What Is The Gleason Score
The Gleason grading system estimates the aggressiveness of the cancer by assigning a pattern to the cancer cells depending on their appearance under the microscope. A number from 1 to 5 is used as a measure of how aggressive the cancer looks under the microscope.
- If the cancerous tissue looks much like normal prostate tissue, a grade of 1 is assigned.
- If the cancer cells and their growth patterns look very abnormal, a grade of 5 is assigned.
- Grades 2 through 4 have features in between these extremes.
The most common type of prostate biopsy is a core needle biopsy. For this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin, hollow needle into the prostate gland. When the needle is pulled out it removes a small cylinder of prostate tissue called a core. This is typically repeated several times to sample different areas of the prostate.
Since multiple core biopsy samples are evaluated and prostate cancers in a single patient often have areas with different grades the pathologist assigns two grades to the examined prostate tissue. The first grade is the most common pattern seen after review of all the biopsy specimens and the 2nd grade is assigned to the next most common pattern.
Gleason 6 Prostate Cancer: Serious Malignancy Or Toothless Lion
Nicholas M. Donin, MDOncology
There is strong evidence from longitudinal cohort studies of men with both treated and untreated Gleason 6 prostate cancer to suggest that Gleason 6 disease, when not associated with higher-grade cancer, virtually never demonstrates the ability to metastasize and thus represents an indolent entity that does not require treatment.
Autopsy studies of men without known prostate cancer suggest that a substantial reservoir of prostate cancer that does not cause symptoms or death exists within the population. The majority of these cancers are Gleason 6 tumors and are frequently detected by prostate-specific antigenbased prostate cancer screening. There is strong evidence from longitudinal cohort studies of men with both treated and untreated Gleason 6 prostate cancer to suggest that Gleason 6 disease, when not associated with higher-grade cancer, virtually never demonstrates the ability to metastasize and thus represents an indolent entity that does not require treatment. Whether Gleason 6 has a propensity to progress to higher-grade cancer is still under investigation. Because the term cancer has historically been used to represent a disease state that leads to progressive illness that is uniformly fatal without treatment, we believe Gleason 6 disease should not be labeled with this term. Our challenge now is to develop the technology to differentiate true Gleason 6 disease from the higher grades of dysplasia with which it can be associated.
What Is The Gleason Grading System
Your Gleason score isn’t a separate test. It’s a number based on the results of your biopsy. You usually get it when you’re first diagnosed with prostate cancer.
The doctor uses the numbers 1 to 5 to grade the most common and second most common patterns of cells found in a tissue sample:
- Grade 1. The cells look very much like normal prostate cells.
- Grades 2-4. Cells that score lower look closest to normal and represent a less aggressive cancer. Those that score higher look the furthest from normal and will probably grow faster.
- Grade 5. Most cells look very different from normal.
The two grades added together are your Gleason score. Cancers will score 6 or more. A score of 7 means the cancer is intermediate, and a higher score means the cancer is more likely to grow and spread.
Your doctor will use this combined score along with the results of your PSA blood test and digital rectal exam to see how advanced your prostate cancer is. They’ll use this information to suggest the best treatment for you.
Read Also: Can Turmeric Help Enlarged Prostate
What Do The Different Gleason Scores Mean
The Gleason Score is based on how aggressive the patients prostate cancer is. The lower the number, the closer to normal the cell tissue is. Lower scores mean the cancer is more likely to be slow-growing. Anything less than 6 is considered not to be cancer.
On the other hand, a higher number means the cancer is more aggressive and more likely to spread. Heres a breakdown of what the different scores mean:
- Low Grade: Gleason Score = 6: This indicates that more than likely the cancer will be slow-growing and not very aggressive. Patients with these scores have the best prognosis.
- Intermediate Grade: Gleason Score = 7: A score of 7 means that the patient has a 50/50 chance of having aggressive prostate cancer. If the patient received a primary grade of 3 and a secondary grade of 4, more than likely the cancer will grow slowly. However, if those numbers are reversed and the primary grade was 4 and the secondary 3, the cancer may be aggressive.
- High Grade: Gleason Score = 8-10: A score of 8-10 means the cancer is aggressive and likely to grow and spread at a fast pace.
