Sites Of Injection For The Periprostatic Nerve Block
The sites of injection for the periprostatic nerve block are determined by the location of neurovascular bundles and branches that supply the prostate gland. The completeness of periprostatic nerve block depends on the correct identification of the injection sites. The neurovascular bundles are not directly visualized on ultrasound and their probable location is interpolated from sonographic landmarks. Bilateral symmetrical injections at each site are imperative to achieve complete nerve block due to decussation of fibers in the prostatic plexus. Although some investigators have used a single site of injection, the best results are achieved when these injections are used in combinations. The various sites of injection are as follows:
Bibasal Injections
Introduced by Nash et al., this is the most common site of injection , when used either alone, or more optimally in combination with other sites of injection. It is a preferred site considering that the major neurovascular bundles of the prostate traverse this site and injection at this site anesthetize a large portion of the prostate gland . This site is identified by an echogenic triangle of fat at the angle between the seminal vesicle and base of the prostate in the para-sagittal longitudinal scan. The appearance is similar to the snow peak of a mountain and hence it is called “the Mount Everest sign” .
Bibasal injection.
Apical Injections
Lateral Injections
Intraprostatic Injections
Combined Method
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
A PET scan is similar to a bone scan, in that a slightly radioactive substance is injected into the blood, which can then be detected with a special camera. But PET scans use different tracers that collect mainly in cancer cells. The most common tracer for standard PET scans is FDG, which is a type of sugar. Unfortunately, this type of PET scan isnt very useful in finding prostate cancer cells in the body.
However, newer tracers, such as fluciclovine F18, sodium fluoride F18, and choline C11, have been found to be better at detecting prostate cancer cells.
Other newer tracers, such as Ga 68 PSMA-11 and 18F-DCFPyl , attach to prostate-specific membrane antigen , a protein that is often found in large amounts on prostate cancer cells. Tests using these types of tracers are sometimes referred to as PSMA PET scans.
These newer types of PET scans are most often used if its not clear if prostate cancer has spread. For example, one of these tests might be done if the results of a bone scan arent clear, or if a man has a rising PSA level after initial treatment but its not clear where the cancer is in the body.
The pictures from a PET scan arent as detailed as MRI or CT scan images, but they can often show areas of cancer anywhere in the body. Some machines can do a PET scan and either an MRI or a CT scan at the same time, which can give more detail about areas that show up on the PET scan.
You May Like: Dying From Prostate Cancer What To Expect
Prostate Biopsy Specimens: Ask For Meticulous Labeling
The way that prostate biopsy samples are handled varies among hospitals. The samples, or cores, are put onto glass slides to be examined under a microscope for signs of cancer. Find out if the physician doing the biopsy will place each core in a separate, labeled container. If cancer is discovered, its location in the prostate gland can affect decisions about further testing and possible treatment.
Individual labeling of biopsy cores is more expensive, and not all hospitals provide this level of service. If all of the samples from the right and left side of the prostate gland are processed together, as opposed to individually, consider having the biopsy done elsewhere, Dr. Garnick says.
Read Also: Is Cialis Good For Bph
Why Do You Need A Prostate Biopsy
A prostate biopsy is done to confirm or rule out prostate cancer.
The doctor may recommend a prostate biopsy for you if
- Your prostate-specific antigen test shows high blood levels of PSA.
- Your digital rectal exam reveals some growths or abnormalities near the prostate.
Sometimes, your doctor may order a repeat biopsy if your previous biopsy shows abnormal prostate cells that were not cancerous or the results of the biopsy were not clear.
