Ed Pills And Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
No part of the human body is immune to the effects of aging. Many men face the double whammy of smaller erections and larger prostates as the clock ticks on. Although both erectile dysfunction and benign prostatic hyperplasia become much more common as men age, they are very different problems with separate causes, unique symptoms, and unrelated consequences. Until now, treatments for the two conditions have also been different in fact, medical and surgical therapies for BPH can sometimes even cause ED. But research suggests that the most popular and effective drugs for ED may substantially reduce the symptoms of BPH.
Enlarged Prostate Doesn’t Raise A Man’s Odds For Cancer
HealthDay Reporter
WEDNESDAY, Aug. 25, 2021 — Does having an enlarged prostate doom you to prostate cancer?
Far from it, a new study suggests.
Also called benign prostatic hyperplasia , the condition may actually provide some protection for men from developing prostate cancer, researchers report.
“Men are often anxious about prostate cancer, as it is the second most common cancer in men, with some worrying BPH increases their risk of prostate cancer,” said lead researcher Dr. Kiran Nandalur. He is vice chief of diagnostic radiology and molecular imaging at Beaumont Hospital in Royal Oak, Mich.
“Some previous studies have demonstrated BPH may increase the risk of cancer, given common driving forces such as genetics, hormones and inflammation. Our study should alleviate their concern, as BPH may decrease their odds of prostate cancer,” Nandalur said.
BPH is common in aging men and can cause a frequent need to urinate, often at night, or a weak flow of urine. This is because the central part of the prostate enlarges and can block urine from leaving the bladder.
Surprisingly, as the prostate continues to enlarge, the odds of prostate cancer goes down, Nandalur explained.
“Moreover, BPH decreases the odds of not just a single focus of cancer, but also more than one site. Based on these findings, BPH may be producing mechanical pressure throughout the gland, which inhibits cancer growth and decreases the odds of prostate cancer,” he added.
More information
How Can Bph Cause Renal Failure
Anything that gets in the way of urine leaving the body can lead to acute renal failure. Kidney stones or blood clots in the urinary tract can cause it. Prostate cancer or BPH can cause it as well.
Symptoms of BPH tend to get worse over time. In the most severe cases, BPH can lead to infection, bladder damage, or kidney damage. Its not common, but BPH can lead to renal failure. Thats why its important to seek treatment for BPH before it causes damage to your kidneys.
The good news is that most men with BPH dont develop kidney damage or renal failure.
Recommended Reading: Flomax No Sperm
Construction Of The Prostate Mesh
Multiple methodologies permit the construction of solid anatomic NURBS models . Because the geometries of the prostate and a solid torus are topologically equivalent, we leveraged a parametric mapping algorithm to deform a torus solid NURBS model to match with a patient-specific prostate surface model. We used 3DSlicer to generate a triangular surface model of the prostate from the contours of the organ and the urethra drawn on the T2-weighted MR images, using the provided prostate segmentation as guidance. The resulting surface was smoothed in MeshLab .
The original torus and prostate NURBS meshes were discretized with 32 × 32 × 8 elements along the toroidal direction, the cross-section circumferential direction, and the cross-section radial direction, respectively. We globally refined the prostate mesh to 256 × 256 × 64 elements, using standard knot insertion to perform our simulations with a good level of accuracy.
How Can Treatment Affect The Risk Of Prostate Cancer
While BHP is not prostate cancer, the 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can reduce a mans risk over time of developing prostate cancer by about 25%. There are two benefits to this: First, it makes prostate cancer easier to detect, and second, it prevents the treatments down the road that cause side effects. These hormonal agents are not as effective on more aggressive prostate cancers, and have not been shown to save lives due to prostate cancer. As always, its important to discuss the risks and benefits of these medicines with your doctor.
That said, symptoms are symptoms, and no matter whats most likely to be causing them, you should get them checked out by a doctor.
