Gleason Scoring And Grade Groups
The Gleason scoring system was introduced in 1966 for the histologic assessment of prostate cancer aggressiveness and is based upon an assessment of the glandular patterns of cancer present in the specimen. The score is presented as a sum of the dominant pattern and the largest minority pattern present in the sample. Gleason initially described 5 patterns ranging from 1 to 5, with pattern 5 being the most poorly differentiated. In 2005 the International Society of Urologic Pathology recommended against the use of patterns 1 and 2, leaving a shortened scoring scale of 6 to 10 . In addition, the consensus recommended that a number of variant patterns previously graded as 3, and all cribriform patterns, should be considered pattern 4. In doing so, there has been an observation of Gleason scoring migration, with a greater number of cancers designated as Gleason score 3+4 or 4+3, as compared with historical cohorts. This migration has led to a reassessment of the accuracy of Gleason scoring in contemporary practice, with most such evaluations demonstrating improved prognostic accuracy . Although the grading system appears to be more prognostically accurate, it has created difficulty in comparing historical outcomes of treatment to contemporary cohorts, given the difference in what is meant by Gleason 3+3 and 3+4/4+3.
Rodrigo Pessoa MD, … Fernando J. Kim MD, MBA, FACS, in, 2018
Grade Groups Of Prostate Cancer
The Grade Group is the most common system doctors use to grade prostate cancer. It is also known as the Gleason score.
The grade of a cancer tells you how much the cancer cells look like normal cells. This gives your doctor an idea of how the cancer might behave and what treatment you need.
To find out the Grade Group, a pathologist
What Is Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer develops in the prostate a small gland that makes seminal fluid. It is one of the most common types of cancer in men. Prostate cancer usually grows over time and in the beginning usually stays within the prostate gland, where it may not cause serious harm. While some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly.
Prostate cancer that is caught early has a better chance of successful treatment.
Read Also: What Causes Castrate Resistant Prostate Cancer
Gleason Score For Grading Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is also given a grade called a Gleason score. This score is based on how much the cancer looks like healthy tissue when viewed under a microscope. Less aggressive tumors generally look more like healthy tissue. Tumors that are more aggressive are likely to grow and spread to other parts of the body. They look less like healthy tissue.
The Gleason scoring system is the most common prostate cancer grading system used. The pathologist looks at how the cancer cells are arranged in the prostate and assigns a score on a scale of 3 to 5 from 2 different locations. Cancer cells that look similar to healthy cells receive a low score. Cancer cells that look less like healthy cells or look more aggressive receive a higher score. To assign the numbers, the pathologist determines the main pattern of cell growth, which is the area where the cancer is most obvious, and then looks for another area of growth. The doctor then gives each area a score from 3 to 5. The scores are added together to come up with an overall score between 6 and 10.
Gleason scores of 5 or lower are not used. The lowest Gleason score is 6, which is a low-grade cancer. A Gleason score of 7 is a medium-grade cancer, and a score of 8, 9, or 10 is a high-grade cancer. A lower-grade cancer grows more slowly and is less likely to spread than a high-grade cancer.
New Approaches To Display Gleason Grades
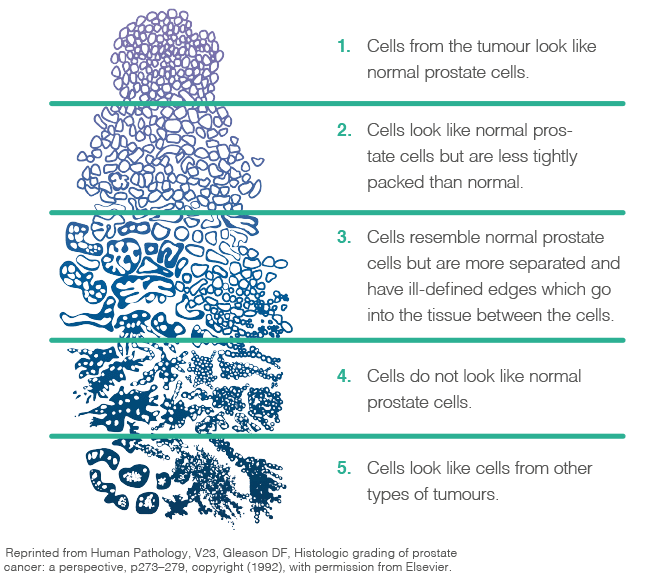
For the 2016 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs, a revised schematic diagram was created with the assistance of David Grignon at the Indiana University School of Medicine . Advantages of the new schematic diagram is that it depicts variants of Gleason pattern 3 including pseudohyperplastic, atrophic, and branching prostate cancer.
