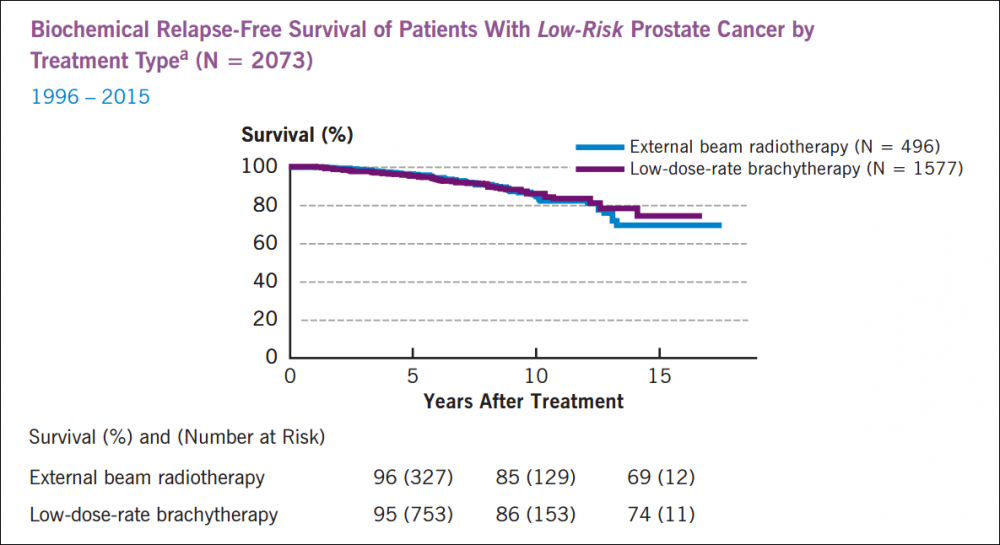
Prostate Cancer Survival By Age
Five-year survival for prostate cancer shows an unusual pattern with age: survival gradually increases from 91% in men aged 15-49 and peaks at 94% in 60-69 year olds survival falls thereafter, reaching its lowest point of 66% in 80-99 year olds patients diagnosed with prostate cancer in England during 2009-2013. The higher survival in men in their sixties is likely to be associated with higher rates of PSA testing in this age group.
Prostate Cancer , Five-Year Net Survival by Age, Men, England, 2009-2013
Be Careful With Saturated Fat
This is essential dietary advice if we want to counter inflammation. Saturated fat converts into inflammatory cytokines in the body. Thats why high-fat diets link with more aggressive diseases. We recommend consuming low-fat dairy, avoiding red meat fat, and healthier cooking methods different from frying.
Prostatecancer Survival Rates Are Favorable Overall
Throughout the article, we have mentioned that prostate cancer is not as bad as other cancer types. Actually, the fact that prostate cancer is diagnosed in seniors contributes to its survival rate. To understand this, lets have an example.
Lets say that a male patient is diagnosed with prostate cancer at 74 years. He has urinary symptoms such as nocturia and weak urinary flow at the moment of the diagnosis. Other than that, he has no signs. Cancer is confined to the prostate and growing very slowly in follow-up exams. There is no reason to treat prostate cancer aggressively, and this man dies 6 years later. Prostate cancer did not play a significant role in his death.
This case is more common than we think. To measure what to expect of cancer, theres something called survival rate. Researchers take a group of patients and follow them up year after year. Then, they write down statistics of life expectancy after the diagnosis. They would only record prostate cancer-related deaths. So, our example above was not included in the statistics because he didnt die from cancer-related causes.
In the case of prostate cancer, the survival rate is higher than other types of cancer.
According to statistics, 92% of cases are diagnosed at an early stage. They are localized prostate cancer or have a regional and minimal spread. Almost all of them are still alive 5 years after the diagnosis is made. But what about 10 years or 15 years?
