/13prostate Cancer Is A Common Type Of Cancer In Males
Prostate cancer is one of the leading cancers in men, with a 5-year survival rate of 64% in India alone. It commonly occurs in males aged 65 and above. However, there has been a rise in prostate cancer cases among the younger population in recent times.
Experts warn against delay in diagnosis and treatment, given that it can prove fatal and untreatable. Most often , the symptoms of prostate cancer are either ignored or neglected, leading to advanced stages of the cancer. That said, take a note of all the early signs of prostate cancer and do not mistake it for a benign illness.
Prostate Cancer Epidemiology In Canada
In Canada, incidence of prostate cancer in men 50 to 59 years of age has increased by 50% in last ten years due to PSA testing.Incidence of loco-regional disease has increased, whereas the incidence of metastatic disease has decreased among Canadian population.
If we compare the incidence of prostate cancer in Canada with other countries then there is significant increase in prostate cancer incidence in Canada due to PSA testing.Countries having high risk of prostate cancer includes United states, Canada, Sweden and Australia and low risk countries include Indonesia, Korea and Germany.
Recommended Reading: What Is Stage 3 Prostate Cancer Mean
Risks For Prostate Cancer
Certain behaviours, substances or conditions can affect your risk, or chance, of developing cancer. Some things increase your risk and some things decrease it. Most cancers are the result of many risks. But sometimes cancer develops in people who don’t have any risks.
The risk for prostate cancer increases as men get older. The chance of being diagnosed with prostate cancer is greater after age 50. Prostate cancer is most often diagnosed in men in their 60s.
The following can increase your risk for prostate cancer. Most of these risks cannot be changed.
Don’t Miss: What Causes An Enlarged Prostate In A Young Man
Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented
No one knows how to prevent prostate cancer, but a healthy lifestyle may be important.
Body weight
Being overweight may increase your risk of being diagnosed with prostate cancer thats aggressive or advanced . Eating healthily and keeping active can help you stay a healthy weight.
- Alanee SR, Glogowski EA, Schrader KA, Eastham JA, Offit K. Clinical features and management of BRCA1 and BRCA2-associated prostate cancer. Front Biosci-Elite. 2014 Jan 1 6:1530.
- Allott EH, Masko EM, Freedland SJ. Obesity and Prostate Cancer: Weighing the Evidence. Eur Urol. 2013 63:800-809. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.11.013
- Barber L, Gerke T, Markt SC, et al. Family History of Breast or Prostate Cancer and Prostate Cancer Risk. Clin Cancer Res. 2018 24:5910-5917. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0370
- Beebe-Dimmer JL, Kapron AL, Fraser AM, Smith KR, Cooney KA. Risk of Prostate Cancer Associated With Familial and Hereditary Cancer Syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jun 38:180713.
- COONEY KA. Inherited Predisposition to Prostate Cancer: From Gene Discovery to Clinical Impact. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2017 128:1423.
- Cozar JM, Robles-Fernandez I, Martinez-Gonzalez LJ, et al. Genetic markers a landscape in prostate cancer. Mutat Res Mutat Res. 2018 775:1-10. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2017.11.004
- Das S, Salami SS, Spratt DE, Kaffenberger SD, Jacobs MF, Morgan TM. Bringing Prostate Cancer Germline Genetics into Clinical Practice. J Urol. 2019 Aug 202:22330.
> > > This Simple Morning Test Will Fix Your Prostate
Another type of prostate issue is chronic prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This condition causes pain in the lower back and groin area, and may cause urinary retention. Symptoms include leaking and discomfort. In severe cases, a catheter may be required to relieve the symptoms. If the problem is unresponsive to other treatments, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure. If these do not work, your symptoms could progress and become chronic.
An acute bacterial infection can cause a burning sensation. Inflammation of the prostate can affect the bladder and result in discomfort and other symptoms. This is the most common urinary tract problem in men under 50, and the third most common in men over 65. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of CPPS. Patients may experience a fever or chills as a result of the infection.
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Camp Lejeune Water
Conflict Of Interest Disclosures
Colin Burnett reports employment by GlaxoSmithKline outside the submitted work. Christopher J. Sweeney reports grants and personal fees from Astellas, Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Bayer and consulting for Lilly outside the submitted work in addition, Sweeney reports patents issued for parthenolide, dimethylamino parthenolide , and abiraterone and cabozantinib . Srikala S. Sridhar reports personal fees from Janssen, Bayer, Sanofi, and Astellas outside the submitted work. The other authors made no disclosures.
