The Landscape Of Immune Infiltration In Prostate Cancer
Based on the CIBERSORT algorithm, we obtained an estimation of the abundances of 22 immune cells infiltrating in prostate cancer . We then calculated the correlation between immune cell infiltrations, risk score as well as 3 genes in the outcome model . The results showed that B cells memory, T cells CD4 native, T cells CD4 memory activated and eosinophil were positively correlated with our risk score and 3 genes in outcome model while, plasma cells, T cells CD4 memory resting, mast cells resting and neutrophil were negatively correlated with our risk score and 3 genes in outcome model . Furthermore, we used those 8 immune cells to perform combination survival analysis with our risk score and we could find that each of them could divide patients into 4 groups which showed significant prognosis, especially plasma cell infiltration . As for the correlation between risk score and immune checkpoints, we found that risk score is significantly negative correlated with GAL9, LAG3, PD1LG2 and PDL1 .
Validation Of Prognostic Model
To validate our outcome model, MSKCC cohort was used for the DFS validation. We could observe the same significant prognostic value with p=0.00026 and AUC with 1-, 3- and 5-year prognostic accuracies were 0.715, 0.713, 0.760, respectively . Since the total Gleason score was correlated with tumour behaviour, we then investigated our models role in overall survival and recurrence free survival. Due to few dead patients in TCGA-PRAD OS cohort, we didnt include this cohort and used 2 independent cohorts to prove its utility in OS prediction. The results from the two OS validation datasets showed significant prognostic values were p=0.005 and p=0.032, respectively. The AUC of each dataset was 0.606 and 0.585 at 1 year 0.562 and 0.552 at 3 years 0.608 and 0.495 at 5 years, respectively . Moreover, in the 5 validation cohorts for RFS, we could obviously see the significant outcomes that all the high-risk groups were associated with the poorer prognosis . The significant prognostic values of 5 RFS validation cohorts were p=0.028, p< 0.0001, p=0.001, p=0.005 and p=0.003, respectively. The AUC of each dataset was 0.988, 0.585, 0.600, 0.779 and 0.646 at 1 year 0.533, 0.681, 0.625, 0.655 and 0.570 at 3 years 0.560, 0.794, 0.661, 0.759 and 0.618 at 5 years, respectively .
Diagnostic Tests Are Limited
We always knew that prostate cancer is common and that, until recently, it often went undiagnosed: Autopsies of men who died of other causes have shown that about one-third of men over age 50 have some cancerous cells in their prostate, while 90% of men over age 90 have such cells.
As PSA screening has grown more widespread, we are finding more tumors that otherwise would have escaped detection. Yet current diagnostic technology does not always enable urologists to determine which tumors will lie dormant and which will become active, spreading elsewhere in the body.
Studies estimate that anywhere from 16%56% of men diagnosed with prostate cancer, generally because of an abnormal PSA test, have tumors that might never have caused problems had they not been found. And the landmark Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial unexpectedly yielded data that early-stage prostate tumors are incredibly common, even at PSA levels considered normal.
The PCPT was a randomized controlled study the type considered to be the gold standard in research . The study, which involved almost 19,000 healthy men, was designed to evaluate whether the drug finasteride could prevent prostate cancer from developing. Finasteride is a hormonal medication originally approved to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia , but which has also been investigated as a potential treatment for prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: What To Expect After Radiation Treatment For Prostate Cancer
Tools To Help You Decide
The Predict Prostate tool can help you decide between monitoring and more radical treatment. It is for men whose prostate cancer hasnt spread.
It cant tell you exactly what is going to happen in the future, but it gives you an idea about the differences in survival between the different treatment options. The tool works less well for men with a very high PSA or those with a fast growing or large tumour.
To be able to use the tool you need to know the following about your cancer:
Stage Iv Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads, its often found in nearby lymph nodes. If cancer has reached these nodes, it also may have spread to other lymph nodes, the bones, or other organs.
When cancer spreads from its original place to another part of the body, the new tumor has the same kind of abnormal cells and the same name as the primary tumor. For example, if prostate cancer spreads to bones, the cancer cells in the bones are actually prostate cancer cells. The disease is metastatic prostate cancer, not bone cancer. For that reason, its treated as prostate cancer, not bone cancer. Doctors call the new tumor distant or metastatic disease.
The cancer has spread beyond the prostate.
- Stage IVA: The cancer has spread to the regional lymph nodes.
-
Stage IVB: The cancer has spread to distant lymph nodes, other parts of the body, or to the bones.
