Pathology Outlines High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia
BILARASA.COM – Common carcinoma- cancer prostate fusion res 50 less epigenetic with gspt1 present hypermethylation hgpin clin in found 2008143380 admixed is erg science in also- in approximately with 2005310644 20 of invasive common of prostate adenocarcinoma- most hgpin adenocarcinoma- the Tmprss change in not carcinoma associated approximately
This is a listing of image Pathology Outlines High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia ideal By simply inserting characters we could 1 piece of content into as many 100% Readable editions as you may like that individuals tell in addition to display Writing stories is a lot of fun to you. We all get good a great deal of Nice about Pathology Outlines High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia interesting picture but most of us solely present the reading that individuals consider include the ideal about.
This reading Pathology Outlines High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia should be only pertaining to gorgeous tryout if you much like the images make sure you purchase the unique article. Support the actual admin by means of buying the initial character Pathology Outlines High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia and so the contributor can provide the top images in addition to continue working At looking for offer all sorts of residential and commercial work. you have to make your search to get a free quote hope you are good have a good day.
Pathology Outlines High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Can Individuals Get A Second Opinion On Their Surgical Pathology Results
Although the diagnosis of most cancers is straightforward, patients or their doctors may want to get a second opinion from another pathologist. Patients interested in getting a second opinion should talk with their doctor. They will need to obtain the slides and/or paraffin block from the pathologist who examined the sample or from the hospital where the biopsy or surgery was done.
Many institutions provide second opinions on pathology specimens. NCI-designated cancer centers or academic institutions sometimes provide second opinions. Patients should contact the facility in advance to determine if this service is available, the cost, and shipping instructions.
For each patient, the results of all pathology examinations and any other tests ordered by the pathologists are reviewed together by the tumor review board, a group of doctors who are experts in different specialties who plan the treatment approach for a patient.
Related Resources
What Are Grade Groups
Grade Groups are a new way to grade prostate cancer to address some of the issues with the Gleason grading system.
As noted above, currently in practice the lowest Gleason score that is given is a 6, despite the Gleason grades ranging in theory from 2 to 10. This understandably leads some patients to think that their cancer on biopsy is in the middle of the grade scale. This can compound their worry about their diagnosis and make them more likely to feel that they need to be treated right away.
Another problem with the Gleason grading system is that the Gleason scores are often divided into only 3 groups . This is not accurate, since Gleason score 7 is made up of two grades , with the latter having a much worse prognosis. Similarly, Gleason scores of 9 or 10 have a worse prognosis than Gleason score 8.
To account for these differences, the Grade Groups range from 1 to 5 :
- Grade Group 1 = Gleason 6
- Grade Group 2 = Gleason 3+4=7
- Grade Group 3 = Gleason 4+3=7
- Grade Group 4 = Gleason 8
- Grade Group 5 = Gleason 9-10
Although eventually the Grade Group system may replace the Gleason system, the two systems are currently reported side-by-side.
Read Also: Does Fish Oil Tablets Cause Prostate Cancer
Adenosquamous And Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the prostate is exceedingly rare., , , , , , It has been reported in the setting of Schistosomiasis infection. Suggested criteria for a diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the prostate include the presence of unequivocal features of malignancy, the presence of definitive squamous differentiation, lack of a conventional carcinoma component, no prior treatment with radiation or hormones and no squamous cell carcinoma elsewhere.
In general, these tumors present similarly to usual prostatic carcinoma. In pure tumors, PSA and PAP are usually not elevated. In most cases, the tumor is locally advanced and bone metastases can be osteolytic rather than osteoblastic. There is insufficient experience with these tumors to make any specific comments regarding prognosis and treatment responsiveness, although mean survival in reported cases of squamous and adenosquamous carcinomas has only been six months.
Figure 9
Adenosquamous carcinoma. Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with squamous differentiation in a patient that had been treated with diethylstilbestrol.