-
The prostate uses male hormones called androgens, such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone , to trigger and maintain male sex characteristics and reproduction. Normally,…
- Copied
Read Also: What Color Represents Prostate Cancer
About Half Of Men Older Than 50 Have An Enlarged Prostate Here Are Some Of The Basic Facts You Need To Know About This Common Condition
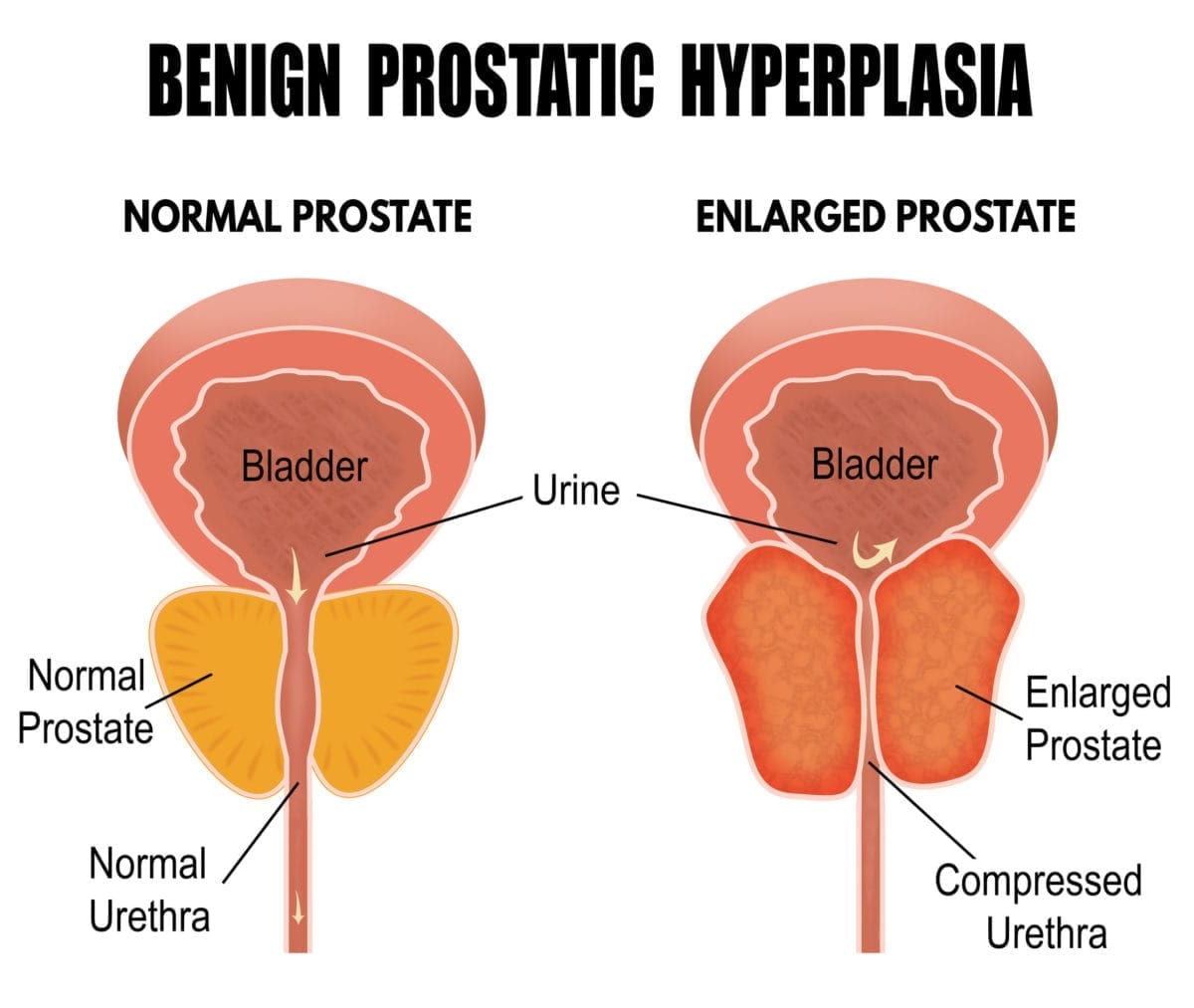
As men age, many experience prostate gland enlargement. This condition is known as benign prostatic hyperplasia .
The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, the hollow tube that carries urine out of the body. When the prostate gets bigger, it can squeeze or partially block the urethra, which leads to problems urinating.
BPH is quite common in older men. In fact, the condition impacts about 50% of men between the ages of 51 and 60. For men 80 and older, the prevalence of BPH is approximately 90%, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
If I Have Bph What Are Next Steps
Past and current research seems to agree that BPH is not an independent risk factor for prostate cancer. Because men who have BPH also undergo diagnostic exams for BPH when symptoms arise or become more severe, this screening process may lead to your healthcare provider finding asymptomatic prostate cancer . For this reason, finding and addressing BPH may lead to a higher chance of finding or diagnosing prostate cancer, but the two are still considered by medical researchers to be independent and unrelated.
BPH can lead to some specific complications including acute or chronic urinary retention, blood in the urine, urinary tract infections , bladder damage, kidney damage, and bladder stones. Most men with BPH do not develop these additional conditions, however, the potential of kidney damage, in particular, can be a serious health threat when it does occur.
