How Common Is Prostate Cancer And Who Is At Risk
Prostate cancer most often affects men between ages 55 and 69. There is a huge gap between the proportion of men diagnosed with prostate cancer and those whose health and lifespan are affected by the disease. American men have a 16 percent lifetime risk of developing prostate cancer, but only 2.9 percent of men die from it.
In fact, many prostate cancers are believed to be slow growing, with men dying from causes other than prostate cancer. Autopsy studies support this, finding that 30 percent of 55-year-old men and 60 percent of men reaching age 80 on whom an autopsy is performed have autopsy-discovered prostate cancer.
There are some factors that increase risk for prostate cancer, including:
Race Race seems to play a role in the frequency and severity of the disease. African-American men are far more likely to develop prostate cancer than white men 203.5 vs. 121.9 cases per 100,000 men. They are also more than twice as likely as white men to die of prostate cancer 44.1 vs. 19.1 deaths per 100,000 men.
Family History Positive family history of prostate cancer is another risk factor.
Elevated Body Mass Index Elevated BMI is another risk factor, linked to an increased risk of prostate-cancer-specific mortality and biochemical recurrence in men with prostate cancer.
Are There Prostate Cancer Risk Factors To Consider
Cancer researchers have identified several factors that could increase a mans risk of developing prostate cancer. In considering whether any of these risk factors apply to you, remember that having one or more of them does not mean you will get the disease. However, you should be sure to get all the prostate cancer screenings your physician recommends. It is also important to know that men without these risk factors may also have prostate cancer.
Risk Factors For Prostate Cancer
Some risk factors have been linked to prostate cancer. A risk factor is something that can raise your chance of developing a disease. Having one or more risk factors doesn’t mean that you will get prostate cancer. It just means that your risk of the disease is greater.
- Age. Men who are 50 or older have a higher risk of prostate cancer.
- Race. African-American men have the highest risk of prostate cancerâthe disease tends to start at younger ages and grows faster than in men of other races. After African-American men, prostate cancer is most common among white men, followed by Hispanic and Native American men. Asian-American men have the lowest rates of prostate cancer.
- Family history. Men whose fathers or brothers have had prostate cancer have a 2 to 3 times higher risk of prostate cancer than men who do not have a family history of the disease. A man who has 3 immediate family members with prostate cancer has about 10 times the risk of a man who does not have a family history of prostate cancer. The younger a man’s relatives are when they have prostate cancer, the greater his risk for developing the disease. Prostate cancer risk also appears to be slightly higher for men from families with a history of breast cancer.
- Diet. The risk of prostate cancer may be higher for men who eat high-fat diets.
You May Like: What’s The Survival Rate For Prostate Cancer
Current Psa Screening Recommendations
PSA-based screening refers to testing healthy men without symptoms.
Until recently, physician societies disagreed on screening recommendations, but with the publication of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Guideline in May 2018, all the major physician groups are broadly in agreement, including the American College of Physicians , the American Cancer Society , American Urological Association , and American Society of Clinical Oncology :
- They advise supporting men so that they make informed decisions about screening that reflect their personal preferences and values.
- Routine screening is not recommended in men between ages 40 and 54 of average risk.
- For men ages 55 to 69 years, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concluded with moderate certainty that the net benefit of PSA-based screening is small for some men, making the decision up to the judgment of the physician and the values of the patient.”
- For men 70 years and older, they recommend against routine screening because the expected harms are thought to outweigh the benefits.
- Your doctor should not screen you unless you express a preference for it.
- A discussion of the benefits and harms of screening should include a family history of prostate cancer, race or ethnicity, any medical conditions that affect your overall health and lifespan, and your values about risk and benefit.
- If you have less than a 10-year life expectancy, screening is not recommended.
