Why Are Prostate Biopsies Done
To learn about the health of your prostate, your doctor may ask questions about your medical and family history and conduct a physical examination known as a digital rectal exam . You also may require a PSA blood test. PSA stands for prostate-specific antigen, a type of protein the prostate produces. Certain PSA levels may indicate that something is abnormal within the prostate.
If PSA results are abnormal, a prostate biopsy may be ordered. In general terms, a biopsy is a medical test that involves extracting cells or tissue from a part of the body to look for the presence of disease. In the case of a prostate biopsy, prostate tissue from the prostate gland is removed and examined under a microscope by a pathologist. Its an important procedure because only a biopsy can definitively diagnose prostate cancer. The PSA blood test and DRE are only indicators that cancer may be present.
What Is A Biopsy And How Effective Is It
A needle biopsy is the only way to diagnose prostate cancer when it is suspected. But there are problems with the method most commonly used, called transrectal ultrasound guided biopsy. These problems often lead to inaccurate diagnosis.
For the last two decades, TRUS biopsy has been used to diagnose prostate malignancy. It is actually a blind and random procedure. Specific prostate tumors, especially very small ones, cannot be identified because ultrasound cannot visually detect specific cancer sites. Therefore, it is blind to tumors. In addition, TRUS biopsies tend to target the peripheral aspects of the gland and are likely to miss 30-40% of prostate cancer located in the anterior, midline transition zone, or apex. This is called sampling error. To attempt to overcome it, TRUS biopsies typically average 12-14 needles saturation biopsies use as many as 24 needles. The more needles used, the greater the risk of discomfort, infection, and urinary or sexual side effects while tumors continued to be missed. No other type of tumor cancer is biopsied this way!
Who Should Have Focal Therapy
Candidates for focal therapy must be carefully selected, most often based on well-performed, image-guided biopsy techniques . Patients with intermediate-grade tumors visible in a single location on imaging may be considered for focal therapy. Low-grade cancers can be treated this way but are usually more suitable for active surveillance. Some doctors feel that cancer close to the urethra can also be treated in this fashion, but there may be a higher risk of side effects or incomplete treatment. Some feel that additional candidates for focal therapy include patients with one dominant tumor as described above and a microfocus of low-grade disease elsewhere. These smaller cancer foci are followed through active surveillance.
Results of ablation therapies to date have been favorable, but the experience and time of follow-up are still limited. In addition, these patients must be evaluated carefully to avoid undertreating their cancer, and after treatment, they need to have periodic imaging, PSA assessment and at least one follow-up biopsy.
You May Like: Does Ejaculation Help Enlarged Prostate
Isnt A Psa Test Enough
The prostate specific antigen test is a common screening test for prostate cancer. PSA is a protein that comes from the prostate gland. The test measures the amount of PSA in your blood. Its a simple blood test, and for some men, it turns out to be a lifesaver.
On the other hand, its value as a diagnostic tool is fairly limited. High PSA levels may be a sign of prostate cancer, but its not enough to diagnose the disease with certainty. Thats because there are other reasons your PSA levels could be high, including urinary tract infection and inflammation of the prostate.
Read more: PSA levels and prostate cancer staging »
Also, a single abnormally high PSA test result cant tell you if the high level is temporary or rising over time.
Low PSA levels cannot definitively rule out prostate cancer, either. The fact is that PSA tests can result in both false positives and false negatives.
PSA tests can be useful during and after treatment for prostate cancer. Rising PSA levels may signal that treatment is not effective or there is a recurrence of the cancer. If your PSA levels are decreasing, your current treatment is probably doing its job.
What Side Effects Can A Prostate Biopsy Have
The possibly low rate of success in prostate biopsies is not the only concern with the procedure.
Patients have raised other concerns when they undergo this diagnostic procedure as well. This would, of course, include the potential side-effects that may occur.
Individuals suspected of prostate cancer need to realize what to expect with any advised procedure. This includes the use of a prostate biopsy to detect cancer cells in their prostate glands.
Certain risks have been associated with a prostate biopsy. Most of these risks are considered mild.
There are, however, a couple of risks that need to be taken more seriously. These risks may lead to more significant damage. The complications can also sometimes become more severe.
Also Check: Can You Remove Entire Prostate
Getting A Prostate Biopsy
For some men, getting a prostate biopsy might be the best option, especially if the initial PSA level is high. A biopsy is a procedure in which small samples of the prostate are removed and then looked at under a microscope. This test is the only way to know for sure if a man has prostate cancer. If prostate cancer is found on a biopsy, this test can also help tell how likely it is that the cancer will grow and spread quickly.