If you have any of these symptoms you should see your healthcare provider, who may refer you to a urologist for testing. Your healthcare provider can discuss treatment options for BPH based on the severity of your symptoms, how much the symptoms affect your daily life and your preferences. You may not need treatment for a mildly enlarged prostate unless your symptoms are bothersome and affecting your quality of life. In these cases, instead of treatment, your urologist may recommend regular checkups.
You May Like: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
Quality Of Included Studies
Overall, the quality of included studies was moderate, with 20 studies achieving an NOS score over 6 points. In terms of the case-control studies, all were adequate in case definition, no participants in the control group had a history of prostate cancer . Nine studiesS9,S10,S12,S16,S17,S19,S21,S23,S24 included consecutive or obviously representative series of cases and 6 studies S8,S10,S20,S21,S23,S24 selected community controls. All of the included studies controlled or adjusted for age or other important factors on the basis of study design or analysis. Two studiesS18,S19 had no description of the ascertainment of exposure and 7 studiesS9,S16,S18,S19,S21,S22,S24 had the same nonresponse rates for both study groups.
As for the 9 included cohort studies, 7S1S3,S5,S6,S13,S14 were considered to be truly or somewhat representative of BPH patients in the community and 6 studiesS2S6,S16 selected the nonexposed cohort from the same community as the exposed cohort. The ascertainment of exposure was not described in 1 studyS13 and 7 studiesS2S4,S6,S13,S14,S16 demonstrated that participants were cancer free at the start of the study. All of the included studies controlled or adjusted for age or other important factors on the basis of the design or analysis. The follow-up was adequate and long enough for outcomes to occur in all the studies. The detailed evaluation of risk of bias was reported in the Supplemental digital contentTables and .
Surgery Surgery Is Used To Treat Bph When Drug Therapy Stops Workingor To Treat Those Who Can’t Urinate At All It Can Also Be Used To Relievesevere Symptoms
Transurethral resection of the prostate
Transurethral resection of the prostate removesprostate tissue through the urethra. It is the surgery most commonly used totreat BPH. While TURP relieves urinary symptoms in most men, urinary problemscan come back over time if the prostate starts to grow again. This is why youngermen may need to have this surgery more than once.
This surgery is done in an operating room. The doctor passes a resectoscope through the urethra to reach the prostate. A resectoscope is a type of endoscope . It has a thin wire that carries an electric current. The doctor uses the electric current to cut away prostate tissue around the urethra. The doctor then removes this tissue through the resectoscope.
The most common side effects of TURP include:
- bleeding
- infection
- semen flowing into the bladder instead of out the end of the penis
In rare cases, you may develop erectile dysfunction orincontinence after TURP. But this surgery has a lower risk of these sideeffects than surgery to remove the prostate .
Read Also: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Five Things You Probably Didnt Know About An Enlarged Prostate
Many people are unaware of a common health condition for men as they grow older: benign prostatic hyperplasia, also known as an enlarged prostate or BPH. There is little discussion about BPH despite the fact that it will affect most men as they age. Here are a few things you should know about BPH and BPH treatments.
Can Bph Cause Testicular Pain
BPH doesnt usually cause testicular pain.
If you have testicular pain, this could be because you have inflammation of the prostate, called prostatitis.
Its possible for men to have either BPH or prostatitis, but also possible to have both conditions at the same time.
One of the common symptoms of prostatitis is discomfort, pain, or aching in your testicles or the area between your testicles and back passage
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Diagnosing Benign Prostate Enlargement
You might have several different tests to find out if you have an enlarged prostate.
A GP may do some of these tests, such as a urine test, but others might need to be done at a hospital.
Some tests may be needed to rule out other conditions that cause similar symptoms to BPE, such as prostate cancer.
Personal And Family Medical History
Taking a personal and family medical history is one of the first things a health care provider may do to help diagnose benign prostatic hyperplasia. A health care provider may ask a man
- what symptoms are present
- when the symptoms began and how often they occur
- whether he has a history of recurrent UTIs
- what medications he takes, both prescription and over the counter
- how much liquid he typically drinks each day
- whether he consumes caffeine and alcohol
- about his general medical history, including any significant illnesses or surgeries
Read Also: Do Females Have Prostate Cancer
Traditional Thinking Regarding Testosterone Replacement Therapy And Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia/lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
To this day, there are warning labels on the available testosterone supplements regarding the risk of BPH and urinary retention. These are empirical concerns based on historical studies, which noted that androgens lead to prostatic growth in the post-pubescent male as described in the previous paragraph. In the late-onset hypogonadal male, the addition of testosterone was hypothesized by extrapolation to increase prostatic size and thus worsened of LUTS secondary to BOO. Indeed, in eugonadal men, studies have demonstrated that the prostate can increase in volume by approximately 12% with the addition of testosterone, which is thought may be enough to decompensate a significantly obstructed bladder.