There Are Different Criteria
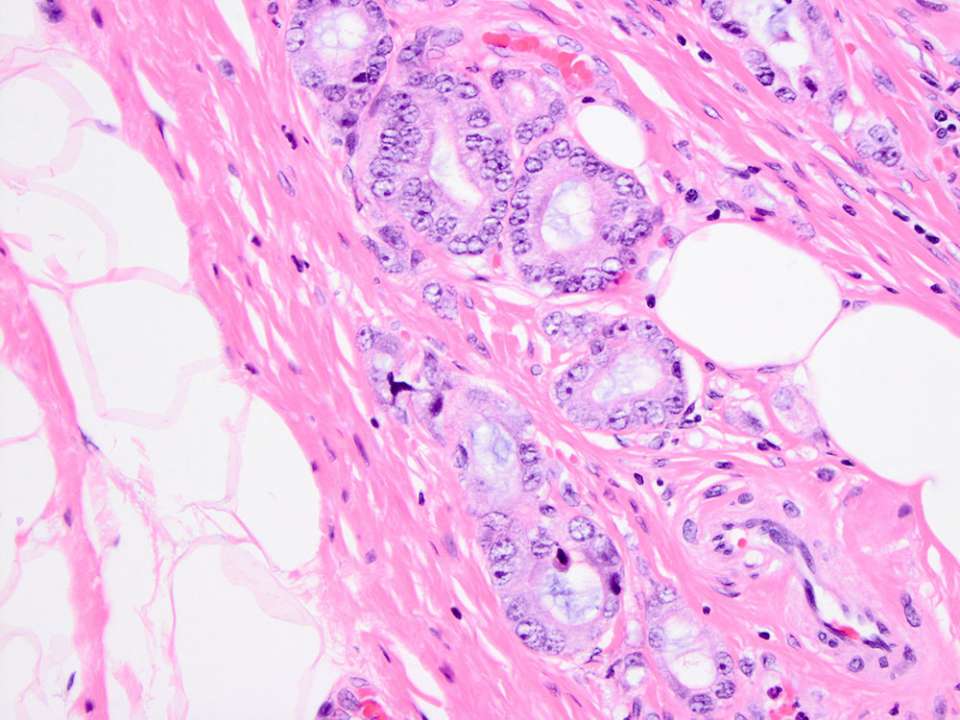
I have been on active surveillance for ten years, and have had no progression in my disease. My recent MRI and biopsy are the same as in 2009. But, while I have enjoyed those years of living normally, I have also been frequently tested within a formal study group.
With your number of positive cores, you would not be accepted into the AS program at Johns Hopkins, but you would be welcomed into our long-time rival program at Sunnybrook. That is Laurence Koltz research group. You can google him for a lot more information.
I recommend that you get a copy of Dr. Mark Scholz new book The Key to Prostate Cancer. In it, 30 prostate cancer experts describe the treatment, including AS, that they provide for men with different risk levels.
Read Also: How Is Prostate Laser Surgery Performed
Also Check: Where Does Prostate Cancer Spread To
What Is A Grade Group
In 2014, the International Society of Urological Pathology released supplementary guidance and a revised prostate cancer grading system, called the Grade Groups.
The Grade Group system is simpler, with just five grades, 1 through 5.
*Risk Groups are defined by the Grade Group of the cancer and other measures, including PSA, clinical tumor stage , PSA density, and number of positive biopsy cores.
Many hospitals report both the Gleason score and the Grade Group, but there may be hospitals that still report only the old Gleason system.
How Is The Gleason Score Measured
The Gleason score is a measure of how aggressive your tumour is. Cancer cells within the prostate are very varied, so the pathologist takes the most common type of cell in your tumour and the second most common type of cell in your tumour to make an assessment. Each cell is given a score, ranging from 1 for the least aggressive, to 5 for the most aggressive. The two scores are then added together to provide your personal Gleason score.
Also Check: Is Testicular Cancer The Same As Prostate Cancer
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Prostate Cancer Surgery Take
Gleason Prostate Cancer Score
1960s as a way to measure how aggressive your prostate cancer may be.
A pathologist determines your Gleason score by looking at a biopsy of your prostate tissue under a microscope. They grade the cells in the biopsy on a scale of 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are healthy prostate, whereas grade 5 cells are highly mutated and dont resemble healthy cells at all.
The pathologist will calculate your Gleason score by adding together the number of the most prevalent type of cell in the sample and the second most prevalent type of cell.
For example, if the most common cell grade in your sample is 4 and the second most common is 4, you would have a score of 8.
A Gleason score of 6 is considered low-grade cancer, 7 is intermediate, and 8 to 10 is high-grade cancer.
> > > 1 Bedtime Hack To Pee Like A Bull
An enlarged prostate can also be the cause of other problems. If the enlarged prostate is causing symptoms, the best treatment would be a natural remedy. In the meantime, there are treatments for a wide range of conditions that cause a man to experience pain. A common surgical procedure involves an electric loop, laser, or electro-stimulation. The procedure is a safe and effective option for treating enlarged or symptomatic BPH.