Definitions Of Disease Categories
ICD codes used in the disease categories were the following : myocardial infarction , other coronary heart disease , cerebrovascular accident , arterial disease , heart failure , pneumonia , chronic lower respiratory disease , external causes , complications of diagnostic or surgical procedures , complications of therapeutic drug or vaccine usage , suicide , traffic accident , falls , other heart disease , gastrointestinal disease , dementia , diabetes , complications of heart disease , urinary system disease , symptoms , pulmonary circulation , nervous system disease , hypertensive disease , other bacterial disease , psychic disease , anemia , tumors other than prostate cancer , and prostate cancer .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Prostate Supplement On The Market
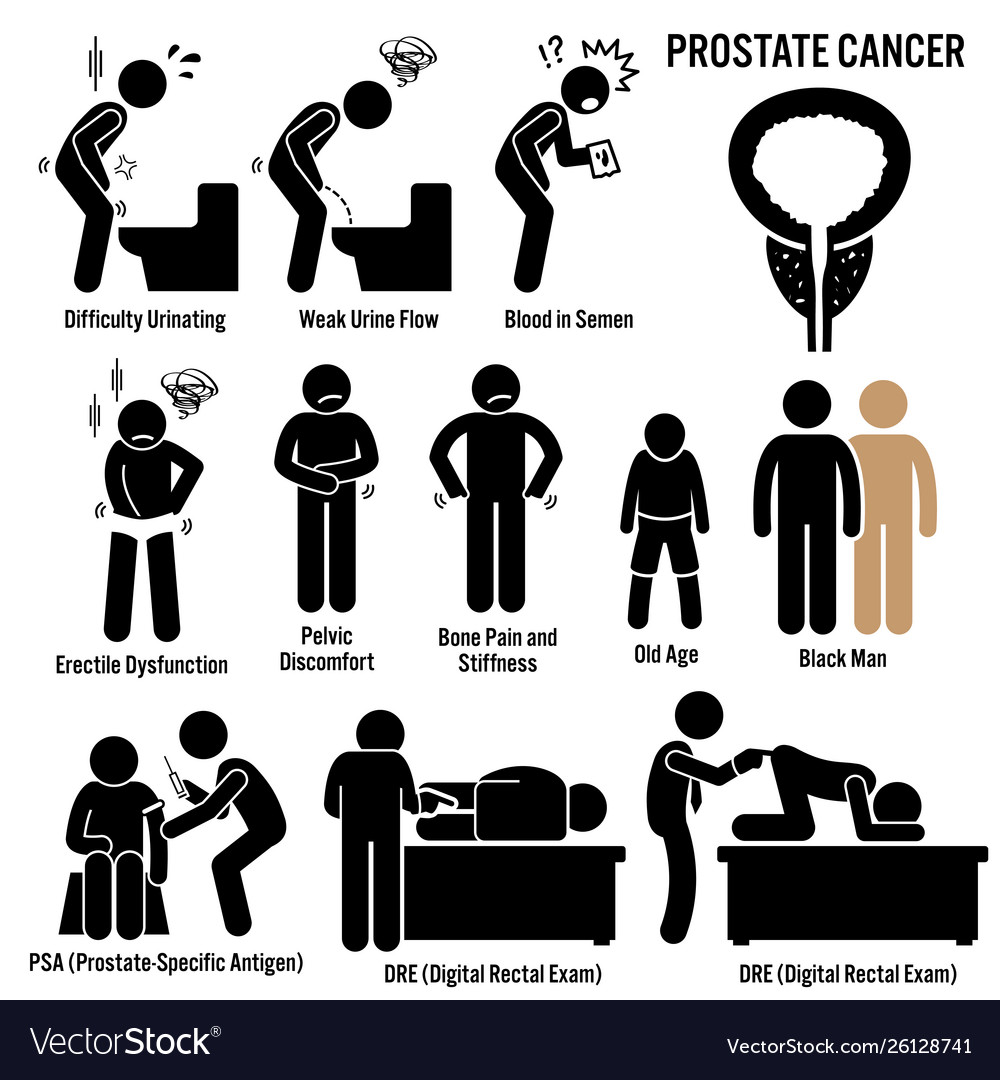
Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
- Posted on:
Prostate cancer is one of the most common kinds of cancer that threatens older men. Although early stage symptoms are harder to detect, there are a number of warning signs that could potentially indicate youre at risk for prostate cancer or have already developed it.
Treatment for prostate cancer is most effective when caught in early stages, so if you know what to look for, your odds are much better than if you were to wait. In this article, well review the 5 warning signs and symptoms of prostate cancer that you should not ignore.
How Do You Know If You Have Prostate Cancer
Theres no way of knowing if you have prostate cancer without visiting your doctor, as most men with early prostate cancer dont have any symptoms. And if you do have symptoms they can be caused by other things.
And you cant check for prostate cancer yourself.
You may want to speak to your GP if you’re over 50 , even if you don’t have any symptoms. These are all things that can increase your risk of prostate cancer. Your GP can give more information or tests if necessary.
If youre not sure about what to say to your GP, print and fill out this form and show it to them. This will help you have the conversation.
I thought I could be at risk after learning that African Caribbean men are more likely to get prostate cancer than white men.