Prostate Cancer: Where Can You Find A Helping Hand
This is your one-stop source for information on prostate cancer. You can easily search for support groups, doctors, and clinical trials. And, your donation to the PCF funds prostate cancer research, with 84 cents of every dollar going toward their research mission.
PCRI focuses on improving the lives of prostate cancer patients and caregivers. We love that you can take a prostate cancer staging quiz to find out more about your prognosis. To take it, youll need to know the results of your PSA, biopsy, digital rectal exam, bone scan, and CT scan.
The American Cancer Society is considered the go-to source for reliable cancer information. Their site offers news releases, clinical trial opportunities, online support groups, and more. We especially like their Understanding Health Insurance page, which navigates you through the often complex process of utilizing health insurance for cancer treatments.
Also Check: What Is C61 Prostate Cancer
Screening For Prostate Cancer In African American Men
Burden
In the United States, African American men are more likely to develop prostate cancer than white men . African American men are also more than twice as likely as white men to die of prostate cancer .1 The higher death rate is attributable in part to an earlier age at cancer onset, more advanced cancer stage at diagnosis, and higher rates of more aggressive cancer . These differences in death from prostate cancer may also reflect that African American men have lower rates of receiving high-quality care.
Available Evidence
The USPSTF searched for evidence about the potential benefits and harms of PSA-based screening for prostate cancer in African American men.
Potential Benefits
The PLCO trial enrolled 4% African American men, which is not enough to determine whether the overall trial results differed for African American men.17 The ERSPC trial did not record or report any race-specific subgroup information. The low proportion of persons of African descent in European countries during the study period makes it likely that these groups were not well represented.
Potential Harms
An analysis from the PLCO trial found that African American men were significantly more likely to have major infections after prostate biopsy than white men .13 Evidence is insufficient to compare the risk of false-positive results, potential for overdiagnosis, and magnitude of harms from prostate cancer treatment in African American vs other men.
Advising African American Men
Incidence And Prevalence Of Prostate Cancer
Somnath Pal, BS , MBA, PhDProfessor of Pharmacy AdministrationCollege of Pharmacy & Allied Health ProfessionsSt. Johns UniversityJamaica, New York
US Pharm. 2009 34:10.
Among men, prostate cancer is the second most common type of cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death, according to the National Cancer Institute. Annually, PC is the diagnosis in one of every three men found to have cancer. PC affects 234,000 U.S. men each year, with death occurring in 27,000. The Prostate Cancer Foundation reported that one new case of PC occurs every 2.5 minutes and one death from it occurs every 19 minutes. One in six males born between 2004 and 2006 will be diagnosed with PC during his lifetime, with 8% developing it between 50 and 70 years of age.
Read Also: What Is The Survival Rate Of Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Am I At Risk Of Prostate Cancer
In the UK, about 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime. We dont know exactly what causes prostate cancer but there are some things that may mean you are more likely to get it these are called risk factors.
There are three main risk factors for getting prostate cancer, which are things you cant change. These are:
- getting older it mainly affects men aged 50 or over
If you have any of these risk factors or if you have any symptoms, speak to your GP. They can talk to you about your risk, and about the tests that are used to diagnose prostate cancer. You can also get in touch with our Specialist Nurses, who can help you understand your risk of prostate cancer.
Read Also: What Color Represents Prostate Cancer
Risk Of Prostate Cancer
About 1 man in 8 will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during his lifetime.
Prostate cancer is more likely to develop in older men and in non-Hispanic Black men. About 6 cases in 10 are diagnosed in men who are 65 or older, and it is rare in men under 40. The average age of men at diagnosis is about 66.
Also Check: How Do They Do Radiation For Prostate Cancer
Family History And Genetics
Your family history is information about any health problems that have affected your family. Families have many common factors, such as their genes, environment and lifestyle. Together, these factors can help suggest if you are more likely to get some health conditions.
Inside every cell in our body is a set of instructions called genes. These are passed down from our parents. Genes control how the body grows, works and what it looks like. If something goes wrong with one or more genes , it can sometimes cause cancer. For example, BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations.
Is prostate cancer hereditary?
If people in your family have prostate cancer, breast cancer or ovarian cancer, it might increase your own risk of getting prostate cancer. This is because you may have inherited the same faulty genes.
My father had prostate cancer. What are my risks?