Read Also: Is Watermelon Good For Your Prostate
Does Untreated Clinical Gleason 6 Disease Cause Symptoms Or Death
Several studies that examined the natural history of untreated prostate cancer diagnosed in the prePSA screening era have suggested that men with Gleason 6 cancers are at risk for prostate cancerspecific mortality beyond 10 years of follow-up. The majority of the Gleason 6 disease was T1a/b disease, which was identified at the time of transurethral resection of the prostate for benign disease. Today, it is extremely rare to diagnose T1a/b disease because fewer TURPs are performed and those undergoing TURP have been prescreened with PSA testing. The results of the natural history studies in the PSA screening era are also problematic because many of the cases were likely misclassified at the outset because of the aforementioned limitations attributable to the random-systematic tissue sampling guided by TRUS.
With reported median follow-up ranging from 22 to 82 months, current active surveillance cohorts remain immature at this time, and longer follow-up will be necessary to draw definitive conclusions. Thus far, cancer-specific survival among these cohorts has been > 97%, and there are no data to suggest inferior outcomes after delayed radical therapy, as compared with immediate therapy.
Overview Of Gleason System
During the first half of the 20th century the absence of a standardized method to distinguish the diverse pathological spectrum of prostate cancer limited clinicians prognostic abilities and hampered emerging treatment and research efforts. Dr. George Mellinger, Chair of Urology at the Minneapolis Veterans Hospital, recognized this deficiency. He recruited Dr. Donald Gleason to the newly established Veterans Administration Cooperative Urological Research Group to develop a uniform prostate cancer grading system.
Gleason reviewed material from 270 consecutive patients with prostate cancer, including 80% with clinical stage IIIIV disease. In 1966 Gleason reported 9 patterns of gland formation ranging from organized and uniform to disordered and infiltrative. The clinical outcomes of patients led him to consolidate these findings into 5 distinct patterns.1 Notably Gleason found many cases harbored more than 1 histological pattern and the overall prognosis was between that predicted by the primary and secondary patterns. Therefore, the group combined the 2 distinct patterns to obtain a histological score. In the earliest versions of the system a final point was attributed for clinical stage.2
Gleason grading system
Don’t Miss: How Long Is Prostate Surgery
Where Prostate Cancer Spreads
If left untreated, diagnosed prostate cancer can grow and possibly spread outside of the prostate to local tissues or distantly to other sites in the body. The first sites of spread are typically to the nearby tissues.
The cancer can spread down the blood vessels, lymphatic channels, or nerves that enter and exit the prostate, or cancer could erode directly through the capsule that surrounds the prostate.
The seminal vesicles are a site of particularly common early spread. More extensive local spread can occur with cancer invading the nearby bladder or rectum.
Further advancement of cancer can occur when cancer cells enter the blood vessels and lymphatic channels. Once cancer has entered into these vessels, prostate cancer cells can seed into virtually any other part of the body.
Prostate cancer is known to have a particular affinity for spreading or metastasizing to the bones especially the lower spine, pelvis, and femur. Other organs such as the liver, brain, or lungs can also be the sites of spread, but these are much rarer.
Recommended Reading: Transurethral Resection Of The Prostate Turp
Can The Gleason Score From A Random Biopsy Really Tell What The Cancer Grade Is In The Entire Prostate
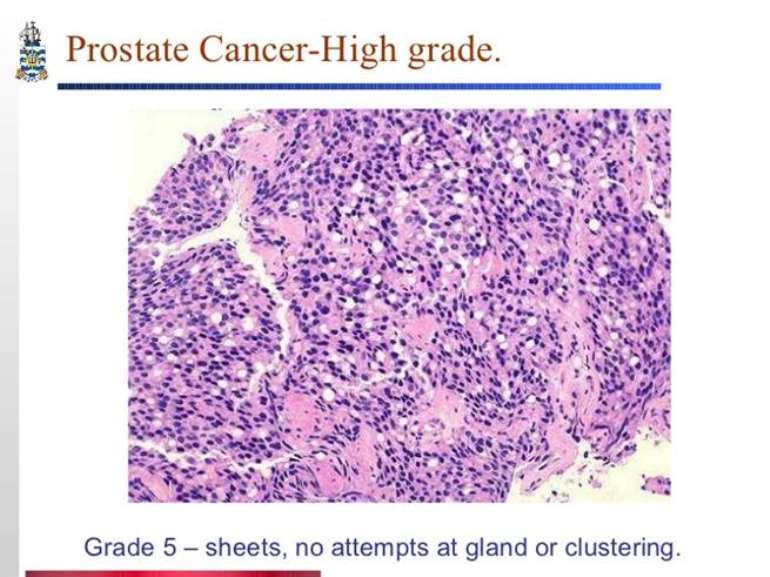
The answer is yes because prostate biopsies are tissue samples from different areas of the prostate. However, in about 20% of individuals, the biopsy may underestimate the true grade because randomly directed biopsy needles occasionally miss a higher grade area of the cancer. This under-grading is more likely to occur in men with larger tumors, higher PSA levels, and/or smaller prostates. Over-grading can also occur but is less common.
