very large may not fit inside certain types of MRI machines.
Bleeding may sometimes occur in the prostate after a biopsy. MR imaging cannot always tell the difference between cancer, inflammation, or the presence of blood. To avoid confusing them, your doctor may perform a repeat MRI six to eight weeks after the biopsy to allow residual bleeding to resolve.
An MRI exam typically costs more and may take more time than other imaging exams. Talk to your insurance provider if you have concerns about the cost of MRI.
What To Expect During An Mri Fusion Biopsy For Elevated Psa
Finding out that your PSA level is high can certainly be unnerving. While the majority of PSA elevations are caused by a benign condition, it’s important to seek further evaluation in order to rule out the presence of prostate cancer. The expert team at Kasraeian Urology, led by renowned board-certified urologists Dr. Ahmad Kasraeian and Dr. Ali Kasraeian, offers advanced diagnostic testing and treatment options for a wide array of urologic conditions in Jacksonville, FL. Learn more about one of the most cutting-edge diagnostic tools for prostate cancer, MRI fusion biopsy, including how it works and what you can expect during the procedure.
Don’t Miss: Can You Ejaculate Without A Prostate
Mri Guided Prostate Biopsy For Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: Now Available At University Hospitals
University Hospitals offers a prostate biopsy procedure guided by magnetic resonance imaging technology. This leading-edge diagnostic tool for prostate cancer is much more efficient than a traditional biopsy and causes less discomfort. In some cases, you can receive a diagnosis and treatment plan in as little as a day.
What Is Prostate Cancer Ablation
To begin, its important to understand what ablation is. Ablation means the removal of diseased body tissue such as cancerous tumors. Image-guided ablation is performed by applying thermal energy that physically destroys the cancer. For prostate cancer, ablation is an alternative to surgery or radiation.
Thermal ablation for prostate cancer has two main advantages over surgery:
- Same day outpatient procedure
- Very rapid recovery time and return to normal activities
Ablation also has a unique advantage over surgery and radiation, which are both whole-gland treatments. Ablation can be done as a focal treatment with added benefits:
- Targets only the tumor plus an extra safety margin
- Avoids damage to healthy prostate tissue
- Greatly reduces the risk of impaired urinary and sexual function as compared to surgery
Today, focal treatment for prostate cancer is recognized as an excellent option for patients who are accurately diagnosed and determined to be appropriate for a focal approach. Besides being clinically qualified, psychologically they desire high quality of life after treatment and are committed to actively participating in their doctors follow-up monitoring protocol using PSA blood tests and multi-parametric MRI scans at prescribed intervals.
Recommended Reading: Life Expectancy Of Stage 4 Prostate Cancer
What Is Focal Laser Ablation
Patient Dr. Michael Bedecs tells his story
Laser ablation generates intense heat that completely encompasses the targeted area. Under real-time MRI guidance, a special optical fiber is guided precisely into place at the core of the tumor. When activated, the laser emitted at the tip of the fiber destroys the tumor within minutes while special tracking called thermometry confirms the proper temperature. Afterward, multi-parametric MRI scans reveal that the destruction is complete, and the laser fiber is removed.
Did you know Focal Laser Ablation can ease the symptoms of BPH?
What Are The Benefits
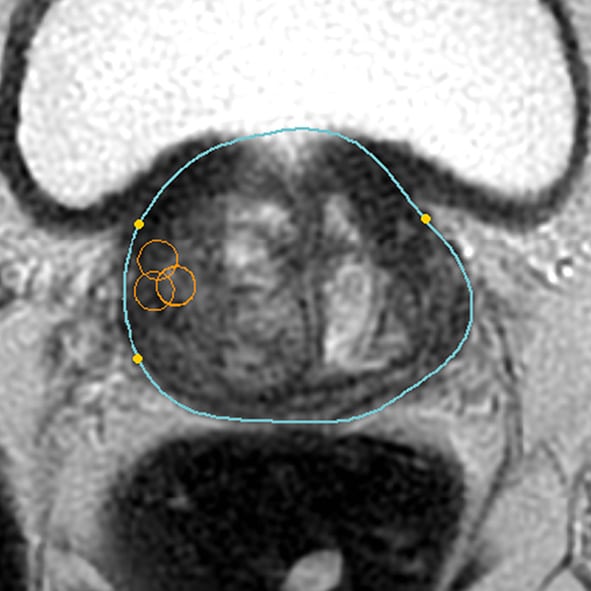
- This technique allows our specialists to find hidden tumors that may be missed by other prostate biopsies.
- We can perform targeted biopsies using sophisticated MRI/ultrasound fused images to focus on the worrisome areas directly.
- The technology, which has proven to be very useful for men with previous negative biopsies, may also help detect aggressive cancers in patients who have not had a previous biopsy.
- It may reduce the number of biopsies you need.
Talk to your doctor or your urologist if you want to learn more about the prostate MRI fusion biopsy. Or call for the Urology department for an appointment with Dr. Chad Tracy.