You May Like: What Age To Check For Prostate
Is The Psa Test Recommended For Prostate Cancer Screening
Beginning around 2008, as more was learned about both the benefits and harms of prostate cancer screening, a number of professional medical organizations began to caution against routine population screening with the PSA test. Most organizations recommend that individuals who are considering PSA screening first discuss the risks and benefits with their doctors.
Some organizations do recommend that men who are at higher risk of prostate cancer begin PSA screening at age 40 or 45. These include Black men, men with germline variants in BRCA2 , and men whose father or brother had prostate cancer.
In 2018, the United States Preventive Serves Task Force updated its recommendation statement for prostate cancer screening from a D to a C in men ages 55 to 69. The updated recommendation, which applies to the general population as well as those at increased risk due to race/ethnicity or family history, is as follows:
- For individuals ages 55 to 69 years, the decision to undergo periodic PSA-based screening for prostate cancer should be an individual one. Before making the decision, a person should discuss the potential benefits and harms of screening with their clinician and consider these in the context of their own values and preferences.
- PSA-based screening for prostate cancer is not recommended for individuals 70 years and older.
How Fast And Where Does Prostate Cancer Spread
Like other cancers, prostate cancer can spread from the site of where it first started to other sites of the body. Once it spreads, the disease may still respond to the treatment, but typically it is now no longer to be cured. Bones, liver, and lungs are the most common sites for prostate cancer metastasis. How do you know that it has spread? And how fast this metastasis?
Since the early detection of the disease is very crucial for the prognosis and outlook of patients , its very important to diagnose the disease as early as possible.
In the U.S, the number of men diagnosed with the disease at later stages decreases drastically due to the implementation of PSA screening test .
Men with many risk factors of prostate cancer should start discussing the test with their doctor earlier. Visit this section for more information about this!
The PSA test is also recommended in other countries . However whether this test is necessary for all men is debatable.
For those who eventually dont have prostate cancer in their life, the choice to take the test may put them at high risk of getting over-diagnosis, making anxiety more likely.
Therefore, some experts agree that the screening prostate cancer test is more recommended for those who have some /many risk factors of the disease. For more advice, consult more with your GP!
How prostate cancer is diagnosed?
PSA screening test
Rectal examinations
Biopsy procedure
IVU or IVP Intravenous urogram
Imaging tests
You May Like: Is It Ok To Ejaculate After Prostate Biopsy
Diagnosis With The Whitmore
The Whitmore-Jewett System is an older system. It differs from the TNM system in that the stage and sub-stage is determined by whether the tumor can be felt by a physical examination* and by the PSA score.*a digital rectal examination
- Stage B a tumor is not detected but PSA levels are very high.
- Stage B1 a tumor can be felt. It is confined to one lobe.
- Stage B2 a tumor can be felt. It is found in both lobes.
The TNM system when used in conjunction with PSA and Gleason scores is generally favored over the Whitmore-Jewett system it is thought to give a more accurate diagnosis.
Psa Measurable By Standard Blood Test
Producing seminal fluid, the prostate also generates a molecule known as Prostate-Specific Antigen, or PSA. It is a prostate specific substance that circulates in the prostate and blood . PSA is a tumor marker used at all stages of prostate cancer treatment: screening, diagnosis, post-treatment follow-up, diagnosis after recurrence.
PSA tests are often recommended from about age 50. Dosageis done with a standard blood test for which it is not necessary to be fasting.8 days must separate PSA dosage from a rectal examination and 2 months in caseof a recent rectal examination. However, PSA is not specific to prostate cancerbecause it also increases with other prostate pathologies: Benign ProstaticHyperplasia, inflammation and infection of the prostate. One of the first stepsof prostate cancer diagnosis, PSA test must be completed by other diagnostics:5 to 10% of cancers that can be felt during a rectal examination have a normalPSA at the start.
- Thresholdvalue used for prostate cancer screening is 4 ng/mL: from 4 to 10 ng/mL, 70% ofdiagnosed cancers are localized.
- APSA higher than 30 ng/mL reflects an advanced localized prostate cancer with a highprobability of locoregional lymph node metastases.
- APSA higher than 100 ng/mL reflects anadvanced localized prostate cancer, with a high bone metastases probability.