QUESTION
Testosterone is a chemical found only in men.See Answer
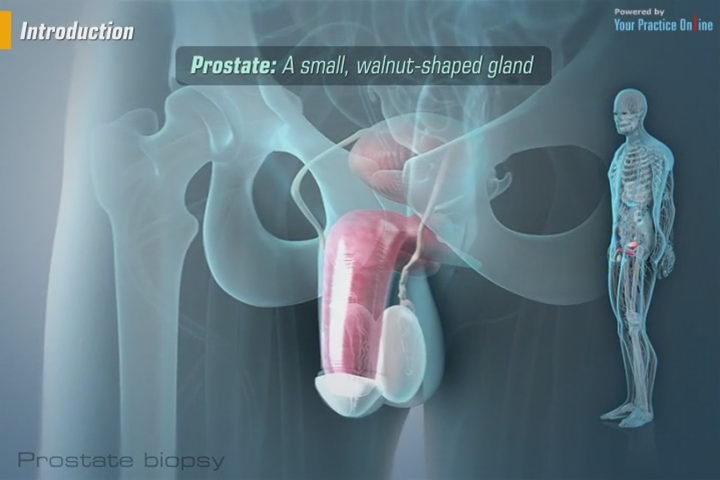
What Is A Transperineal Biopsy
This is where the doctor inserts the biopsy needle into the prostate through the skin between the testicles and the back passage . In the past, hospitals would only offer a transperineal biopsy if other health problems meant you couldnt have a TRUS biopsy. But many hospitals have stopped doing TRUS biopsies and now only do transperineal biopsies.
A transperineal biopsy is normally done under general anaesthetic, so you will be asleep and wont feel anything. A general anaesthetic can cause side effects your doctor or nurse should explain these before you have your biopsy. Some hospitals now do transperineal biopsies using a local anaesthetic, which numbs the prostate and the area around it, or a spinal anaesthetic, where you cant feel anything in your lower body.
The doctor will put an ultrasound probe into your back passage, using a gel to make this easier. An image of the prostate will appear on a screen, which will help the doctor to guide the biopsy needle.
If youve had an MRI scan, the doctor may just take a few samples from the area of the prostate that looked unusual on the scan images. This is known as a targeted biopsy.
You May Like: Finding The Prostate Externally
What Is Prostate Cancer Screening
The diagnosis of prostate cancer usually follows a biopsy prompted by a significantly elevated initial PSA level, an increase in PSA levels over time, or an abnormal digital rectal examination. According to JAMA, patients with a prostate cancer history benefit from extended PSA monitoring. Elevated PSA levels may help determine when to go in for a prostate MRI and hopefully avoid unnecessary or repeat prostate biopsies.
The American Journal of Mens Health reports that prostate cancer diagnosis occurs most often in men older than 50. Other factors influencing the rate of prostate cancer are ethnicity and family history. Screening is vital because localized prostate cancer sometimes causes no symptoms or warning signs.
Types Of Prostate Biopsy Method
Prostate biopsy tests can be gathered in various ways. Your prostate biopsy may include:
- The needle going through the mass of the rectum . This is the most widely recognized method for performing a prostate biopsy.
- Inserting the needle through the area of skin between the butt and scrotum . A little cut is made in the skin area between the butt and the scrotum. The biopsy needle is embedded through the cut and into the prostate to draw out a specimen of tissue. An MRI or CT output is for the most part used to guide this technique.
Recommended Reading: Fiducials Prostate Cancer
What Does The Gleason Score Or Grade Group Mean
The higher your Gleason score or grade group, the more aggressive the cancer and the more likely it is to grow and spread. We’ve explained the different Gleason scores and grade groups that can be given after a prostate biopsy below. This is just a guide. Your doctor or nurse will talk you through what your results mean.
Gleason score 6 All of the cancer cells found in the biopsy look likely to grow very slowly, if at all .
Gleason score 7 Most of the cancer cells found in the biopsy look likely to grow very slowly, if at all. There are some cancer cells that look likely to grow at a moderate rate .
Gleason score 7 Most of the cancer cells found in the biopsy look likely to grow at a moderate rate. There are some cancer cells that look likely to grow slowly .
Gleason score 8 Most of the cancer cells found in the biopsy look likely to grow slowly. There are some cancer cells that look likely to grow quickly .
Gleason score 8 All of the cancer cells found in the biopsy look likely to grow at a moderate rate .
Gleason score 8 Most of the cancer cells found in the biopsy look likely to grow quickly. There are some cancer cells that look likely to grow slowly .
Gleason score 9 Most of the cancer cells found in the biopsy look likely to grow at a moderate rate. There are some cancer cells that are likely to grow quickly .
Gleason score 10 All of the cancer cells found in the biopsy look likely to grow quickly .