Don’t Miss: Can You See Prostate Cancer Ct Scan
Advanced Magnetic Resonance Mapping Targets Cancer
Using a cutting-edge technique for prostate cancer diagnosis and management, our team at University Hospitals uses MRI mapping to identify the exact location of suspicious tissue. We use images from the MRI to distinguish abnormal tissue from normal tissue. This allows our physicians to more accurately identify prostate cancer tumors and lesions, while also tracking their growth.
Although historically believed that MRI machines couldnt detect cancerous tissue, we now know that MRI images accurately identify aggressive cancers. So, with this knowledge, UH physicians developed the non-invasive fingerprinting technique to map the prostate and help distinguish normal from abnormal prostate tissue.
This breakthrough procedure lets UH physicians also monitor the prostate without making men go through unnecessary biopsies or other invasive examinations. As part of our active surveillance treatment, our team is able to monitor the growth of the tumor and determine if more interventional prostate cancer treatment is needed.
Future benefits may be even brighter: University Hospitals has been awarded a $5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to further develop MRI mapping and the use of artificial intelligence to predict the likelihood of a cancer diagnosis.
What To Expect From An Mri Fusion Biopsy
Available mostly at larger academic medical centers, multiparametric MRI takes about a half-hour to complete. Patients are given an intravenous contrast solution, which allows for visualization of the prostate. The MRI is not recommended for people with chronic kidney disease or who have allergies to the contrast solution. It also may not be suitable if you have problems with confined spaces.
Another potential complication of biopsy is infection. But, with todays prophylactic antibiotic regimens, the risk of serious infections is very low 0.5% at Cleveland Clinic, Dr. Klein says.
Also Check: Active Surveillance Prostate Cancer Guidelines
Role Of Repeat Biopsy
Patients receiving a PI-RADS assessment category of 3 to 5 warrant repeat biopsy with image guided targeting . At least 2 targeted cores should be obtained from each MRI defined target. Each man must be individually assessed as to whether a concurrent systematic sampling is warranted. Performing solely targeted biopsy should only be considered once quality assurance efforts have validated the performance of prostate MRI interpretations with results consistent with the published literature . In patients with negative or low suspicion MRI , other ancillary markers may be of value in identifying patients warranting repeat systematic biopsy. If a repeat biopsy is deferred on the basis of MRI findings, then continued clinical and laboratory follow-up is advised and consideration should be given to incorporating repeat MRI in this diagnostic surveillance regimen. Among men with very high suspicion and a negative targeted biopsy, early consideration should be given to repeat biopsy.
Mri Fusion Prostate Biopsy
MRI ultrasound fusion prostate biopsy is the most effective way to diagnose prostate cancer.
The MRI fusion prostate biopsy is a two-step process. A couple of weeks before the procedure, you will get an MRI of the prostate. MRI of the prostate provides an image of the inside of the prostate. The images are interpreted by a radiologist who will identify areas suspicious for cancer. The images are provided to the urologist, who will then perform the second step, the transrectal ultrasound guided biopsy of the prostate. While the biopsy is performed, the MRI images are fused over the real time ultrasound images for accurate targeting of suspicious lesions. The urologist will obtain the biopsies as identified from the suspicious areas, in addition to the standard 12 core biopsies from the prostate.
Don’t Miss: What Can You Take For An Enlarged Prostate
Study Selection And Extraction Of Data
Data retrieval was performed by 2 independent reviewers and discrepancies between them were solved through discussions or consulting a third reviewer. Titles and abstracts were examined for relevance before full-text reviews of articles. Information on the article, participant, MRI, as well as biopsy features were recorded in a standard form as follows: 1) article: origin , definition of csPCa, definition of high risk PCa 2) study participant: clinical setting , number of participants , MRI sequence for defining target, age, mean prostate volume, and mean PSA 3) MRI: magnet strength, MRI sequences, and number of patients with positive MRI scan 4) biopsy: core numbers and lesion numbers for MRI-TB/SB, previous biopsy status, rates of detection of csPCa, overall PCa, cisPCa, as well as high risk PCa.
Psa: Whats Normal And What Does It Mean
A higher-than-normal PSA can indicate noncancerous conditions such as aging-related enlargement, inflammation, or infection. Certain activities, such as riding a bike or having sex can trigger a temporary increase in PSA that has nothing to do with disease.
On the other hand, up to 15% of men with normal PSA levels can still have prostate cancer.8 Even when PSA levels are abnormal, as many as 75% of men end up not having prostate cancer yet have had unnecessary biopsies and worried for nothing.9
Also, the Digital Rectal Exam is not reliable for detecting prostate cancer. The doctor can only feel the surface of the gland closest to the rectal wall, completely missing small tumors located more deeply where most prostate cancer begins. It is neither thorough nor accurate.10
Since the likelihood of having prostate cancer increases proportionately with PSA level, there is no threshold below which a man can be reassured that prostate cancer does not exist. PSA levels greater than 4 ng/mL are generally considered suspicious. As levels increase above 10.0 ng/mL, the probability of cancer increases dramatically. However, not all men with prostate cancer have elevated PSA levels, and not all normal PSA levels guarantee that no cancer is present. A small percentage of prostate cancers can present with a PSA level of less than 4.0 ng/mL. This is why doctors may use lower thresholds to decide when to do a biopsy.
Also Check: 4 3 7 Prostate Cancer
