Number 1 Heart Disease
Heart disease is a term that includes many specific heart conditions. According to the CDC, coronary artery disease , which can lead to heart attacks, is the most common heart disease in the United States. Other heart conditions include chest pain known as angina, heart failure, and irregular heartbeats known as arrhythmias.
> > > One Crazy Prostate Trick All Men Over 40 Should Try
Symptomatic treatment of an enlarged prostate usually involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may be the best option if you suffer from chronic urination. It will help the body adjust to the increased size of the prostate. Also, taking regular urination intervals will help retrain the bladder to function properly. Inactivity also contributes to urine retention, and cold temperatures can increase the urge to urinate.
Invasive treatment of enlarged prostate includes medication that relieves the pressure on the urethra and bladder. However, if the condition is severe, it may require surgical intervention. If treatment is not successful, the enlarged prostate can become a potentially life-threatening disease. As the hormone levels in the body change, the enlarged prostate can lead to various complications, including urinary retention and even cancer. This is why it is critical to see a doctor for further evaluation.
Data Source And Methods
The data shown in this report reflect information collected by CDCs National Center for Health Statistics from death certificates filed in all 50 states and the District of Columbia and compiled into the National Vital Statistics System. Deaths were classified using the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. Cancer deaths were identified using underlying cause-of-death codes C00-C97 . Heart disease deaths were identified using underlying cause-of-death codes I00-I09, I11, I13, and I20-I51. COVID-19 deaths were identified using underlying cause-of-death code U07.1. Rates were age-adjusted to the 2000 US standard population.
Also Check: What Is The Best Prostate Massager
Vitamin And Mineral Supplements
Vitamin D
An inverse relationship was observed between sunlight, or UVB exposure, and incidence of prostate cancer , suggesting that vitamin D deficiency might increase prostate cancer risk development . Similarly, discoveries were made by Barnett and Beer who found that people living in âsunnyâ countries were at lower risk of developing secondary solid cancer after melanoma compared to people living in âless sunnyâ countries.
The incidence of prostate cancer in African-American men is twice that of Caucasians, suggesting that race might play a role. There might be a role for vitamin D deficiency in this as UV radiation is blocked in darkly pigmented skin due to high melanin levels and this mechanism inhibits the conversion to vitamin D3 .
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a vitamin which is fat soluble. Vegetable oils, egg yolks, and nuts are the important dietary sources of vitamin E. Tocopherols present in vitamin E have both potent cellular anti-oxidant with anticancer properties . Studies investigating the relationship between vitamin E and prostate cancer risk have shown contradicting results. The ATBC trial showed that in men who smoked supplementing daily vitamin E was not able to reduce the incidence of prostate cancer . In another large clinical trial , vitamin E supplementation did not show any benefit in 31,000 men with incident prostate cancer .
Selenium
Folate and vitamin B12
Who Dies From This Cancer
Because we have screening for prostate cancer, most of the time it is caught before it spreads to other parts of the body. Men who have prostate cancer that is characterized as localized or regional are not as likely to die as men whose cancer is distant. In general prostate cancer has excellent survival rates, but death rates are higher in African American men, men who have advanced stage cancer, and men who are between the ages of 75 and 84. Prostate cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer death in the United States. The death rate was 18.8 per 100,000 men per year based on 20162020, age-adjusted.