You May Like: Prostate Cancer Medication Side Effects
Your Unique And Personal Experience
Receiving a diagnosis of cancer is emotional, scary, overwhelming and can make you feel like youve lost control. Your cancer and the way you respond to treatments are individual and personal. Most people know about cancer through the experience of someone else, often a family member or friend. There are many types of cancer and other peoples experiences will not be the same as yours. We encourage you to express your emotions, ask questions and allow us to teach you how to be an advocate for yourself.
Several cancers today have excellent outcomes and can be cured with new technologies and advancements. In other cases, treatments may be given which either extend or maintain your quality of life. The first step to regaining control and alleviating much of your anxiety is to educate yourself about your cancer. Few cancers require emergency treatment so you have time to learn about your diagnosis and treatment options. We encourage you to ask questions and seek additional medical information.
There are many websites with information about cancer. In addition to our site, we recommend using reliable sources, including The American Cancer Society and The National Cancer Institute.
Does Prostate Cancer Have Any Symptoms
Most men with early prostate cancer dont have any signs or symptoms.
One reason for this is the way the cancer grows. Youll usually only get early symptoms if the cancer grows near the tube you urinate through and presses against it, changing the way you urinate . But because prostate cancer usually starts to grow in a different part of the prostate, early prostate cancer doesnt often press on the urethra and cause symptoms.
If you do notice changes in the way you urinate, this is more likely to be a sign of a very common non-cancerous problem called an enlarged prostate, or another health problem. But its still a good idea to get it checked out. Possible changes include:
- difficulty starting to urinate or emptying your bladder
- a weak flow when you urinate
- a feeling that your bladder hasnt emptied properly
- dribbling urine after you finish urinating
- needing to urinate more often than usual, especially at night
- a sudden need to urinate you may sometimes leak urine before you get to the toilet.
If prostate cancer breaks out of the prostate or spreads to other parts of the body , it can cause other symptoms, including:
- back pain, hip pain or pelvis pain
- problems getting or keeping an erection
- unexplained weight loss.
These symptoms can all be caused by other health problems. But its still a good idea to tell your GP about any symptoms so they can find out whats causing them and make sure you get the right treatment, if you need it.
Also Check: What Age To Check Prostate Cancer
Early Stage Prostate Cancer
If the cancer is small and localized, a doctor may recommend:
Watchful waiting or monitoring
The doctor may check PSA blood levels regularly but take no immediate action. Prostate cancer grows slowly, and the risk of treatment side effects may outweigh the need for immediate treatment.
Surgery
A surgeon may carry out a radical prostatectomy to remove the tumor. In addition to removing the prostate, the procedure may also involve the removal of the surrounding tissue, seminal vesicles, and nearby lymph nodes. A doctor can perform this procedure using either open, laparoscopic, or robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery.
Radiation therapy
This uses radiation to kill cancer cells or prevent them from growing. Options for early stage prostate cancer may include :
External radiation therapy: This method uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer cells. Conformal radiation therapy is a type of external radiation that uses a computer to help guide and target a specific area, minimizing the risk to healthy tissue and allowing a high dose of radiation to reach the prostate tumor.
Internal radiation therapy: Also known as brachytherapy, this method uses radioactive seeds that a doctor implants near the prostate. A surgeon uses imaging scans, such as ultrasound or computed tomography to help guide the placement of the radioactive substance.
Treatment will depend on various factors. A doctor will discuss the best option for the individual.
Have Any Of These Symptoms Visit Norman Urology
Theres no sense in worrying needlessly come see us at Norman Urology. We take urological care seriously for both men and women. Whether you have a benign condition or something more serious, you can count on superior, specialized care from experienced, compassionate professionals.
Reach out to us today to schedule an appointment. We cant wait to meet you.
Read Also: When Should You Have A Prostate Exam Uk
Loss Of Bladder Control
Loss of bladder control can be another warning symptom. In medical terms, this condition is widely known as urinary incontinence. Different types of urinary incontinence can occur in prostate cancer. Stress incontinence and urge incontinence are the two major types reported by the patients. Loss of bladder control can occur as a part of the disease process, but mostly radiation therapy and prostatectomy are the major causes of loss of bladder control.