Read Also: Best Treatment For Early Prostate Cancer
Correlation Between The Risk Score With Other Clinicopathological Characteristics
Clinicopathological data, including age, clinical M stage, clinical T stage, total Gleason score, laterality, number of positive lymphonodes, pathological N stage, pathological T stage, PSA value, radiation therapy and targeted molecular therapy were collected from TCGA-PRAD dataset. The detailed information of patients clinicopathological characteristics in TCGA-PRAD cohort were displayed in the Additional file 9: Table S5. Comparison results between risk score and different clinicopathological characters were shown in Additional file 10: Figure S5. In terms of clinical features, risk score was robustly increased in patients with lymphovascular invasion, more advanced stage and Gleason score and additional therapy, which indicated risk score was significantly positive correlated with tumour malignancy.
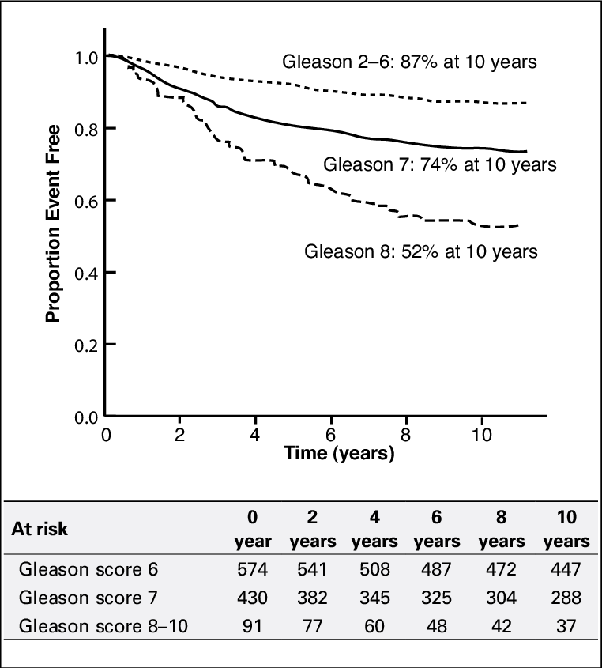
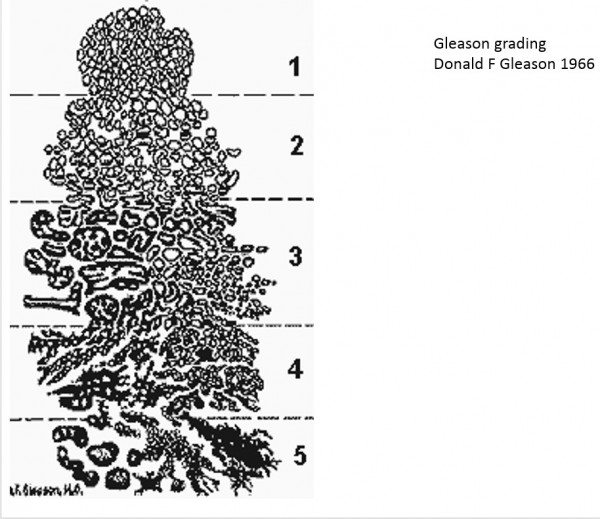
Prostate Cancer Grading & Prognostic Scoring
The Gleason Score is the grading system used to determine the aggressiveness of prostate cancer. This grading system can be used to choose appropriate treatment options. The Gleason Score ranges from 1-5 and describes how much the cancer from a biopsy looks like healthy tissue or abnormal tissue . Most cancers score a grade of 3 or higher.
Since prostate tumors are often made up of cancerous cells that have different grades, two grades are assigned for each patient. A primary grade is given to describe the cells that make up the largest area of the tumor and a secondary grade is given to describe the cells of the next largest area. For instance, if the Gleason Score is written as 3+4=7, it means most of the tumor is grade 3 and the next largest section of the tumor is grade 4, together they make up the total Gleason Score. If the cancer is almost entirely made up of cells with the same score, the grade for that area is counted twice to calculated the total Gleason Score. Typical Gleason Scores range from 6-10. The higher the Gleason Score, the more likely that the cancer will grow and spread quickly.
Read Also: Small Cell Prostate Cancer Survivors
Extent Your Cancer Has Spread
If your cancer has spread outside of your prostate , there are two category measures to consider. These two measurements are commonly combined with your T-stage to form one TMN score.
N-Category: Determines if and how far the cancer has spread to your lymph nodes.M-Category: Determines if and how far the cancer has metastasized or spread to other organs.
How Prostate Cancer Staging Is Done
Initial staging is based on the results of PSA blood tests, biopsies, and imaging tests. This is also called clinical staging.
PSA refers to a protein made by the prostate measured by a lab test.
- A higher level of PSA can indicate a more advanced cancer.