Death Rate per 100,000 Persons by Race/Ethnicity: Prostate Cancer
Males
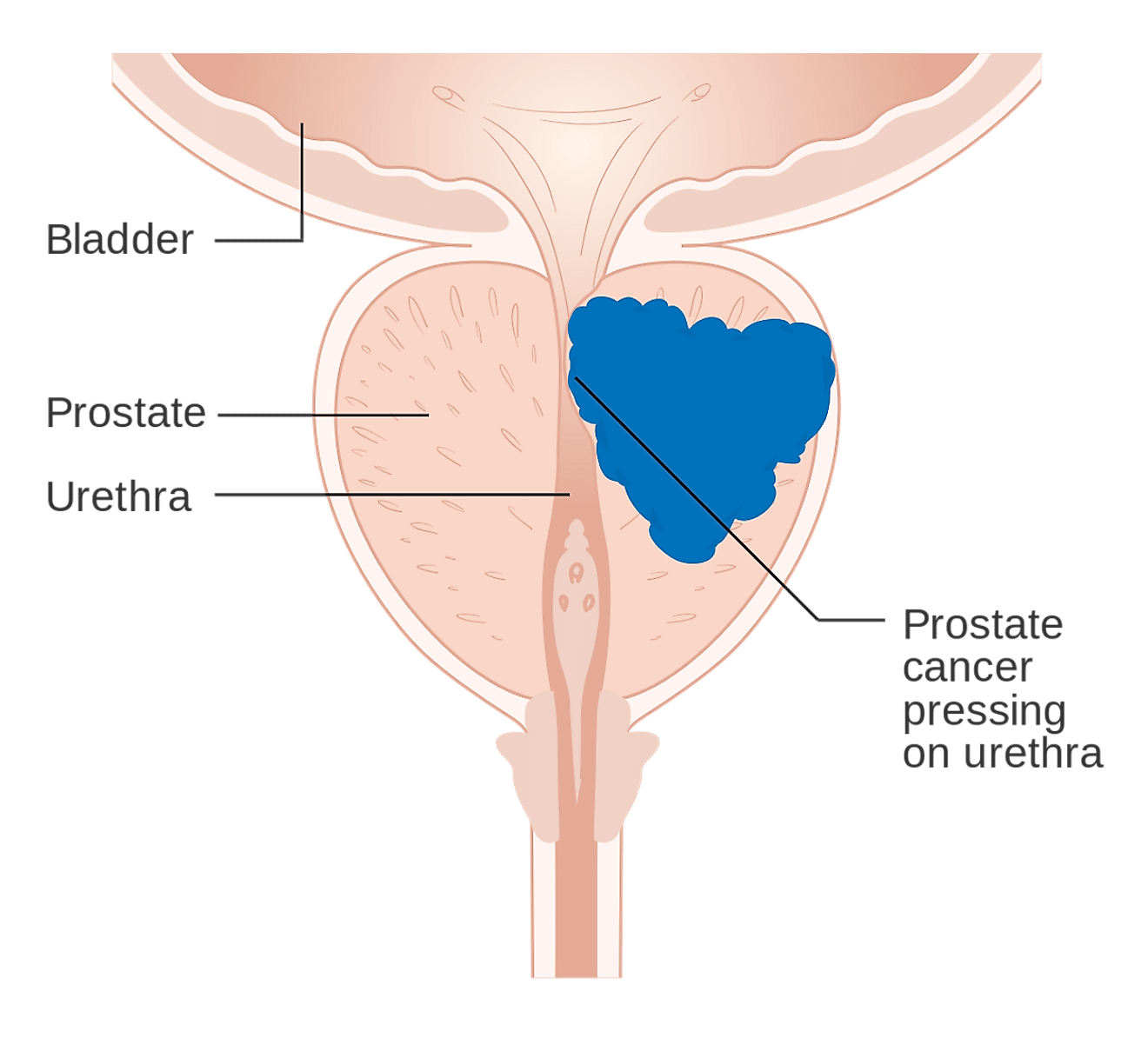
Figure: Prostate and Nearby Organs
This cancer forms in tissues of the prostate . The prostate surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows. A healthy prostate is about the size of a walnut. If the prostate grows too large, it squeezes the urethra. This may slow or stop the normal flow of urine. Prostate cancer usually occurs in older men.
Additional Information
Read Also: Next Generation Prostate Cancer Risk Calculator
Family History And Genetic Factors
It is estimated that about 20% of patients with prostate cancer report a family history, which may develop not only because of shared genes but also for a similar pattern of exposure to certain environmental carcinogens and common lifestyle habits . Several studies reported that inherited genetic background is associated with increased risk for prostate cancer, contributing to about 5% of disease risks . Particularly, this risk is increased by several folds when high-penetrance genetic âriskâ alleles are inherited, conversely to more common low-penetrance loci that increase the risk only modestly.