Also Check: The Etiology Of Prostate Cancer Is:
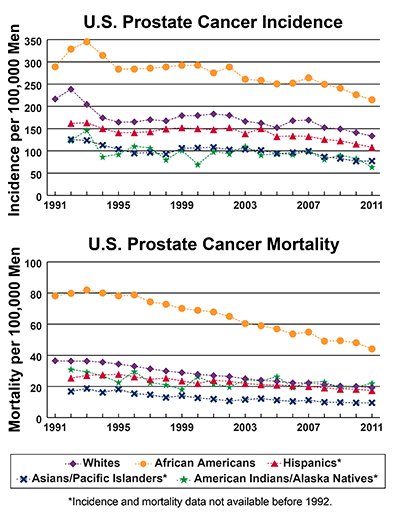
Prostate Cancer Incidence And Mortality
Trends in US incidence and mortality rates for black and white Americans from 1975 to 2008 are shown in Figure 1 . Approximately 10% of the American population is black or African American. The overall American male prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates closely follow that of white men.
Prostate cancer incidence and mortality . Age-adjusted prostate cancer incidence and mortality rates per 100 000 for black and white Americans as measured in the National Cancer Institute Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results program. Overall US male rates are very similar to US white rates. Data is age-adjusted to the year 2000 population standard.
The incidence rate rose approximately 2% per year from 1975 into the late 1980s. This trend was caused by incidentally detected disease associated with the increased use of transurethral resection of prostate for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia . TURP-detected cancers were half of all detected cancers in the mid-1980s, but the proportion of TURP-detected tumors fell off as the use of the procedure declined .
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Cancer staging is first described using what is called a TNM system. The “T” refers to a description of the size or extent of the primary, or original, tumor. “N” describes the presence or absence of, and extent of spread of cancer to lymph nodes that may be nearby or further from the original tumor. “M” describes the presence or absence of metastases — usually distant areas elsewhere in the body other than regional lymph nodes to which cancer has spread. Cancers with specific TNM characteristics are then grouped into stages, and the stages are then assigned Roman numerals with the numerals used in increasing order as the extent of the cancer being staged increases or the cancer prognosis worsens. Prognosis is finally reflected by considering the patient’s PSA score at presentation as well as their Gleason score in assigning a final stage designation.
The American Joint Commission on Cancer system for prostate cancer staging is as follows:
The primary tumor
Traditionally, advanced prostate cancer was defined as a disease that had widely metastasized beyond the prostate, the surrounding tissue, and the pelvic lymph nodes and was incurable. However, a more contemporary definition includes patients with the lower-grade disease with an increased risk of progression and/or death from prostate cancer in addition to those with widely metastatic disease.
CT scan is used for the initial staging in select patients including
The regional lymph nodes
The distant metastasis
Also Check: What Is Stage 9 Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
The only well-established risk factors for prostate cancer are age, race/ethnicity, and family history of the disease. In the United States, history of screening has become a risk factor for diagnosis.
Age
Prostate cancer is primarily a disease of older men. Over the last 30 years, there has been a trend toward a larger number of younger men being diagnosed. Prior to the PSA screening era, the median age at diagnosis was 70 years. The median age at diagnosis over the past decade was 67 years. The incidence rate in 2005 relative to 1986 was 0.56 in men aged 80 years and older, 1.09 in men aged 7079 years, 1.91 in men aged 6069 years, 3.64 in men aged 5059 years, and 7.23 in men younger than age 50 years .
In 2005, less then 10% of men diagnosed in the United States were less than 55 years old. Approximately one-third were aged 5564 years, another third were aged 6574, and nearly one-fourth of all men diagnosed were aged 75 years or older.
The age distribution of men diagnosed during the period 20032008 is shown in Table 2. Age-specific incidence and mortality rates for black and white Americans are shown in Figure 2. Risk of diagnosis goes down dramatically after age 80, but risk of prostate cancer death increases throughout adult life.
Age-specific incidence and mortality rates for black and white American men as measured in the National Cancer Institute Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results program for diagnosis or death between 2003 and 2007.
Screening
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates: What They Mean
As cancer diagnoses go, prostate cancer is often a less serious one. Prostate cancer is frequently slow-growing and slow to spread. For many men, prostate cancer is less serious than their other medical conditions.
For these reasons, and possibly because of earlier detection of low-grade prostate cancers, prostate cancer has one of the highest survival rates of any type of cancer. WebMD takes a look at prostate cancer survival rates and what they mean to you.
Recommended Reading: Is Peanut Good For Prostate
Prostate Cancer Survival Rates: Prognosis And Risk Factors
The word cancer has horrible connotations, and it is probably the worst diagnosis one can get.