Read more about: prostate biopsy recovery
Types Of Prostate Biopsy
A prostate biopsy may be done in several different ways:
- Transrectal method
At the moment, most biopsies are done using a transrectal ultrasound-guided technique. A TRUS prostate biopsy is where the needle goes through the wall of the back passage .
- Perineal method
This is done through the skin between the scrotum and the rectum.
- Transurethral method
This is a type of biopsy done through the urethra using a cystoscope .
- Transperineal biopsy
Unlike the TRUS Guided Biopsy, this is where the doctor inserts a needle into the prostate through the skin between the testicles and the anus. This area is the perineum.
The needle is inserted through a template or grid. This is a targeted biopsy, which can be target a specific area of the prostate using MRI scans. An advantage of the TP biopsy is that it can now be performed under local anesthesia.
A patient may take about four to six weeks or even more recover after a prostate biopsy. The recovery process after biopsy usually depends on the patients health and age. Doctors may recommend only light activities for 24-48 hours after a prostate biopsy. The doctor prescribes painkillers, vitamins, and antibiotics for a few days to speed up the healing process.
After the biopsy, it is normal to experience the following sensations or symptoms:
Post-biopsy restrictions and instructions:
Dont Miss: Psa In Bph And Prostate Cancer
Also Check: Define Prostate
What Is Ultrasound
Doctors use ultrasound- and MRI-guided biopsy to collect tissue samples from the prostate gland. A pathologist examines the samples and determines whether or not cancer is present.
Doctors most commonly perform biopsies using ultrasound guidance. The doctor inserts a special biopsy needle into the prostate through the wall of the rectum to remove several small samples of tissue for lab analysis. This is known as transrectal ultrasound guided biopsy.
The doctor may also access the prostate through the perineum . Your doctor may use this approach:
- if cancer is suspected at the front of the prostate gland too far away from the rectum for TRUS
- if transrectal ultrasound is not feasible due to prior rectal surgery
- for some mapping biopsies
Your doctor can also biopsy the prostate using magnetic resonance imaging or Mp-MRI . MRI and Mp-MRI provide more detailed images of the prostate than ultrasound can. Mp-MRI is an advanced imaging method that combines three MRI techniques to provide information on the structure and function of the prostate.
Before the biopsy, the doctor will examine the MR images, sometimes with the help of computer-aided detection software. This will pinpoint specific areas that may require further evaluation. The doctor may perform MRI-guided in-bore biopsy using either a transperineal or transrectal approach. Both methods typically use software to guide the needle to the desired position within the prostate.
What Is An Mri
What makes an MRI different from other medical imaging techniques like X-rays and CT scans? X-rays take projection images of hard tissues like bones, while CT scans take images of both hard bony tissues and soft tissue. Both systems use ionizing radiation, which passes through the body to create images that are transferred to photographic film or to a video monitor.
An MRI works differently. Magnetic resonance imaging uses a magnetic field to create sound waves that are received, digitized, and displayed in real-time. When tissue is abnormal, its composition changes, so the images reflect damaged areas.
Read Also: Is Zinc Good For Prostate
Comparison Of Satisfaction With Procedure And Willingness To Repeat Biopsy Procedure And Incidence Of Complications Between Groups
The results of this study revealed that there was no statistical difference in the level of satisfaction experienced by the participants of either groups. This was in contrast to the report by Na Wang and colleagues . In their study of 190 men, over half in the CB group while only 24.2% of the men in PPNB+IRLA group reported excellent satisfaction with the procedure . However, the difference in proportion was less pronounced when the sum of men who reported either excellent or good levels of satisfaction were compared between the groups: 84.7% versus 75.8% for CB and PPNB+IRLA, respectively.
The willingness to repeat the prostate biopsy using the same method of analgesia was similar across the groups. Obi et al. reported similar proportions of men willing to have a repeat biopsy 72% of the men who had PPNB and 88% men who had saddle block were willing to have a repeat prostate biopsy .
The results showed a low incidence of complications, with no significant difference between the groups. This was similar to the findings by Na Wang et al. where out of 95 persons per group, one man, 2 men and 6 men had hematuria, fever and urinary retention, respectively in the CB group, while 3 men, 4 men and 4 men with similar complications, respectively, in the PPNB+IRLA group. Similarly, there was no significant difference in the incidence of complications between the groups in the study by Urabe et al. .