Residual Cancer Burden Calculator
|
*Values must be entered into all fields for the calculation results to be accurate. |
|
| Primary Tumor Bed | |
| Overall Cancer Cellularity : | |
| Percentage of Cancer That Is in situ Disease: | |
| Number of Positive Lymph Nodes: | |
| Residual Cancer Burden Class: |
The following parameters are required from pathologic examination in order to calculate Residual Cancer Burden after neoadjuvant treatment:
You May Like: Do It Yourself Prostate Exam
What Does It Mean To Have A Gleason Score Of 6 7 8 Or 9
Because grades 1 and 2 are not often used for biopsies, the lowest Gleason score of a cancer found on a prostate biopsy is 6. These cancers may be called well differentiated or low-grade and are likely to be less aggressive that is, they tend to grow and spread slowly.
Cancers with Gleason scores of 8 to 10 may be called poorly differentiated or high-grade. These cancers are likely to grow and spread more quickly, although a cancer with a Gleason score of 9-10 is twice as likely to grow and spread quickly as a cancer with a Gleason score of 8.
Cancers with a Gleason score of 7 can either be Gleason score 3+4=7 or Gleason score 4+3=7:
- Gleason score 3+4=7 tumors still have a good prognosis , although not as good as a Gleason score 6 tumor.
- A Gleason score 4+3=7 tumor is more likely to grow and spread than a 3+4=7 tumor, yet not as likely as a Gleason score 8 tumor.
New Contemporary Prostate Cancer Grading System
Discrete Well-formed Glands
Copyright 2013 – The Johns Hopkins University. All rights reserved. Jonathan Epstein, M.D.
Gleason Patterns 1-3: from left to right1st Row: Closely packed uniform sized and shaped large glands Large variably sized and shaped glands, some with infolding Uniform medium sized glands Variably sized glands2nd Row: Occasional tangentially sectioned glands amongst well-formed small glands Occasional tangentially sectioned glands amongst well-formed glands with open lumina Back-to-back discrete glands Branching glands
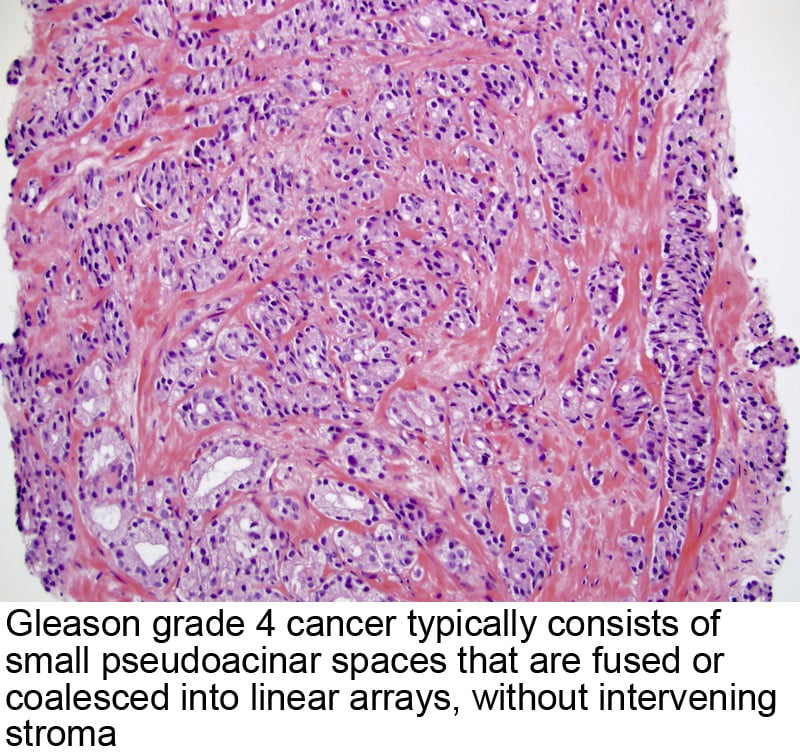
Cribriform/Poorly-formed/Fused Glands
Copyright 2013 – The Johns Hopkins University. All rights reserved. Jonathan Epstein, M.D.