For more details on the prostate biopsy and how it is done, see Tests to Diagnose and Stage Prostate Cancer.
For more information about the possible results of a prostate biopsy, see the Prostate Pathology section of our website.
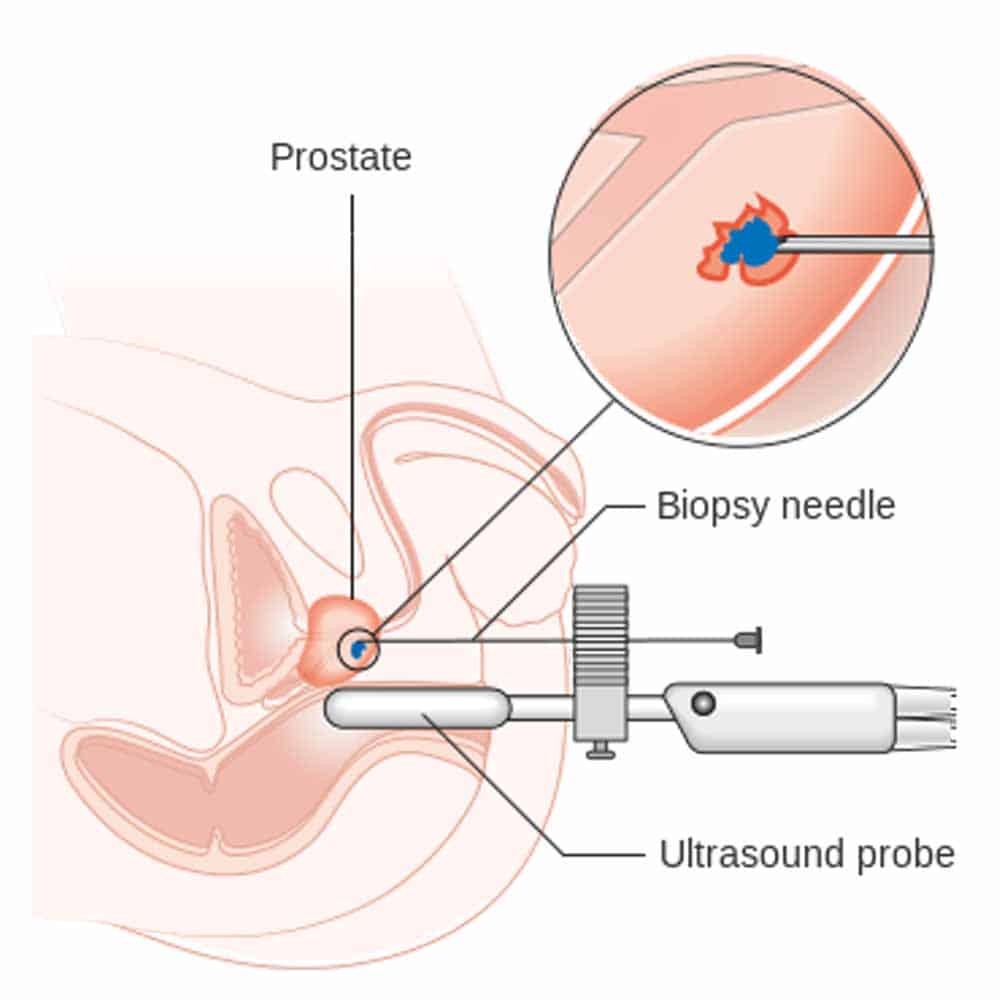
Whats The Purpose Of A Transrectal Ultrasound
A transrectal ultrasound is a procedure that produces an image of the prostate. Its usually ordered after an abnormal PSA and DRE. For the test, a small probe is inserted into the rectum. The probe then uses sound waves to produce a picture on a computer screen.
The test is uncomfortable, but not painful. It can be done in your doctors office or on an outpatient basis in about 10 minutes. It can help estimate the size of the prostate and spot abnormalities that may indicate cancer. However, a TRUS cant confirm the diagnosis of prostate cancer.
A TRUS can also be used to guide a biopsy.
Also Check: Can You Milk Your Prostate
Use In Men Already Diagnosed With Prostate Cancer
The PSA test can also be useful if you have already been diagnosed with prostate cancer.
- In men just diagnosed with prostate cancer, the PSA level can be used together with physical exam results and tumor grade to help decide if other tests are needed.