The X chromosome is also believed to have a role in prostate cancer inheritance, because it contains the androgen receptor and because small deletions in Xq26.3-q27.3 region were noted in sporadic and hereditary forms of prostate cancer . More recent studies in 301 hereditary prostate cancer affected families defined a number of other loci that may contribute to hereditary prostate cancer .
Trends Of Cause Of Death Among Pca Patients By Time After Cancer Diagnosis
Non-cancer deaths accounted for the highest proportion of deaths throughout the follow-up period. As the follow-up time increased, the proportion of deaths from PCa gradually decreased, and the proportion of non-cancer deaths gradually increased. Beginning in the second year after diagnosis, the gap in the proportion of PCa-specific deaths and non-cancer deaths continued to widen . After the 10th year, non-cancer deaths accounted for 67.1% of all deaths, which was four times that of PCa-specific deaths . The cumulative mortality rate of the index cancer and non-index cancer increased slowly by time after diagnosis. The 5-year and 10-year CMRs of index cancer were 8.1% and 13.5%, respectively. The 5-year and 10-year CMRs of non-index cancer were 3.2% and 7.7%, separately. In contrast, the CMR of non-cancer causes increased rapidly, and the 5-year and 10-year CMR were 10.7% and 23.9%, respectively .
Figure 4 Cumulative mortality rate by time after diagnosis.
The SMRs of non-cancer deaths increased with prolonged survival time, and it was highest more than 10 years after diagnosis, with an SMR of 2.98 . This increasing trend was observed for most causes of death and was highest for Alzheimers disease. However, the SMRs of suicide and gastroduodenal ulcer death were significantly higher in the first year after diagnosis than 15 years after diagnosis .
Don’t Miss: What Can You Do To Help Prevent Prostate Cancer
Mens Health Month: Prostate Cancer Second Leading Cause Of Cancer Death
BOWLING GREEN, Ky. – June is Mens Health Awareness Month and this week WBKO News is focusing on prostate health. We spoke with Dr. Grover C. Dils, a doctor of internal medicine at Med Center Health and the StayWell Clinic.
Dr. Dils says maintaining screenings and keeping in check with your prostate health is importance for diagnosing conditions early and treating them quickly. Dr. Dils says the typical age to start prostate exams is 55, but for some ethnic groups that age may be lower.
Men are going to be screened usually starting at age 55. If theres not any risk factors. African American and Scandinavian heritage have increased risk factors for prostate cancer and they should start screening at age 45. About one to nine men will get prostate cancer, said Dr. Dils.
Larger majority of men will get problems with enlargement of the prostate, up even 50% and theyll have symptoms, said Dr. Dils.
Dr. Dils described the symptoms of an enlarged prostate and an infection of the prostate, Difficulty initiating a urine stream, having to urinate more frequently, a decrease in the stream. They need to get up at night to urinate more frequently. Those are probably the most common symptoms youll see. If you have an infection of the prostate, which can cause similar symptoms. Youre usually also may have fever, develop pain in your back, said Dr. Dils.
Chronic Inflammation And Prostatitis
There is a strong link between prostate cancer and inflammation, and in 1863, Rudolf Virchow was the first to identify the high density of leukocytes in neoplastic samples, suggesting a positive association between inflammation and cancer . After that, both epidemiological and biological studies provided evidence that inflammation is behind the high-grade or aggressive prostate tumors and ultimately metastatic spread . The evidence-based knowledge so far supports the role of inflammatory responses in the regulation of tumor microenvironment through the remodeling of the extracellular matrix and initiation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition . Indeed, inflammatory cells release growth factors and cytokines within the tumor microenvironment to promote angiogenesis and remodeling of the ECM, while further inflammatory cytokines released within the reactive stroma induce EMT-mediated responses .
Patients with elevated PSA often present with intraprostatic inflammation detected with biopsies . Recently, an inflammatory effector, pentraxin 3, has been identified as a biomarker for predicting tumor progression due to prostatic inflammation in prostate cancer patients .
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland that is hard to diagnose because it is often asymptomatic . Notably, men with symptoms of prostatitis are more likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer as a result of the increased prevalence of biopsy .