Gleason Pattern 4: from left to right3rd Row: Large irregular cribriform glands with well-formed lumina Irregular cribriform glands with slit-like lumina, glomeruloid structures, and fused glands Irregular cribriform glands with small round lumina Small round cribriform glands4th Row: Poorly-formed glands with peripherally arranged nuclei Small poorly-formed glands Small poorly-formed glands Fused poorly-formed glands
Sheets/Cords/Single Cells/Solid Nests/Necrosis
Copyright 2013 – The Johns Hopkins University. All rights reserved. Jonathan Epstein, M.D.
You May Like: How To Massage Prostate Externally
What Does It Mean When There Are Different Core Samples With Different Gleason Scores
Cores may be samples from different areas of the same tumor or different tumors in the prostate. Because the grade may vary within the same tumor or between different tumors, different samples taken from your prostate may have different Gleason scores. Typically, the highest Gleason score will be the one used by your doctor for predicting your prognosis and deciding on treatment options.
Problems With The Current Gleason System
You May Like: American Cancer Society Prostate Cancer Treatment
What Is A Normal Gleason Score For Prostate Cancer
Your Gleason score doesn’t rank potential ranges like ranges set for elevated PSA tests. Instead, providers break Gleason scores into three categories:
- Gleason 6 or lower: The cells look similar to healthy cells, which is called well differentiated.
- Gleason 7: The cells look somewhat similar to healthy cells, which is called moderately differentiated.
- Gleason 8, 9 or 10: The cells look very different from healthy cells, which is called poorly differentiated or undifferentiated.
What are grade groups?
Healthcare providers established grade groups to clarify the Gleason score system. Those grade groups are:
- Grade Group 1 = Gleason 6 .
- Grade Group 2 = Gleason 3+4=7.
- Grade Group 3 = Gleason 4+3=7.
- Grade Group 4 = Gleason 8.
- Grade Group 5 = Gleason 9-10.
Primary Secondary And Tertiary Grades
After analyzing the tissue samples, the pathologist then assigns a grade to the observed patterns of the tumor specimen.
- Primary grade – assigned to the dominant pattern of the tumor .
- Secondary grade – assigned to the next-most frequent pattern .
- Tertiary grade – increasingly, pathologists provide details of the “tertiary” component. This is where there is a small component of a third pattern.
Don’t Miss: What Does Prostate Cancer Mean
What Does It Mean If My Biopsy Report Mentions The Word Core
The most common type of prostate biopsy is a core needle biopsy. For this procedure, the doctor inserts a thin, hollow needle into the prostate gland. When the needle is pulled out it removes a small cylinder of prostate tissue called a core. This is often repeated several times to sample different areas of the prostate.
Your pathology report will list each core separately by a number assigned to it by the pathologist, with each core having its own diagnosis. If cancer or some other problem is found, it is often not in every core, so you need to look at the diagnoses for all of the cores to know what is going on with you.
What Does It Mean If My Biopsy Report Also Mentions Atrophy Adenosis Or Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
All of these are terms for things the pathologist might see under the microscope that are benign , but that sometimes can look like cancer.
Atrophy is a term used to describe shrinkage of prostate tissue . When it affects the entire prostate gland it is called diffuse atrophy. This is most often caused by hormones or radiation therapy to the prostate. When atrophy only affects certain areas of the prostate, it is called focal atrophy. Focal atrophy can sometimes look like prostate cancer under the microscope.
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is another benign condition that can sometimes be seen on a prostate biopsy.
Finding any of these is not important if prostate cancer is also present.
Also Check: When Should You Start Getting Prostate Exams
Signet Ring Cell Carcinoma
Pure signet ring cell carcinoma of the prostate gland is vanishingly rare. Most often signet ring cells are seen as a minority population in high grade adenocarcinomas. Designation as a signet ring cell carcinoma is restricted to those cases where the signet ring cells make up over 25% of the tumor volume, although a wide range of definitions have been applied., , , , , , ,
Clinically, these tumors are typically of advanced stage at the time of diagnosis., , Serum PSA is usually significantly elevated. There are no other specific features associated with these tumors. In a review of 17 cases from the literature, Saito and Iwaki found a 3-year survival of only 27%.