Current clinical guidelines reflect these concerns to varying degrees.,, The European Association of Urology guidelines warn that androgen deprivation therapy is contraindicated in men with severe LUTS . They note, however, that this assertion is not supported by strong clinical evidence and that once a man’s LUTS is appropriately treated there is no longer a contraindication to TRT.
How Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Diagnosed
Your doctor will look at your medical history and give you a complete physical examination.
Your doctor will perform a digital rectal examination by inserting a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum to feel the prostate, estimate its size and detect any hard areas that could be cancer.
Several studies may be performed to help diagnose your condition:
- A survey to evaluate how severe your symptoms are.
- A flow study may be conducted to measure how slow the urinary stream is compared with normal urine flow.
- A study to detect how much urine is left in the bladder after you finish urinating.
- A cystoscopy to look into the bladder.
Also Check: Bisphosphonates For Prostate Cancer
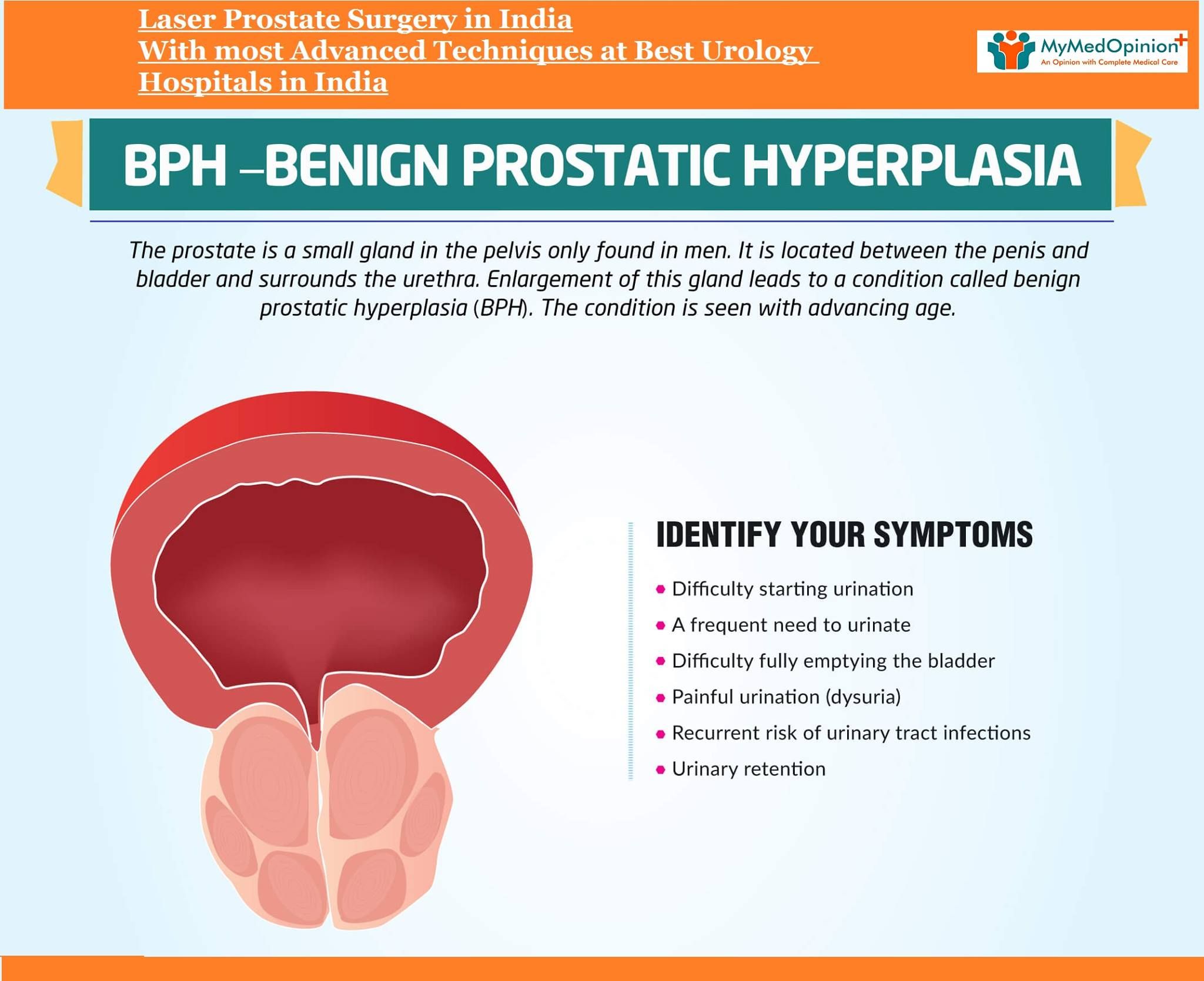
Symptoms Of Prostate Disease
In its earliest stages, prostate disease may or may not be associated with symptoms. The symptoms of prostate disease depend on the condition, but may include:
- difficulties urinating, such as trouble starting the flow of urine
- the urge to urinate often, particularly at night
- feeling as though the bladder can’t be fully emptied
- painful urination
- blood in the urine or blood coming from the urethra independent of urination.