Figure 3
Also Check: Prostate Cancer With Normal Psa
You May Like: Do Doctors Still Do Prostate Exams
The 2005 And 2014 Modified Gleason Grading Systems
One of the biggest changes to the Gleason grading system was the classification of Grades 1 and 2. Grade 1 tumors are generally benign, and Grade 2 tumors do not appear to differ from those classified as Grade 3. In 2005, Grade 2 was recommended to be used rarely, if ever, and in the 2014 modified Gleason grading system, grading started from 3. This modification accounted for some of the observed rises in Gleason scores. A second change causing an increase in Gleason scores was the narrowing of the definition of Gleason 3 and concomitant expansion of Gleason 4.
From the 2005 to the 2014 consensus conferences, the histologic criteria for Gleason patterns 3 and 4 changed, resulting in the reduction of pattern 3 and expansion of pattern 4. In the original system, pattern 3 included some cribriform as well as poorly formed glands. Only well-formed discrete glands are included in pattern 3 in the 2014 modified Gleason grading system. In particular, cribriform glands lacking basal cells, independently of their morphology and size, are considered as pattern 4 in the 2014 modified Gleason system.,,,,,,,,,,, Fused, poorly formed, and glomeruloid glands are part of the morphologic spectrum of the current Gleason pattern 4.
Main limitations of the 2005 and 2014 modified Gleason scoring systems
From a clinical perspective, the 2005 and 2014 modified Gleason systems are suboptimal due to several reasons as follows:,,,,,
How Do Doctors Find Out Your Grade Group
The pathologist grades each sample of prostate cancer cells from 3 to 5 based on how quickly they are likely to grow or how aggressive the cells look. You may hear this score being called the Gleason grade.
Doctors then work out an overall Gleason score by adding together the 2 most common Gleason grades. So for example, if the most common Gleason grade is 3, and the second most common is 4, then the overall Gleason score is 7. Or they might write the scores separately as 3 + 4 = 7. This combined score is now called the Grade Group.
There are 5 Grade Groups. Grade Group 1 is the least aggressive and Grade Group 5 is the most aggressive.
This is how the Gleason score and Grade Groups match up and what it means:
| Gleason score |
|---|
You May Like: Psa Blood Test For Prostate Cancer
How Is The Gleason Score Derived
The pathologist looking at the biopsy sample will assign one Gleason grade to the most predominant pattern in your biopsy and a second Gleason grade to the second most predominant pattern. For example: 3 + 4. The two grades will then be added together to determine your Gleason score. Theoretically, Gleason scores range from 2-10. However, since Dr. Gleasons original classification, pathologists almost never assign scores 2-5, and Gleason scores assigned will range from 6 to 10, with 6 being the lowest grade cancer.
What Is A Bad Gleason Score For Prostate Cancer
Gleason scores aren’t good or bad, per se. They predict how quickly your prostate cancer might grow. Tumors with higher Gleason scores are likely to grow quickly. And Gleason scores aren’t the only factors healthcare providers consider when creating your treatment plan.
What other factors do healthcare providers consider?
Providers consider the results of other tests and additional biopsy information. For example, when you had your biopsy, your healthcare provider obtained several samples or cores from your prostate. They checked how many cores contained cancer and whether most of the cells in the cores were cancerous cells.
Other factors may include:
- Imaging test results like ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging or positron emission tomography scan.
- Whether cancer was found in both sides of your prostate.
- Whether cancer has spread outside of your prostate.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Healthcare providers use Gleason scores to learn more about your prostate cancer. But numbers don’t tell the whole story about your prostate cancer. That story starts with your treatment plan and understanding what to expect from your treatment. Think of your Gleason score and other analysis as the next chapter in your story. Talk to your healthcare provider any time you have questions about your Gleason score or any other test result. They’ll be glad to help you understand what the numbers mean.
You May Like: Is Prostate Cancer And Breast Cancer Related
What Does It Mean If My Biopsy Report Also Mentions Atrophy Adenosis Or Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
All of these are terms for things the pathologist might see under the microscope that are benign , but that sometimes can look like cancer.
Atrophy is a term used to describe shrinkage of prostate tissue . When it affects the entire prostate gland it is called diffuse atrophy. This is most often caused by hormones or radiation therapy to the prostate. When atrophy only affects certain areas of the prostate, it is called focal atrophy. Focal atrophy can sometimes look like prostate cancer under the microscope.
Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia is another benign condition that can sometimes be seen on a prostate biopsy.
Finding any of these is not important if prostate cancer is also present.