We immediately think of chemotherapy, losing hair, metastasis, and pain. But the aggressiveness of cancer depends on different factors. One of them is the type and location of the primary tumor. The other has to do with the patient, his comorbidities, and his risk factors.
In many cases, prostate cancer is not a life-threatening diagnosis. In this location, most cancer cells grow very slowly and do not frequently spread.
As technology improves, we can now detect more low-grade prostate cancer cases from an initial stage. Thus, the survival rate of this type of cancer is higher than others. However, we shouldnt neglect prostate cancer. There will always be a patient with an aggressive type.
In this article, were reviewing prostate cancer survival rates, patient prognosis, and risk factors. How dangerous is prostate cancer? What makes the disease more aggressive? How can you reduce your risk?
What Can Affect My Outlook
No one can tell you exactly what will happen. How prostate cancer affects you will depend on many things.
- Your stage Whether your cancer is localised, locally advanced, or advanced.
- Your Gleason score or grade group The higher your Gleason score, the more aggressive the cancer, and the more likely it is to spread.
- Your treatment options You may be able to have treatment aimed at getting rid of the cancer. Or you may be able to have treatment to keep the cancer under control. Read more about choosing your treatment.
- Your health If you have other health problems, you may have fewer treatment options. And you may be more likely to die from another condition, such as heart disease.
- Your PSA level After youve been diagnosed, PSA tests are a good way of monitoring your prostate cancer and seeing how youre responding to treatment.
- How successful your treatment is Your treatment may be successful at getting rid of your cancer or keeping it under control. But for some men, treatment may not work as well as expected.
Don’t Miss: How To Shrink Your Prostate
National Cost Of Prostate Cancer Care
The estimated cost of prostate cancer in 2020 was $22.3 million dollars, according to the NCI.
- The estimated cost of prescription drugs for prostate cancer in 2020 was $1.7 million, according to the NCI.
- In 2020, the estimated cost of treating prostate cancer in a person at the initial stage of their diagnosis was just over $28,000, according to the NCI. The cost of continued care is $2,602, and the cost during the last year of life is about $74,000.
- In 2020, the estimated cost for a person’s oral prescription medication for prostate cancer was $312 at the initial diagnosis, according to the NCI. The costs for continued medication was also $312 per person. During the last year of life, the cost of prescription medication is estimated to be $5,800.
Outlook For Men With Localised Prostate Cancer
Most localised prostate cancer is slow-growing and may not need treatment or shorten a mans life. For many men who have treatment for localised prostate cancer, the treatment will get rid of the cancer. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment.
Read Also: What Is The Best Prostate Supplement On The Market
What Are Prostate Cancer Survival Rates By Stage
Staging evaluation is essential for the planning of treatment for prostate cancer.
- A basic staging evaluation includes the patient examination, blood tests, and the prostate biopsy including ultrasound images of the prostate.
- Further testing and calculations may be performed to best estimate a patient’s prognosis and help the doctor and patient decide upon treatment options.
Prognosis refers to the likelihood that cancer can be cured by treatment, and what the patient’s life expectancy is likely to be as a consequence of having had a prostate cancer diagnosis.
If cancer is cured, your life expectancy is what it would have been had you never been diagnosed with prostate cancer. If cancer cannot be cured due to it recurring in distant locations as metastases, or recurs either locally or in an area no longer able to be treated in a curative manner, then estimates can be made of what is likely to be your survival-based again on group statistics for people who have been in the same situation.
Nomograms are charts or computer-based tools that use complex math from the analysis of many patients’ treatment results.
The prognosis for prostate cancer varies widely and depends on many factors, including the age and health of the patient, the stage of the tumor when it was diagnosed, the aggressiveness of the tumor, and cancer’s responsiveness to treatment, among other factors.
The 5 and 10-year survival rate of prostate cancer chart
| Stage and 5-Year Survival |
|---|
Staging Of Prostate Cancer
- Stage I : The Gleason score is 6 or less, and the PSA level is less than 10. Cancer at this stage is normally not detectable in an ultrasound test or in a DRE test, as the tumor is very small. It is within the prostate and has not spread to nearby lymph nodes. It is usually discovered accidentally during a surgery carried out for another purpose. Prostate ultrasound and biopsy can be performed after detection of elevated blood PSA levels.