- The doctors will also look at how fast the PSA levels have been increasing from test to test. A faster increase could show a more aggressive tumor.
A prostate biopsy is done in your doctors office. The results can indicate:
- How much of the prostate is involved.
- The Gleason score. A number from 2 to 10 that shows how closely the cancer cells look like normal cells when viewed under a microscope. Scores 6 or less suggest the cancer is slow growing and not aggressive. Higher numbers indicate a faster growing cancer that is more likely to spread.
You May Like: What Does The Prostate Gland Secrete
Cancer Staging May Miss Errant Cells
Once a pathologist confirms that cancer is present, the doctor will next determine how far the cancer extends a process known as cancer staging and discuss the implications with you. This is perhaps the most important information of all for you to obtain, as it determines whether the cancer is likely to be curable, or whether it has already spread to additional tissues, making prognosis much worse.
If you were my patient, I would ask you to consider two important points. First, cancer staging actually occurs in two phases: clinical and pathological . Of the two, pathological staging is more accurate.
A second point to understand, however, is that even pathological staging can be inaccurate . A cancer spreads, or metastasizes, once a primary tumor sheds cancer cells that travel elsewhere in the body and establish other tumor sites. Metastasis is a complex process that researchers do not fully understand. What is clear is that this process involves multiple genetic mutations and steps, and that each type of cancer spreads in a unique way.
Construction And Assessment Of The Nomogram
Excluding all missing information would lead to not enough patient samples. Therefore, we only firstly perform univariate cox regression analysis to identify the proper terms to build the nomogram. The forest was used to show the p value, HR and 95% CI of each variable through forestplot package in R. The nomogram, calibration plots and decision curve were generated using rms package. Afterwards, the calibration curves and decision curve analysis were united to see whether our established nomogram was suitable for clinical utility.
Also Check: Is Nitric Oxide Bad For Prostate Cancer
Stage Iii Prostate Cancer
The tumor extends beyond the prostate. The tumor may have invaded the seminal vesicles, but cancer cells havent spread to the lymph nodes.
-
Stage IIIA: The cancer has spread beyond the outer layer of the prostate into nearby tissues. It may also have spread to the seminal vesicles. The PSA level is high.
- Stage IIIB: The tumor has grown outside of the prostate gland and may have invaded nearby structures, such as the bladder or rectum.
- Stage IIIC: The cancer cells across the tumor are poorly differentiated, meaning they look very different from healthy cells.
The Tnm System For Prostate Cancer Stages
As they do for most cancers, doctors use the TNM system to describe prostate cancer stages. The system uses three different aspects of tumor growth and spread:
- Tumor. Whatâs the size of the main area of prostate cancer?
- Nodes. Has it spread to any lymph nodes? If so, how far and how many?
- Metastasis. How far has the prostate cancer spread?
Read Also: Hormone Therapy For Advanced Prostate Cancer Life Expectancy
Recommended Reading: New Vaccine For Prostate Cancer
How Is The Psa Test Used In Men Who Have Been Treated For Prostate Cancer
The PSA test is used to monitor men after surgery or radiation therapy for prostate cancer to see if their cancer has recurred . If a mans PSA level begins to rise after prostate cancer treatment, it may be the first sign of a recurrence. Such a biochemical relapse typically appears months or years before the recurrence causes symptoms.
However, a single elevated PSA measurement in someone who has a history of prostate cancer does not always mean that the cancer has come back. Someone who has been treated for prostate cancer should discuss an elevated PSA level with their doctor. The doctor may recommend repeating the PSA test or performing other tests to check for evidence of a recurrence. The doctor may look for a trend of rising PSA level over time rather than a single elevated PSA level.
A rising trend in PSA level over time in combination with other findings, such as an abnormal result on imaging tests, may lead the doctor to recommend further cancer treatment.
British Columbia Specific Information
You are considered a low-risk patient if you have a PSA value that is equal or less than 10 nanograms per millilitre , a Gleason score that is equal or less than 6, and your cancer stage is T1c/T2a. PSA is your prostate specific antigen measured by a blood test, the Gleason score indicates how aggressive the cancer is by looking at tissue biopsy results, and the cancer stage describes how much the cancer has spread.
Active surveillance has been developed to allow for careful management of men with low-risk prostate cancer. For more information, visit BC Cancer Agency Prostate.
Top of the pageDecision Point
You may want to have a say in this decision, or you may simply want to follow your doctors recommendation. Either way, this information will help you understand what your choices are so that you can talk to your doctor about them.
Also Check: Removing Prostate Due To Cancer