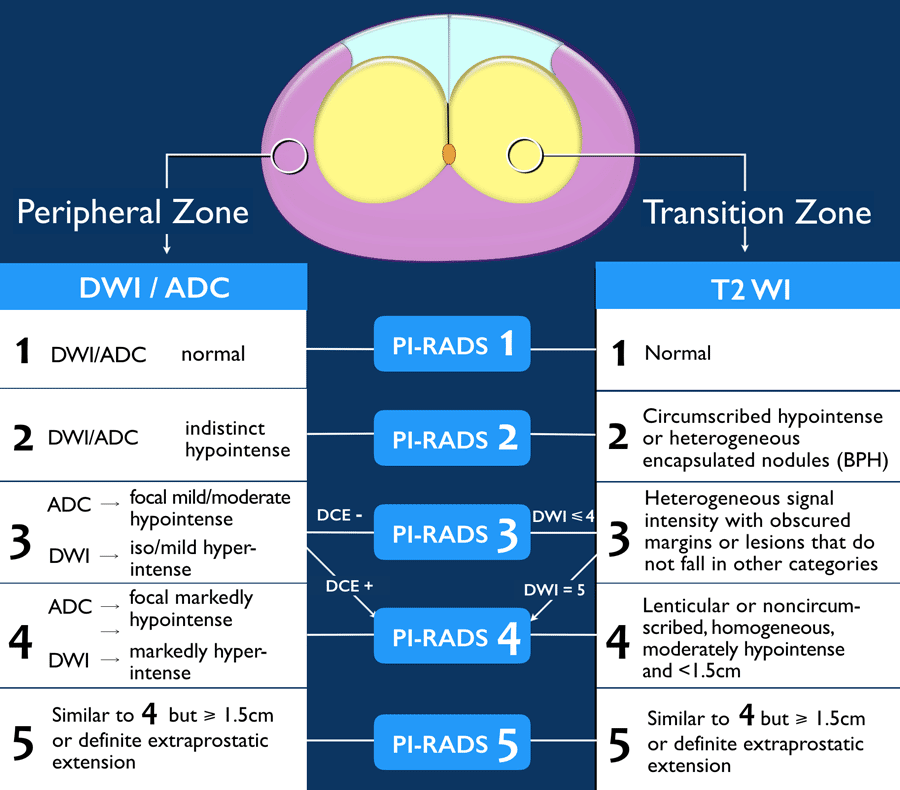
How Sensitive Or Reliable Is Mri Of The Prostate
Comparing MRI of the prostate with TRUS biopsy.
Because an 3Tesla multiparametric MRI of the prostate does not just look at a shadow in the prostate gland alone, but also look at other parameters and behaviours of the abnormal area as discussed above, it has a very high sensitivity and specificity.
A TRUS biopsy is only reliable about 50 % of the time .
In comparison, an MRI of the prostate has over 90% reliability in the detection of prostate cancer. The combination of a positive PSA test , a high PSA velocity and a PI-RADs of 4 or more makes the presence of prostate cancer more likely in a patient. Even a Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System score of 3 should trigger the possibility of an increased probability of prostate cancer, warranting periodic follow up and screening.
You May Like: How To Do Prostate Exam At Home
How Important Is The Gleason Score
The Gleason score is very important in predicting the behavior of a prostate cancer and determining the best treatment options. Still, other factors are also important, such as:
- The blood PSA level
- How much of each core is made up of cancer
- The number of cores that contain cancer
- Whether cancer was found in both sides of the prostate
- Whether the cancer has spread outside the prostate
Should Gleason Score 6 Cancer Be Renamed As Non
From a pathologists viewpoint, Gleason score 6 is still cancer with many of the same morphological features of higher-grade cancer, along with a lack of a basal cell layer and the potential to locally invade. Gleason pattern 3 cancer harbors many of the molecular alterations associated with higher-grade cancers including overexpression of -methylacyl-CoA racemase, glutathione S-transferase hypermethylation and downregulation, and TMPRSS2:ERG gene fusions. From a clinical perspective, renaming Gleason score 3+3=6 as an IDLE tumor on biopsy carries the risk that patients on active surveillance will not adhere to long-term follow-up as they have been told they do not have cancer. The need for close follow-up results from the risk of unsampled higher-grade carcinoma. The likelihood of upgrading from a Gleason score 6 on biopsy to Gleason score 7 at RP has been reported to be as high as 36%. If Gleason score 6 on biopsy was not labeled as cancer, the potential for higher grade or more extensive disease might be ignored, and compliance with recommendations for careful monitoring may not occur.
You May Like: Best Prostate Cancer Doctor In Philadelphia
Recommended Reading: Is It Possible To Check Your Own Prostate
What Is A Normal Gleason Score For Prostate Cancer
Your Gleason score doesn’t rank potential ranges like ranges set for elevated PSA tests. Instead, providers break Gleason scores into three categories:
- Gleason 6 or lower: The cells look similar to healthy cells, which is called well differentiated.
- Gleason 7: The cells look somewhat similar to healthy cells, which is called moderately differentiated.
- Gleason 8, 9 or 10: The cells look very different from healthy cells, which is called poorly differentiated or undifferentiated.