Blood in the urine is often due to causes not related to the prostate. Always see your doctor if you find blood in your urine.
Prostate Disease And Ageing
Around 25 per cent of men aged 55 years and over have a prostate condition. This increases to 50 per cent by the age of 70 years. Early stages of prostate disease may have no symptoms.
If you are a man and you are in your 50s or 60s, talk to your doctor about whether you need to have your prostate gland checked and, if so, how often. If you have a family history of prostate disease , talk to your doctor earlier about when prostate checks might be suitable for you.
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
What Psa Level Indicates Bph
High PSA levels do not always mean that you have prostate cancer or any other prostate problem.
Many factors can affect your PSA levels. Therefore, your doctor wont consider your PSA level on its own.
There is no specific normal or abnormal level of PSA because factors such as age and ethnicity make it hard for researchers to establish a normal range.
However, most doctors consider PSA levels of 4.0 ng/ml as high and would often recommend a prostate biopsy.
One study shows that men with this level of PSA often have prostate cancer.
Low PSA levels also dont always mean that you dont have prostate cancer. Studies show that some men with a PSA below 4.0 ng/ml do have prostate cancer.
What Are The Symptoms Of Bph And Renal Failure
The most common complaint of men with BPH is the need to get up during the night to urinate. It might feel like your bladder is full, even if you urinated recently. There might be a sense of urgency, but the stream may be weak. You may have to strain to urinate. If it gets bad enough, you may find it difficult to urinate at all.
Symptoms of renal failure include:
- diminished urine volume
Also Check: Expressed Prostatic Secretion
What Causes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The cause of benign prostatic hyperplasia is not well understood however, it occurs mainly in older men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not develop in men whose testicles were removed before puberty. For this reason, some researchers believe factors related to aging and the testicles may cause benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Throughout their lives, men produce testosterone, a male hormone, and small amounts of estrogen, a female hormone. As men age, the amount of active testosterone in their blood decreases, which leaves a higher proportion of estrogen. Scientific studies have suggested that benign prostatic hyperplasia may occur because the higher proportion of estrogen within the prostate increases the activity of substances that promote prostate cell growth.
Another theory focuses on dihydrotestosterone , a male hormone that plays a role in prostate development and growth. Some research has indicated that even with a drop in blood testosterone levels, older men continue to produce and accumulate high levels of DHT in the prostate. This accumulation of DHT may encourage prostate cells to continue to grow. Scientists have noted that men who do not produce DHT do not develop benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The Prostate And Testosterone
Natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia
The prostate is small at birth and remains so until early puberty when it increases in size via an androgen-dependent pubescent growth phase from 10 g to an average of 20 g in young adults., After this initial growth and remodeling phase, which involves the entire prostate gland , there is a second selective growth phase of the transitional zone that occurs in approximately 50% of men by age 50, and 90% of men older than 80 years. This growth is pathologically recognized as BPH and clinically noted as benign prostatic enlargement or benign prostatic obstruction/BOO. It is thought that the normal interactions between the epithelial and fibromuscular stromal components of the transitional zone prostate tissue are altered leading to a reduced epithelial/stromal ratio and thus micronodular remodeling that characterizes BPH.
Testosterone and benign prostatic hyperplasia
It has long been recognized that the volume of the prostate increases with age in normal men due to BPH but not in their untreated hypogonadal counterparts. This has been clearly demonstrated in animal studies, in which testosterone replacement for younger castrated dogs permits the development of BPH. Furthermore, after initial regression of BPH in older castrated dogs, BPH was restored following testosterone replacement.
Effect of aging
Don’t Miss: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