Recommended Reading: Does Fish Oil Increase Risk Of Prostate Cancer
Calculating The Gleason Score
A doctor will use the results of a biopsy to calculate the Gleason score.
During a biopsy, a healthcare professional will take tissue samples from different areas of the prostate. The cancer is not always present in all parts of the prostate. For this reason, they will often collect several samples.
After examining the samples under a microscope, they will identify the two areas with the most cancer cells. They will then assign a score to each of these areas. Then, they will add these scores together to give a combined score, often referred to as the Gleason sum.
It is important to note that sometimes, a doctor will use a different method for calculating the Gleason score.
For example, when a biopsy sample has either a large number of high grade cancer cells or shows three different grades of mutation, they will modify the Gleason score to more accurately reflect how aggressive they deem the cancer to be.
A persons Gleason score can technically range from 210, but it is much more likely to range from 610. We will explain why this is in the sections below.
The Initial Causes What Is Gleason Score 6 Prostate Cancer
One of the first symptoms of prostate issues is pain or tenderness in the groin or lower back. This can be the result of a noncancerous condition called enlarged prostatic tissue, or it could be an infection of the bladder. In either case, its important to see a doctor as soon as possible. If youre suffering from prostate pain, you may want to consider reducing your caffeine intake.
Another symptom of a potentially enlarged prostate is difficulty starting a stream of urine, leaking, or dribbling. These symptoms are not serious, but theyre still alarming. Most men put up with an enlarged prostate for years before seeking medical attention, but they typically seek treatment as soon as they notice symptoms. Even if you dont have symptoms, its worth getting checked to determine if you have any prostate issues.
If you experience nightly bathroom runs, you may be experiencing an enlarged prostate. You may be having difficulty starting a stream of urine, or you may even be dribbling or leaking during the day. These problems arent life-threatening, but can become a nuisance. You should not ignore these signs and seek treatment as soon as you notice them. If you feel any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Don’t Miss: Why Do You Have To Cough During A Prostate Exam
Prostate Cancer: The Gleason Score Explained
How aggressive is my prostate cancer? Is it growing slowly or quickly?
If youve been diagnosed with prostate cancerand this year alone nearly 165,000 men nationwide will bethese may be among the first questions youll ask your doctor. And the answers will most likely take into account something called a Gleason score.
The Gleason score is a grading system used by urologists to assess a prostate cancers aggressiveness based on how cells from the tumor look under a microscope. Less-aggressive tumors are more likely to resemble healthy prostate tissue. More-aggressive tumors look less like normal tissue.
The higher the Gleason score, the more aggressive your cancer is likely to beand the greater the chance that it will spread. Doctors use the Gleason score to help choose appropriate treatments.
So Why Does Gleason 3+3 Mean Cancer
Thats the question raised by Wolinsky. If we strictly interpret the original Gleason scores, a grade of 3 is given once cells that look like cancer are starting to appear, disrupting the structure of normal prostate tissue. Tucked into this score is the assumption that these early cancer cells will inevitably mutate into increasingly aggressive rogue cells.
This assumption may very well be fake news. The facts show otherwise. According to PCa expert Dr. Laurence Klotz, who is one of the earliest proponents of the notion that Gleason 3+3 is NOT cancer, we now know that Gleason 3 and Gleason 4 are like night and day, that the molecular genetics of most Gleason 3 is normal. The metastatic potential is approximately zero.
This means that just because it looks like a cancer cell under the microscope doesnt mean it behaves like a cancer cell. Most types of tumor cancers become more aggressive, eventually spreading to other organs and parts of the body. Klotz and others point to three cancers that are exceptions:
- Glioblastoma, a deadly brain cancer that infiltrates throughout the brain but does not metastasize beyond the brain
- Basal cell carcinoma, a common skin cancer that can grow but almost never metastasizes beyond itself
- Gleason 3+3 prostate cancer, in itself, has never been proven to metastasize.
Wolinsky quotes Dr. Scott Eggener of the University of Chicago:
Also Check: Can Prostate Problems Cause Ejaculation Problems
What Can Affect My Outlook
No one can tell you exactly what will happen. How prostate cancer affects you will depend on many things.
- Your stage Whether your cancer is localised, locally advanced, or advanced.
- Your Gleason score or grade group The higher your Gleason score, the more aggressive the cancer, and the more likely it is to spread.
- Your treatment options You may be able to have treatment aimed at getting rid of the cancer. Or you may be able to have treatment to keep the cancer under control. Read more about choosing your treatment.
- Your health If you have other health problems, you may have fewer treatment options. And you may be more likely to die from another condition, such as heart disease.
- Your PSA level After youve been diagnosed, PSA tests are a good way of monitoring your prostate cancer and seeing how youre responding to treatment.
- How successful your treatment is Your treatment may be successful at getting rid of your cancer or keeping it under control. But for some men, treatment may not work as well as expected.