- The PSA level is used to help determine the stage of your cancer. This can affect your treatment options, since some treatments are not likely to be helpful if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- PSA tests are often an important part of determining how well treatment is working, as well as in watching for a possible recurrence of the cancer after treatment .
Screening Tests For Prostate Cancer
Screening is testing to find cancer in people before they have symptoms. Its not clear, however, if the benefits of prostate cancer screening outweigh the risks for most men. Still, after discussing the pros and cons of screening with their doctors, some men might reasonably choose to be screened.
The screening tests discussed here are used to look for possible signs of prostate cancer. But these tests cant tell for sure if you have cancer. If the result of one of these tests is abnormal, you will probably need a prostate biopsy to know for sure if you have cancer.
Don’t Miss: Can Enlarged Prostate Cause Blood Clots In Urine
What Is Free Psa
The routine PSA test measures total PSA in your blood. But there are two types of PSA. Bound PSA is attached to a protein. Free PSA is not. The free PSA test breaks the results down and provides your doctor with a ratio. Men with prostate cancer tend to have lower levels of free PSA than men who dont have prostate cancer.
Its a simple blood test, but theres no consensus among doctors on the ideal ratio of free to bound PSA. The free PSA test is valuable in that it gathers more information, which can help in the biopsy decision.
On its own, the free PSA test cant confirm or rule out a prostate cancer diagnosis.
What To Watch For Afterward
Here are the most common complications of prostate biopsy:
- Blood in your urine for a few days to several weeks.
- Blood in the stool for a day or so. If it lasts longer, notify your physician.
Make sure to notify your doctor if rectal or urinary bleeding get worse. Also, be on guard in the first 24 to 48 hours for signs of a serious infection in the urinary tract or prostate gland. “The alarm signs are fever or chills,” Dr. Garnick says. “If you experience this, get to a hospital immediately for intravenous antibiotics.” A runaway infection can be dangerous, so don’t ignore the signs.
Another uncommon but dangerous complication is urinary retentionthe inability to pass urine caused by an infection. Seek care immediately if you stop being able to urinate after a biopsy.
Image: Alex011973/Getty Images
Recommended Reading: What Is The Survival Rate Of Metastatic Prostate Cancer
What Is An Mri
What makes an MRI different from other medical imaging techniques like X-rays and CT scans?
X-rays take projection images of hard tissues like bones, while CT scans take images of both hard bony tissues and soft tissue. Both systems use ionizing radiation, which passes through the body to create images that are transferred to photographic film or to a video monitor.
An MRI works differently. Magnetic resonance imaging uses a magnetic field to create sound waves that are received, digitized, and displayed in real-time. When tissue is abnormal, its composition changes, so the images reflect damaged areas.
How To Get The Best Results
Most men do not find prostate biopsy excessively painful or uncomfortable, and the complications are usually not seriousbut can be. Certain steps taken before, during, and after the procedure can improve the outcome:
Take antibiotics. Taking preventive antibioticsbefore and after the procedurecuts the risk of infection substantially. Most infections are not dangerous but could become so if they get out of control. The overall chance of being hospitalized with an infection after prostate biopsy is 1% to 3%.
Review medications. Before the biopsy, your doctor may advise you to stop taking daily low-dose aspirin or an anticoagulant such as warfarin , dabigatran , edoxaban , rivaroxaban , or apixaban . These drugs reduce the blood’s ability to clot. Your doctor will weigh the chance of bleeding against the need for anticoagulants to prevent heart problems or stroke.
Expect anesthesia. Get local anesthesia for the biopsy. This means an injection of a numbing drug into the prostate gland to reduce pain during the biopsy.
Also Check: How To Train Your Bladder After Prostate Surgery
Take The Next Step Today
Request your free consultation with Dr. Sperling and well work together to create the best diagnostic plan for you.
NOTE: This content is solely for purposes of information and does not substitute for diagnostic or medical advice. Talk to your doctor if you are experiencing pelvic pain, or have any other health concerns or questions of a personal medical nature.
Prince M, Foster BR, Kaempf A, Liu JJ et al. In-Bore Versus Fusion MRI-Targeted Prostate Biopsy of PI-RADS Category 4 or 5 Lesions: A Retrospective Comparative Analysis Using Propensity Score Weighting. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 Mar 1. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.25207. Online ahead of print.
Controversies And Misconceptions Surrounding Prostate Biopsies
The PSA test measures the levels of PSA proteins in the body, and when it was first developed, it was quickly implemented by many physicians as a screening test for prostate cancer. The thought was that since PSA proteins are only produced by the prostate, elevated levels could be an indication of prostate cancer. As a result, most men with an abnormal PSA test underwent a prostate biopsy.