You May Like: Can The Prostate Grow Back After Surgery
Factors That May Worsen The Pain
- Anxiety levels: It is a fact that anxious individuals have a lower pain threshold. In other words, they are more susceptible and reactive to pain symptoms. Thus, along with painkillers, patients should also use alternative treatments to relieve anxiety levels. Music, aromatherapy, and herbs to wind down are very effective for some.
- Prostate volume: An enlarged prostate is more likely to add pressure to the nerves and cause significant pain. It is usually affected by inflammation and prone to swelling and becoming tender.
- The number of biopsy cores: In other words, the more samples the doctor needs to take, the more likely it will cause pain. Each sample requires a new insertion of the needle and increases the chance of inflammation and pain.
- Younger age: Younger patients can be more sensitive to pain than older adults. There is also the case of early-onset prostate cancer, which is more dangerous and may lead to significant inflammation of the prostate. In these patients, the prostate will be significantly tender after the procedure.
- Positioning: According to certain authors, adopting the left lateral decubitus position is slightly better than a lithotomy position.
Read Also: External Prostate Massage Prostatitis
Prostate Biopsy: Everything You Need To Know
Although the DRE and PSA tests are useful, they are not enough to make a clear diagnosis of prostate cancer. When results are abnormal or questionable, the doctor may order a transrectal ultrasound and a biopsy. These examinations usually provide enough information for a precise diagnosis.
Abnormalities detected during a digital rectal exam and a high PSA level often lead to a prostate biopsy. This procedure consists of taking small tissue samples of your prostate in order for the pathologist to examine them under a microscope to determine if they are cancerous or not. If cancer is detected, the pathologist will use the same samples to calculate your grade .
A prostate biopsy is usually performed with the help of a transrectal ultrasound . The images taken with the ultrasound help guide a fine needle to the areas selected for sampling. The spring-loaded needle is attached to the ultrasound probe and enters the prostate through the rectum. Usually between 6 12 prostatic tissue samples are obtained and the entire procedure lasts about 10 minutes. A local anesthetic can be used to numb the area and reduce any pain.
Eating And Drinking And Medicines
You usually have a TRUS biopsy under local anaesthetic, so you can generally eat and drink normally beforehand and afterwards.
Take your usual medicines as normal, unless your doctor tells you otherwise. But if you take warfarin to thin your blood you should stop this before you have your biopsy. Your doctor will tell you when you need to stop taking it.
Read Also: Viagra And Enlarged Prostate
The Digital Rectal Exam
The prostate gland comprises three zones. Most cancers originate in the peripheral zone. Proctologists, urologists, and oncologists are trained to feel this area while performing a digital rectal exam .
Here, digital doesnt refer to technology. Instead, it refers to the fingers . In a DRE, your doctor inserts a well-lubricated gloved finger gently into the rectum to reach the prostate. Prostate enlargement and suspicious lesions may be felt during a DRE.
Origin Of Pain Associated With Prostate Biopsy And Anatomical Considerations
Pain during prostate biopsy can be due to the following factors:
1) Ultrasound transducer insertion: the first painful step during TRUS-guided prostate biopsy is the initial ultrasound probe insertion, and it results from mechanical stretching of an un-relaxed anal sphincter and direct contact of the ultrasound transducer . Increased anal tone in a young patient and local inflammatory conditions like fissures or fistula-in-ano exacerbate pain during insertion.
2) Biopsy of the prostate: the most painful step is 10-12 passes of a 16-G or 18-G core-biopsy needle into the prostate and anorectum.
3) Needle punctures while depositing the local anesthetic . When the periprostatic nerve block is used, the actual biopsy itself is rendered painless by the block and the few extra needle punctures for periprostatic nerve block add to the total procedural pain and paradoxically, this becomes the most painful step .
Anatomical structures that contribute to the pain are as follows:
Dentate or pectinate line. Dentate or pectinate line is located within anal canal just above level of anal crypts/valves . It is watershed junction between splanchnic and somatic innervations of ano-rectum. Above this line, there is predominantly splanchnic innervation and mucosa is relatively insensitive to pain, while segment below this line is extremely pain-sensitive due to somatic innervation via inferior rectal nerve.
Don’t Miss: Find Prostate Externally