- Stage II : From this stage onwards, the Gleason score and the PSA level may vary from person to person. As the tumor grows in size, it can be detected in a DRE test or sonogram, but the tumor is still confined to the prostate gland. It is in one half or less of only one side of the prostate. It hasnt spread to lymph nodes and nearby organs, or it has spread to nearby lymph nodes, but has not invaded nearby organs.
- Stage III : The cancerous cells spread out from the original site and invade the seminal vesicles. They do not spread to nearby lymph nodes or to nearby organs in the body.
- Stage IV : The cancer moves out of the seminal vesicles and invades the lymph nodes. The size and number of tumors increase, and the cancerous cells spread into the nearby organs, such as the bladder and the rectum. In stage four prostate cancer, even bones and other parts of the body like lungs and liver are likely to be invaded by the cancerous cells.
You May Like: Does Super Beta Prostate Work
What Are Next Steps
Bone metastasis have a profound effect on the long-term outlook for prostate cancer. But its important to remember that the numbers are only statistics.
The good news is that life expectancy for advanced prostate cancer continues to increase. New treatments and therapies offer both longer life and better quality of life. Speak to your doctor about your treatment options and long-term outlook.
Everyones cancer experience is different. You may find support through sharing your treatment plan with friends and family. Or you can turn to local community groups or online forums like Male Care for advice and reassurance.
Survival Rates For Prostate Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. These rates cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Ask your doctor, who is familiar with your situation, how these numbers may apply to you.
You May Like: How To Diagnose An Enlarged Prostate
Survival By Disease Progression
The extent prostate cancer has progressed can influence survival rates.
Prostate-specific antigen is a protein produced by cells of the prostate gland by normal and malignant cells. In men with prostate cancer, blood levels of PSA are often elevated.
Doctors can use PSA as a marker to better understand the progression of prostate cancer and the resulting prognosis.
One way doctors assess the progression of the disease is through PSA doubling time. This refers to the number of months it takes for PSA to double.
One study suggests a short doubling time means a poorer prognosis for patients with stage IV prostate cancer. Median survival was 16.5 months for those with a PSA doubling time lower than 45 days compared with 26 months for patients with a longer PSA doubling time.
Whether or not the cancer has metastasized and spread to other areas of the body outside the prostate can also influence survival. In distant or stage IV prostate cancer, when cancer has spread from the prostate to other organs like the liver or lungs, the five-year survival rate is 31% compared with localized cancer, which has a five-year survival rate of nearly 100%.
Cause Of Increasing Incidence
We have considered several possible explanations for the increasing incidence, including improved recognition , screening practices, overdiagnosis, racial/ethnic shifts, societal factors, exogenous carcinogenic exposures, and increasing obesity among AYAs.
Improved recognition
Because prostate cancer originally was rarely considered in a young male, it may not have been recognized previously and thus was underdiagnosed. The increased incidence could have resulted from the increased implementation of diagnostic methodologies, including those for genomic predisposition syndromes. Figure C suggests a degree of underdiagnosis in that the youngest men have the higher proportion of metastatic disease at diagnosis. There may have been delays because of underdiagnosis that allowed the cancer ultimately to present with signs and/or symptoms of metastases. That these patients also had the highest proportion of unstaged disease may have been because of underdiagnosis related to less comprehensive workup and understaging. The increasing capability to detect and diagnose prostate cancer in young men is consistent with the observation that nearly all of the increase was of earlier stage disease rather than late-stage disease with distant metastases.
Prostate-specific antigen screening
Figure 7Am J Clin Pathol
Overdiagnosis
Human papillomavirus
Racial, ethnic, and familial factors
Environmental carcinogens
Obesity
Exercise
Societal factors
Read Also: How Quickly Does Prostate Cancer Spread
Prostate Cancer Prognosis And Survival Rates
Prostate cancer is the most common non-skin cancer affecting men in the United States. While this statistic is striking, the prognosis for prostate cancer is among the best of all cancers. Its important to remember that survival rates for prostate cancer arent set in stone as each person responds differently to treatment.