What are grade groups?
Healthcare providers established grade groups to clarify the Gleason score system. Those grade groups are:
- Grade Group 1 = Gleason 6 .
- Grade Group 2 = Gleason 3+4=7.
- Grade Group 3 = Gleason 4+3=7.
- Grade Group 4 = Gleason 8.
- Grade Group 5 = Gleason 9-10.
How Prostate Cancer Is Diagnosed And Staged
Cancer staging helps you and your doctor understand how advanced your cancer is and how much it has spread at the time of diagnosis. Knowing your cancer stage also helps your doctor determine the best treatment options for you and estimate your chance of survival.
The most widely used staging system for cancer is the TNM system that classifies cancer from stage 1 to stage 4.
TNM stands for:
- Tumor: the size and extent of the tumor
- Nodes: the number or extent of nearby lymph node involvement
- Metastasis: whether cancer has spread to distant sites in the body
The TNM scale is used for many types of cancer. When a doctor uses it to determine your prostate cancer stage, theyll consider several other factors as well, including:
You May Like: Is Beer Bad For Prostate
Modified Gleason Grading System
The original Gleason system92 has been widely used by pathologists, urologists, and medical and radiation oncologists in the United States and throughout the world as the preferred grading system for prostate adenocarcinoma for many years. The Gleason scoring system is based primarily on the growth pattern of neoplastic glands on low-power magnification. The tumor is divided into five patterns based on the tumor differentiation, with 1 being best differentiated and 5 being worst differentiated. Because of the frequent heterogeneity of tumor differentiation, prostate cancers often have more than one pattern. In the original Gleason grading system, the two most common patterns are recorded.92 However, in the revised Gleason grading system, the score has been revised to the most common primary and worst patterns instead of the second most common pattern for biopsy grading.188,189 The sum of these patterns constitutes a score that ranges from 2 to 10.183185
Liang Cheng, … Rodolfo Montironi, in, 2010
Gleason Prostate Cancer Score
1960s as a way to measure how aggressive your prostate cancer may be.
A pathologist determines your Gleason score by looking at a biopsy of your prostate tissue under a microscope. They grade the cells in the biopsy on a scale of 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are healthy prostate, whereas grade 5 cells are highly mutated and dont resemble healthy cells at all.
The pathologist will calculate your Gleason score by adding together the number of the most prevalent type of cell in the sample and the second most prevalent type of cell.
For example, if the most common cell grade in your sample is 4 and the second most common is 4, you would have a score of 8.
A Gleason score of 6 is considered low-grade cancer, 7 is intermediate, and 8 to 10 is high-grade cancer.
Also Check: Abiraterone Prostate Cancer Life Expectancy
What Is A Gleason Score
Cancer cells donât look the same as healthy cells. The more different they appear, the more aggressive the cancer tends to be.
The Gleason system uses the numbers 1 to 5 to grade the most common and second most common patterns of cells found in a tissue sample.
- Grade 1: The tissue looks very much like normal prostate cells.
- Grades 2-4: Cells that score lower look closest to normal and represent a less aggressive cancer. Those that score higher look the furthest from normal and will probably grow faster.
- Grade 5: Most cells look very different from normal.
Doctors add your primary and secondary numbers together to form your total Gleason score. That tells you how aggressive the cancer is. The lowest score for a cancer is 6, which is a low-grade cancer. A Gleason score of 7 is a medium-grade cancer, and a score of 8, 9, or 10 is a high-grade cancer.
Generally speaking, the higher your Gleason score, the more aggressive the cancer. That means itâs more likely to grow and spread to other parts of your body. Doctors use this information, along with the stage of the cancer, to choose the best treatment for you.
What Does It Mean If My Biopsy Mentions That There Is Perineural Invasion
Perineural invasion means that cancer cells were seen surrounding or tracking along a nerve fiber within the prostate. When this is found on a biopsy, it means that there is a higher chance that the cancer has spread outside the prostate. Still, perineural invasion doesnt mean that the cancer has spread, and other factors, such as the Gleason score and amount of cancer in the cores, are more important. In some cases, finding perineural invasion may affect treatment, so if your report mentions perineural invasion, you should discuss it with your doctor.
Recommended Reading: Prostate Radiation Therapy Side Effects Treatment
What Is A Grade Group
In 2014, the International Society of Urological Pathology released supplementary guidance and a revised prostate cancer grading system, called the Grade Groups.
The Grade Group system is simpler, with just five grades, 1 through 5.
*Risk Groups are defined by the Grade Group of the cancer and other measures, including PSA, clinical tumor stage , PSA density, and number of positive biopsy cores.
Many hospitals report both the Gleason score and the Grade Group, but there may be hospitals that still report only the old Gleason system.