- You are two and a half times more likely to get prostate cancer if your father or brother has had it, compared to a man who has no relatives with prostate cancer.
- Your chance of getting prostate cancer may be even greater if your father or brother was under 60 when he was diagnosed, or if you have more than one close relative with prostate cancer.
- Your risk of getting prostate cancer may also be higher if your mother or sister has had breast cancer or ovarian cancer.
Do you have a family history of prostate cancer?
What are BRCA1 and BRCA2?
Am I more at risk of prostate cancer if I have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation?
Effectiveness Of Early Detection
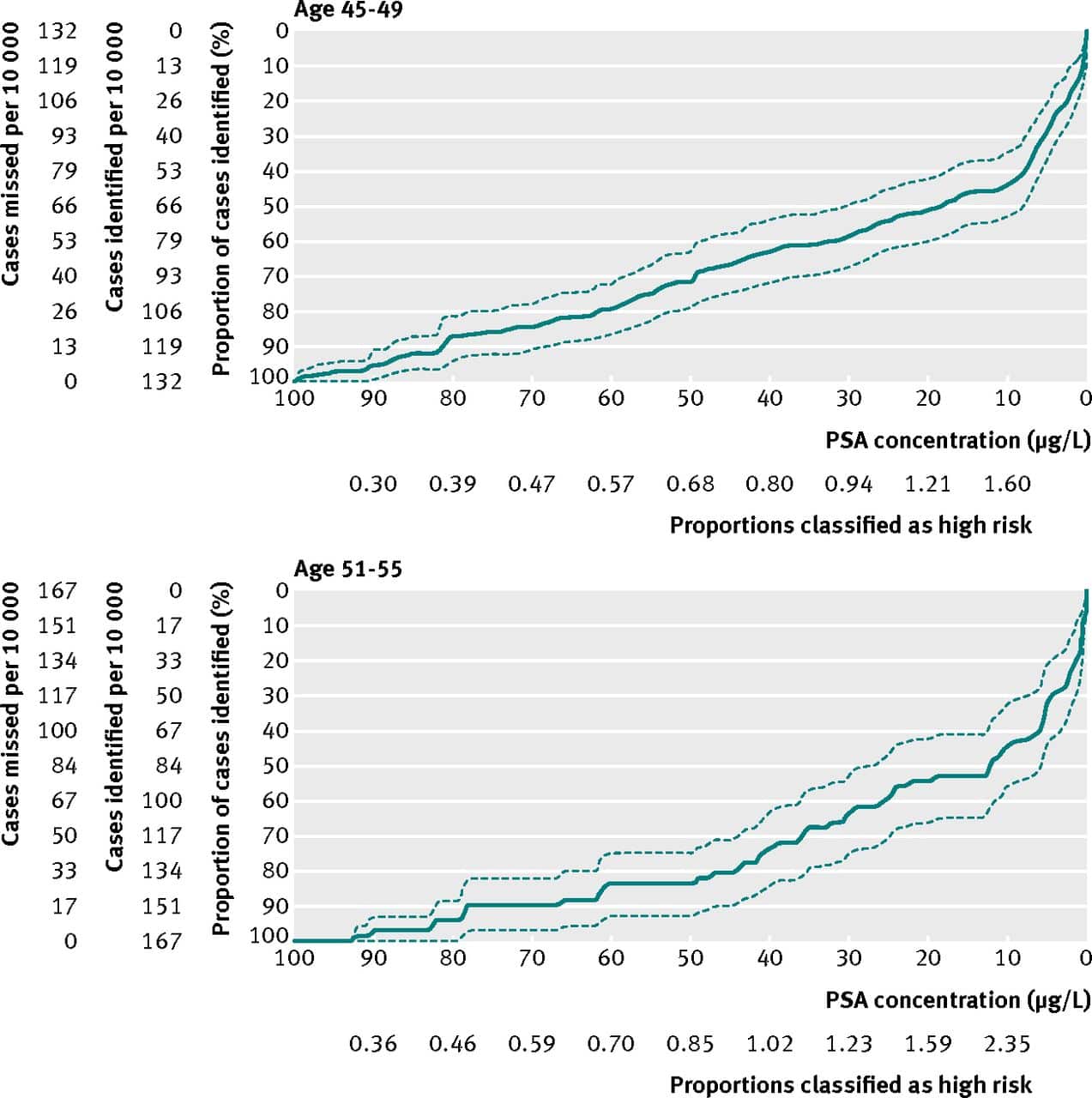
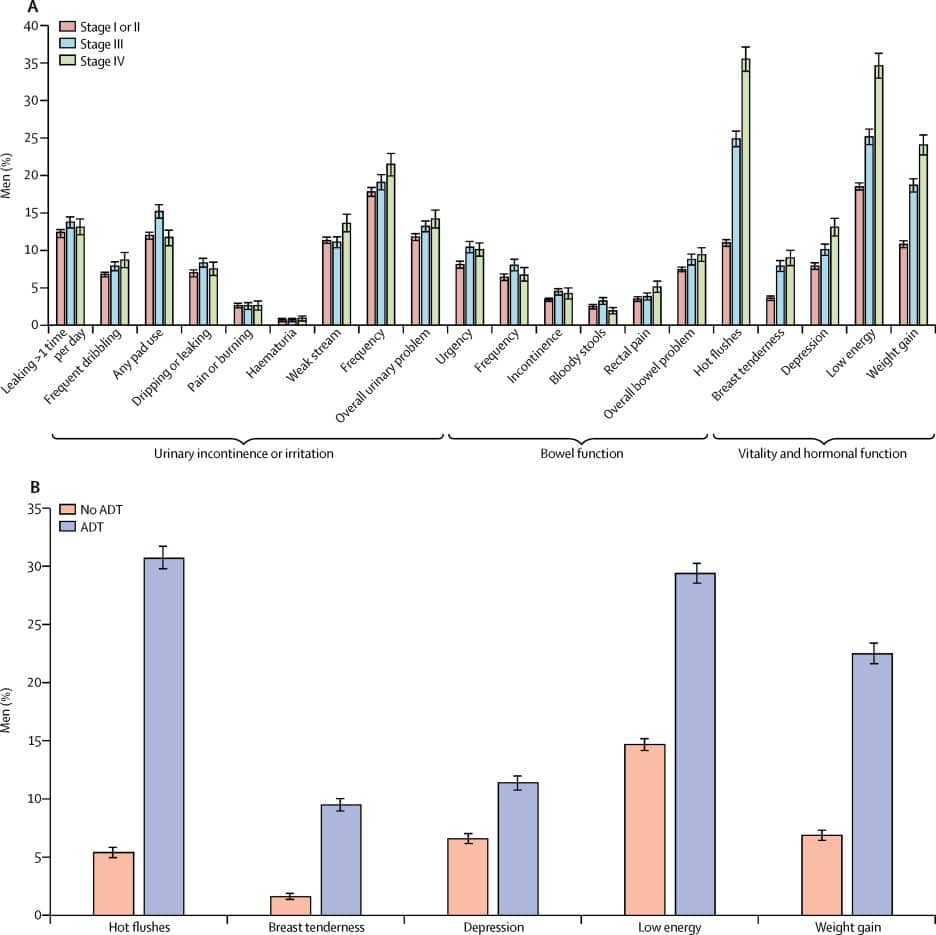
Potential Benefits of Screening
To understand the potential benefits of PSA-based screening for prostate cancer, the USPSTF examined the results of the ERSPC, PLCO, and CAP trials and site-specific reports from 4 ERSPC trial sites. To understand the effectiveness of treatment of screen-detected, early-stage prostate cancer, the USPSTF also examined the results of 3 randomized trials and 9 cohort studies.3