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Infection
What Were The Leading Causes Of Cancer Death In 2020
Lung cancer was the leading cause of cancer death, accounting for 23% of all cancer deaths. Other common causes of cancer death were cancers of the colon and rectum , pancreas , female breast , prostate , and liver and intrahepatic bile duct . Other cancers individually accounted for less than 5% of cancer deaths.
In 2020
- 136,084 people died of lung cancer .
- 51,869 people died of colorectal cancer .
- 46,774 people died of pancreatic cancer .
- 42,275 females died of breast cancer.
- 32,707 males died of prostate cancer.
- 28,227 people died of liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer .
NOTES: Deaths were classified using the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision. Cancer deaths were identified using underlying cause-of-death codes C00-C97 .
National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, Mortality Data.
Causes Of Death Among Prostate Cancer Patients Aged 40 Years And Older In The United States
- 1Department of Urology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Purpose: Little is known about the detailed spectrum of the cause of death associated with prostate cancer . This study systematically characterized the cause of death among patients with PCa.
Methods: Patients aged 40 years and older with primary PCa were identified from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program. Mortality rates were estimated. Standardized mortality ratios of non-cancer deaths were calculated to evaluate the risk of death and to compare with the cancer-free population.
Results: This study included 1,170,489 patients with PCa. There were 501,262 deaths, of which 27.4% were due to PCa and 57.0% were due to non-cancer causes. Non-cancer deaths increased over time from 1975 to 2016, and index cancer death decreased continually. The risk of non-cancer deaths was 1.45 times that of the general population. Cardiovascular disease was the most common non-cancer cause of death, accounting for 30.2% of all deaths among PCa patients. Alzheimers disease had the highest risk of death. The mortality rate and SMR of non-cancer deaths increased with increased follow-up after diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Does Swollen Prostate Cause Ed
More Men Die With Prostate Cancer Than Because Of It
Prevalence of autopsy-detected prostate cancer is 21% across all ages.
-
There is no significant difference between 21st century studies and earlier studies.
-
Autopsy-detected incidental prostate cancers are typically small, low grade, and only occasionally locally advanced or metastatic.
-
Prostate cancer prevalence increases with age, and is detected in over half of men aged 90 years.
-
The frequency of high-grade prostate cancer doubles with each increasing 10-year age category.
> > > This Simple Morning Test Will Fix Your Prostate
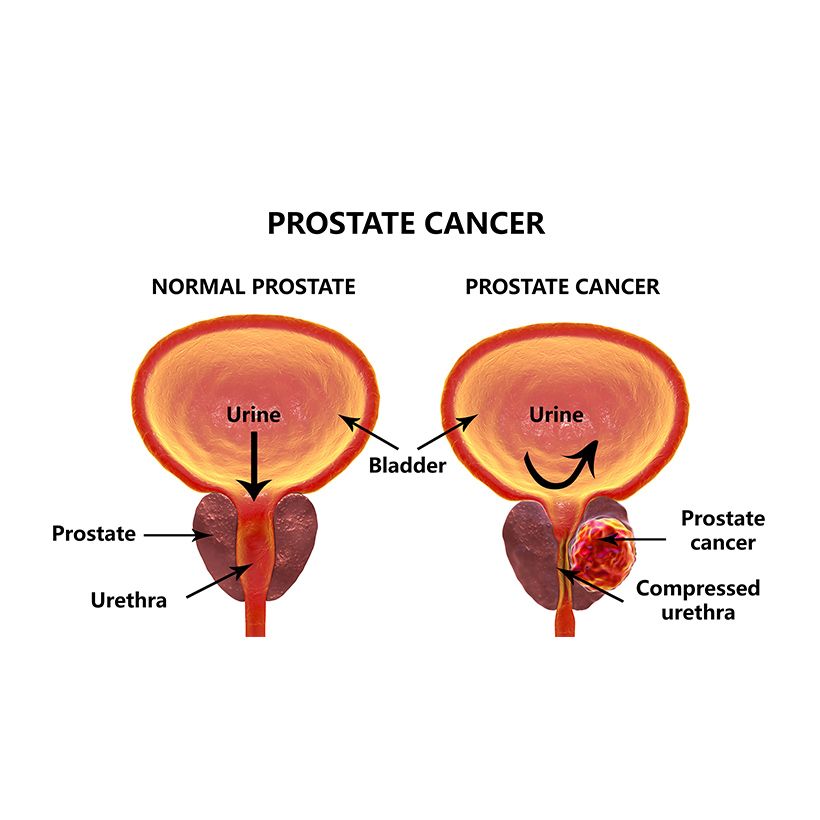
Another type of prostate issue is chronic prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This condition causes pain in the lower back and groin area, and may cause urinary retention. Symptoms include leaking and discomfort. In severe cases, a catheter may be required to relieve the symptoms. If the problem is unresponsive to other treatments, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure. If these do not work, your symptoms could progress and become chronic.