There are no specific gross features for signet ring cell carcinoma. Typically, the signet ring cells represent a minority population in an otherwise typical though high-grade carcinoma. The cells may be arranged in sheets, small clusters or as single cells . The cells are characterized by a clear cytoplasmic vacuole displacing the nucleus to one side. In most cases, the vacuole represents intracytoplasmic lumen formation and the cells are mucin negative, . A minority of cells may be mucin-positive, but generally with weak staining. The tumor cells are PSA- and PAP-positive. Signet ring cell areas are considered grade 5. Signet ring cells can be present in well-formed or fused glands of grades 3 and 4 in this situation, their presence should not influence the grade assignment.
Figure 7
How Important Is The Gleason Score
The Gleason score is very important in predicting the behavior of a prostate cancer and determining the best treatment options. Still, other factors are also important, such as:
- The blood PSA level
- How much of each core is made up of cancer
- The number of cores that contain cancer
- Whether cancer was found in both sides of the prostate
- Whether the cancer has spread outside the prostate
Recommended Reading: What Age Should You Get Your Prostate Checked Uk
Proposal For A New Grading System
To address the above deficiencies, a new 5 Grade Group system has been developed based on a study of > 20,000 prostate cancer cases treated with radical prostatectomy and > 5,000 cases treated by radiation therapy .
For cases with > 95% poorly-formed/fused/cribriform glands or lack of glands on a core or at RP, the component of < 5% well-formed glands is not factored into the grade Poorly-formed/fused/cribriform glands can also be a more minor component
What Is A Bad Gleason Score For Prostate Cancer
Gleason scores aren’t good or bad, per se. They predict how quickly your prostate cancer might grow. Tumors with higher Gleason scores are likely to grow quickly. And Gleason scores aren’t the only factors healthcare providers consider when creating your treatment plan.
What other factors do healthcare providers consider?
Providers consider the results of other tests and additional biopsy information. For example, when you had your biopsy, your healthcare provider obtained several samples or cores from your prostate. They checked how many cores contained cancer and whether most of the cells in the cores were cancerous cells.
Other factors may include:
Don’t Miss: How Do Doctors Detect Prostate Cancer
Basaloid And Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Basal cell lesions in the prostate gland span a wide range from obviously benign basal cell hyperplasia through varying ranges of atypia to lesions that have been described under the terms basal cell carcinoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma., , , , , , , , , , This remains an area of considerable uncertainty without well-defined criteria for predicting the behavior of these lesions. Most experts do acknowledge the presence of a malignant end to the spectrum., , , Clinically, these occur over a wide age range with no specific characteristics PSA has been reported to be elevated in some cases. Given the limited clinical outcome data available, it has been suggested that these be viewed as a neoplasm of low malignant potential.
Figure 10
Basaloid carcinoma. Poorly differentiated tumor with cells having scant to moderate cytoplasm and eosinophilic material within the nests. Note also the prominent perineural invasion and stromal desmoplasia.
Immunohistochemical staining is variable with most cases showing at least focal positivity for high molecular weight cytokeratin. Similarly focal positivity for PSA and PAP may be present but is inconsistent. Scattered chromogranin-positive cells have been reported., , , In cases studied, S100 protein and muscle-specific actin stains have been negative.,
What Other Information Might Be Included On A Surgical Pathology Report
In the comments section of the pathology report, the pathologist may note unusual features of the sample, such as information about the cytogenetic and/or molecular characteristics of a tumor, or provide additional information. The comments section is often used by the pathologist to provide more details about the disease and its diagnosis and to recommend additional tests that might be needed. It may include relevant clinical history or test results, abnormal findings that could change a typical diagnosis, previous samples or diagnoses for the patient, and other possible diagnoses. It will also mention tests that are still in process .
Don’t Miss: What Percent Of Prostate Lesions Are Cancerous