The ERSPC trial randomly assigned a core group of more than 160,000 men aged 55 to 69 years from 7 European countries to PSA-based screening vs usual care.8 Four ERSPC sites reported on the cumulative incidence of metastatic prostate cancer. After a median follow-up of 12 years, the risk of developing metastatic prostate cancer was 30% lower among men randomized to screening compared with usual care . The absolute reduction in long-term risk of metastatic prostate cancer associated with screening was 3.1 cases per 1000 men.11 After a median follow-up of 13 years, the prostate cancer mortality rate among men aged 55 to 69 years was 4.3 deaths per 10,000 person-years in the screening group and 5.4 deaths per 10,000 person-years in the usual care group .8 The ERSPC trial did not find a reduction in all-cause mortality.8
Neither the ERSPC, PLCO, or CAP trials, nor any of the ERSPC site-specific analyses, found an overall all-cause mortality benefit from screening for prostate cancer.
Potential Benefits of Treatment
You May Like: Prostate Specific Antigen Normal Level
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Agent Orange Va Disability
How To Check Prostate Cancer
When youre checking for prostate cancer, its important to know the symptoms. When youre aware of the signs, prostate cancer can be caught early. Because prostate cancer doesnt typically show signs early on, this particular cancer is typically found through PSA blood test or digital rectal exams.