An acute bacterial infection can cause a burning sensation. Inflammation of the prostate can affect the bladder and result in discomfort and other symptoms. This is the most common urinary tract problem in men under 50, and the third most common in men over 65. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of CPPS. Patients may experience a fever or chills as a result of the infection.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Function Of Prostate Gland In Human Body
Us Cancer Statistics Data Visualizations Tool
The Data Visualizations tool makes it easy for anyone to explore and use the latest official federal government cancer data from United States Cancer Statistics. It includes the latest cancer data covering the U.S. population.
See how the rates of new prostate cancers or prostate cancer deaths changed over time for the entire United States and individual states.Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website’s privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance on other federal or private website.
Diagnostic Radiologic Procedure And Ultraviolet Light Exposure
The radiation generated from X-ray, CT and nuclear imaging is ionizing radiation that penetrates the tissue to reveal the bodyâs internal organs. However, ionizing radiation can damage DNA, and although cells repair most of the damage, sometimes small area may remain altered consequently leading to DNA mutations that may contribute to cancer development years down the road. The first study investigating the connection between low-dose ionization radiation from diagnostic X-ray procedures and risk for prostate cancer reported that exposure to a hip/pelvic X-ray significantly increased prostate cancer risk independently of other known risk factors such as family history of cancer . However, unless men were exposed to high doses of radiation during cancer treatment in youth, any increase in the risk for cancer due to medical radiation appears to be slight. Considering that the increase in high-dose imaging has occurred only since 1980 and the effects of radiation damage typically take many years to appear, this may explain the weak association between ionizing radiation and prostate cancer risk observed thus far.
Finally, exposure to solar UV radiation is inversely associated with both the incidence and mortality of prostate cancer . The biological explanation of this fact is based on the synthesis and physiological actions of vitamin D .
Also Check: What Is The Best Cure For Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer: Second Leading Cause Of Cancer Death In American Men September 9 2021
According to the American Cancer Society, prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in American men, behind lung cancer. About one man in 41 will die of prostate cancer.
This year the American Cancer Society has estimated there will be about 248,530 new cases of prostate cancer and about 34,130 deaths from prostate cancer in the United States.
Prostate cancer is rare in men younger than 40, but the chance of having prostate cancer increases significantly after age 50, especially in African American men or those with a family history of prostate cancer, explained ARH Oncologist Mohamed Shanshal, MD.
The American Cancer Society recommends these screening guidelines:
- Age 50 for men who are at average risk of prostate cancer and are expected to live at least 10 more years.
- Age 45 for men at high risk of developing prostate cancer. This includes African Americans and men who have a first-degree relative diagnosed with prostate cancer at an early age .
- Age 40 for men at even higher risk .
According to the guidelines from U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, having a father or brother with prostate cancer more than doubles a mans risk of developing this disease. The risk is much higher for men with several affected relatives, particularly if their relatives were young when the cancer was found.
Myth: Prostate Cancer Is For Older Men
Fact: While its true that the majority of men diagnosed with prostate cancer are older, it can strike younger men, too. About 40 percent of all cases occur in men younger than 65, according to the ACS. Its not uncommon at all for men in their fifties and some in their forties to have prostate cancer, says Sartor.
The exact age you should start getting regularly screened for prostate cancer is still an area of confusion and debate. At least start talking to your doctor about PSA testing once youre 50 years old, the ACS recommends. The exception to this is if the disease runs in your family, in which case its a good idea to start PSA screening earlier, at age 40 or 45.
Read Also: How Do You Die From Prostate Cancer