The increase in biopsies resulted in the number of advanced, untreatable prostate cancers decreasing significantly because more prostate cancers were caught earlier, when the disease is easier to treat. But the problem with many patients being diagnosed sooner was that some patients were being aggressively treated when they should have been monitored instead.
Though many in the field of urology believe it was flawed, a controversial study attempted to assess the benefits of the PSA test as a screening tool for prostate cancer, and its results led to the recommendation that most men shouldn’t get the test because it didnt appear to improve mortality rates from prostate cancer. This, combined with growing awareness that many cases of prostate cancer were being treated unnecessarily or prematurely, led to a reduction in prostate biopsies. This controversy led to a reduction in prostate cancer screening and an increase in the number of diagnoses of advanced prostate cancer.
Read Also: Hormone Therapy Vs Radiation For Prostate Cancer
The Digital Rectal Exam
The prostate gland comprises three zones. Most cancers originate in the peripheral zone. Proctologists, urologists, and oncologists are trained to feel this area while performing a digital rectal exam .
Here, digital doesnt refer to technology. Instead, it refers to the fingers . In a DRE, your doctor inserts a well-lubricated gloved finger gently into the rectum to reach the prostate. Prostate enlargement and suspicious lesions may be felt during a DRE.
A Tough Path To The Clinic
Implementing this pre-biopsy testing in clinical practice may not yet be practical because of the limited availability of the T2:ERG test, Dr. Srivastava said.
But Dr. Sanda is hopeful that, based on the studys findings, that may change. Nevertheless, the situation demonstrates that even well-conducted, definitive biomarker studies are really just one step on the pathway to in clinical practice, he added.
This type of work is a key next step to further enhance the utility of urinary markers to refine detection of aggressive prostate cancer, Dr. Srivastava said.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Function Of Prostate Gland In Human Body
Imaging Tests For Prostate Cancer
Imaging tests use x-rays, magnetic fields, sound waves, or radioactive substances to create pictures of the inside of your body. One or more imaging tests might be used:
- To look for cancer in the prostate
- To help the doctor see the prostate during certain procedures
- To look for spread of prostate cancer to other parts of the body
Which tests you might need will depend on the situation. For example, a prostate biopsy is typically done with transrectal ultrasound and/or MRI to help guide the biopsy. If you are found to have prostate cancer, you might need imaging tests of other parts of your body to look for possible cancer spread.
The imaging tests used most often to look for prostate cancer spread include:
Can You Find Cancer Without A Biopsy
A biopsy takes tissue from your body to test it for cancer and other diseases. The procedure can also reveal important information about the type of a disease you have and how you should treat it.
You can find certain types of cancer without a biopsy. There are a few different ways to do this, depending on the type of cancer you have and how much it has grown.
You may have certain symptoms: You could have a bad cough if you have lung cancer or pee blood if you have bladder cancer. Your doctor may be able to find a mass in your breast or belly or prostate by examining you.
Doctors have other tools to help them decide if you have cancer. Two of the most common ones are:
- Biomarkers: Substances in your blood that could mean cancer
- Imaging: Pictures of the inside of your body that show lumps or growths
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Robotic Surgery Recovery
What Are The Side Effects Of A Biopsy
Having a biopsy can cause side effects. These will affect each man differently, and you may not get all of the possible side effects.
Pain or discomfort
Some men find the biopsy painful, but others have only slight discomfort. Your nurse or doctor may suggest taking mild pain-relieving drugs, such as paracetamol, to help with any pain.
If you have any pain or discomfort that doesnt go away, talk to your nurse or doctor.
Short-term bleeding
A small number of men who have a TRUS biopsy may have more serious bleeding in their urine or from their back passage . This can also happen if you have a transperineal biopsy but it isn’t very common. If you have severe bleeding or are passing lots of blood clots, this is not normal. Contact your doctor or nurse at the hospital straight away, or go to the accident and emergency department at the hospital.
Infection
Some men get an infection after their biopsy. This is more likely after a TRUS biopsy than after a transperineal biopsy. It’s very important to take any antibiotics youre given, as prescribed, to help prevent this. But you might still get an infection even if you take antibiotics.
Symptoms of a urine infection may include:
- pain or a burning feeling when you urinate
- dark or cloudy urine with a strong smell
- needing to urinate more often than usual
- pain in your lower abdomen .
If you have any of these symptoms, contact your doctor or nurse at the hospital straight away. If you cant get in touch with them, call your GP.