Prostate also helps in controlling the flow of urine through the urethra from the bladder. After prostatectomy to control the spread of prostate cancer, bladder fails to hold the urine resulting in dribbling and nocturia. Surgery of the prostate can cause damage to nerves that supply the bladder resulting in urinary incontinence. External beam of radiation can also cause damage to bladder and urethra to worsen the condition further. 25 percent of men suffer from loss of bladder control due to prostate cancer and its treatment options. You should seek the advice of the doctor as soon as possible if you are suspecting these warning signs.
Page 12 of 14
Further Treatments To Control The Cancer
Your first treatment may help keep your cancer under control. But over time, the cancer may change and start to grow again. If this happens you might be offered other treatments, including:
- more hormone therapy
- clinical trials
More hormone therapy
Your prostate cancer may respond well to other types of hormone therapy, such as abiraterone , enzalutamide , steroids or oestrogens, or to a combination of treatments.
More chemotherapy
If youve had hormone therapy on its own as a first treatment, you might be offered a chemotherapy drug called docetaxel . This may help some men to live longer, and can help to improve and delay symptoms. If youve already had docetaxel, you might be offered more docetaxel or another chemotherapy drug called cabazitaxel .
Radium-223
This is a type of internal radiotherapy that may be an option if your cancer has spread to your bones and is causing pain. A radioactive liquid is injected into your arm and collects in bones that have been damaged by the cancer. It kills cancer cells in the bones and helps some men to live longer. It can also help to reduce bone pain and delay some symptoms, such as bone fractures. Read more about radiotherapy for advanced prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: How To Determine Prostate Cancer Stage
No Symptoms In Early Stages
The problem is, early stage prostate cancer is a silent lurker with no symptoms. However, a growing tumor will eventually cause symptoms. Since many noncancerous conditions like infection or normal age-related prostate enlargement can cause similar symptoms, only a doctor can tell the difference.
Here are 10 prostate cancer warning signs you should pay attention to. To help you remember them, I have divided them into three categories: urinary function, sexual function, and pain.
What Causes Prostate Cancer
Put simply, prostate cancer is caused by changes in a person’s genetic code or DNA. There are two important types of genes that may play a role in the development of prostate cancer:
- Genes that help cells grow, divide, and stay alive are called oncogenes.
- Genes that keep cell growth under control, repair mistakes in our DNA, or trigger cellular death at the right time are called tumor suppressor genes.
If either gene type changes , then it can result in cells growing out of control e.g., cancer.
Also Check: How Long Is Recovery From Prostate Surgery
Diagnostic Radiologic Procedure And Ultraviolet Light Exposure
The radiation generated from X-ray, CT and nuclear imaging is ionizing radiation that penetrates the tissue to reveal the bodyâs internal organs. However, ionizing radiation can damage DNA, and although cells repair most of the damage, sometimes small area may remain altered consequently leading to DNA mutations that may contribute to cancer development years down the road. The first study investigating the connection between low-dose ionization radiation from diagnostic X-ray procedures and risk for prostate cancer reported that exposure to a hip/pelvic X-ray significantly increased prostate cancer risk independently of other known risk factors such as family history of cancer . However, unless men were exposed to high doses of radiation during cancer treatment in youth, any increase in the risk for cancer due to medical radiation appears to be slight. Considering that the increase in high-dose imaging has occurred only since 1980 and the effects of radiation damage typically take many years to appear, this may explain the weak association between ionizing radiation and prostate cancer risk observed thus far.
Finally, exposure to solar UV radiation is inversely associated with both the incidence and mortality of prostate cancer . The biological explanation of this fact is based on the synthesis and physiological actions of vitamin D .
Ontogenesis Of Postural And Sphincter Anticipatory Adjustments
The control of body position in space develops with different intensity during life span . As an example, Zaino and McCoy showed that young healthy children exhibit much higher variability of posture control than older healthy children . It is also reported that the age 79 years is an important period of their life in which children master postural control . Moreover, Schmitz et al. showed that children 34 years old develop APA, although they show coexistence of both adult-like and immature patterns, concluding that this anticipatory activities are being set up and that children are progressively mastering them.
Changes in brain structure are continuous throughout life . By the age 2, the brain has reached 75% of its adult weight and the processes of synaptic pruning and cell death are most active during these early years . During the school-age years, strong signs of brain maturation are appreciable, especially in its connectivity . MRI measures of the structure in fibers tracts correlate with behavioral indices that also change in this period . Later changes involve the associative neocortex, which continues to develop well into the third decade , and the corpus callosum, which connects all major subdivisions of the cerebrum .
Recommended Reading: Is Pumpkin Seeds Good For Your Prostate
You May Like: What Is The Normal Level For Prostate