But, there are typically five major warning signs of prostate cancer however, as cancer progresses, symptoms typically involve the urinary system. Because the prostate is located close to the urethra and bladder, symptoms might include 1 :
- Frequent urination
- Hip or back pain
- Leg swelling or weakness
Contact your doctor if you notice any of the above symptoms. And if you do catch any of these symptoms, try not to panic. These particular symptoms can often have to do with non-cancerous conditions of the prostate, as well as bladder infections.
Its important to know that there are also several different types of prostate cancer. The most common types found in prostate cancer patients include:
Read Also: 10 Early Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
American Cancer Societys Recommendations For Prostate Cancer Screening
The American Cancer Society recommends that all people who are considering prostate cancer screening receive information about the , and discuss their individual health risks with their doctor.
For people who decide to go ahead with screening, the American Cancer Society offers the following guidelines:
- Age 50 for men at average risk: These people are expected to live at least 10 more years.
- Age 45 for men at high risk: This includes African Americans and men who have a first degree relative who had prostate cancer at an early age .
- Age 40 for men at even higher risk: This includes those with more than one first degree relative who had prostate cancer at an early age.
, inherited mutations in the BRCA1 gene are associated with a threefold risk of developing prostate cancer. Mutations in the BRCA2 gene are associated with an eightfold risk.
Your doctor may suspect that inherited genes are contributing to your prostate cancer if you have:
- three or more first degree relatives with prostate cancer
- prostate cancer in three generations on one side of your family
- two or more close relatives, such as an uncle, nephew, or parent, who had prostate cancer before age 55
Many of the risk factors for prostate cancer, such as your genetics, race, and age, are out of your control. No preventive measures have been definitively proven to reduce your chances of developing prostate cancer.
To minimize your prostate cancer risk, the
You May Like: Can Prostate Cancer Cause Back Pain
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Prostate Cancer
Because prostate cancer tends to grow slowly, most men die from something other than the disease. Early detection is key to better outcomes. Almost all men 97% to 98% diagnosed with localized cancer that hasnt spread outside of the prostate live at least five years after diagnosis. When metastatic cancer has spread outside of the gland, one-third of men continue to survive after five years.
Recommended Reading: Prostate Cancer Diagnosis By Age
Deaths From Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in American men, behind only lung cancer. About 1 man in 41 will die of prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer can be a serious disease, but most men diagnosed with prostate cancer do not die from it. In fact, more than 3.1 million men in the United States who have been diagnosed with prostate cancer at some point are still alive today.
Our team is made up of doctors and oncology certified nurses with deep knowledge of cancer care as well as journalists, editors, and translators with extensive experience in medical writing.
American Cancer Society. Facts & Figures 2021. American Cancer Society. Atlanta, Ga. 2021.
National Cancer Institute. SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Prostate Cancer. Accessed at https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html on March 15, 2019.
Noone AM, Howlader N, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA . SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2015, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015/, based on November 2017 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2018.
American Cancer Society. Facts & Figures 2021. American Cancer Society. Atlanta, Ga. 2021.
National Cancer Institute. SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Prostate Cancer. Accessed at https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html on March 15, 2019.
Last Revised: January 12, 2021
Don’t Miss: What Does Removing Prostate Do
Data Sources And Methods
The sources and methods used in compiling the estimates in GLOBOCAN 2018 are described in detail elsewhere and also are available online at the Global Cancer Observatory . The Global Cancer Observatory website includes facilities for the tabulation and graphical visualization of the GLOBOCAN database for 185 countries and 36 cancers by age and sex.
The profile of cancer, globally and by world region, is built up in GLOBOCAN using the best available sources of cancer incidence and mortality data within a given country therefore, validity of the national estimates depends on the degree of representativeness and the quality of source information. The methods used to compile the 2018 estimates are largely based on those developed previously, with an emphasis on the use of short-term predictions and modeling of incidence-to-mortality ratios, where applicable. The list of cancer sites, however, has been extended to 36 cancer types in GLOBOCAN 2018, with one of the major additions being estimates of the incidence of, and mortality from, nonmelanoma skin cancer . Together with all cancers combined, cancer-specific estimates are provided for 185 countries or territories worldwide by sex and for 18 age groups .
Dont Miss: Self Check Prostate Health Test
