More Information About Prostatitis
The following is an English-language resource that may be useful. Please note that THE MANUAL is not responsible for the content of this resource.
-
Prostatitis Foundation: This organization provides access to relevant publications , patient testimonials, a list of providers who treat prostatitis in the United States and the United Kingdom, and access to third-party prostatitis-based web sites in French, Swedish, and Italian.
Identifying Potential Prostate Problems
Touching Your Prostate With Your Finger
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Perineural Invasion
When Should You Call Your Doctor
if you have sudden fever, chills, and urinary symptoms, such as pain or burning with urination or blood or pus in the urine. These symptoms may point to acute prostatitis.
- Urinary symptoms and persistent pain in the low back, scrotum, penis, or the area between the scrotum and anus, or if you have pain with ejaculation or with a bowel movement.
- Recurring urinary tract infections .
- Discharge from your penis or sores on your genitals.
- Problems urinating, such as excessive nighttime urination, trouble starting urinating, decreased urinary stream, or frequent urination that isn’t related to drinking lots of fluids.
When To Get Medical Advice
See a GP if you have symptoms of prostatitis, such as pelvic pain, difficulty or pain when peeing, or painful ejaculation.
They’ll ask about the problems you’re having and examine your tummy.
You may also have a rectal examination. This is where a doctor inserts a gloved finger into your bottom to feel for anything unusual. You may have some discomfort during this examination if your prostate is swollen or tender.
Your urine will usually be tested for signs of infection, and you may be referred to a specialist for further tests to rule out other conditions.
See a GP straight away if you get sudden and severe symptoms of prostatitis.
You may have acute prostatitis, which needs to be assessed and treated quickly because it can cause serious problems, such as suddenly being unable to pee.
If you have persistent symptoms , you may be referred to a doctor who specialises in urinary problems .
Don’t Miss: How Long Can You Take Lupron For Prostate Cancer
> > > One Crazy Prostate Trick All Men Over 40 Should Try
Symptomatic treatment of an enlarged prostate usually involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may be the best option if you suffer from chronic urination. It will help the body adjust to the increased size of the prostate. Also, taking regular urination intervals will help retrain the bladder to function properly. Inactivity also contributes to urine retention, and cold temperatures can increase the urge to urinate.
Invasive treatment of enlarged prostate includes medication that relieves the pressure on the urethra and bladder. However, if the condition is severe, it may require surgical intervention. If treatment is not successful, the enlarged prostate can become a potentially life-threatening disease. As the hormone levels in the body change, the enlarged prostate can lead to various complications, including urinary retention and even cancer. This is why it is critical to see a doctor for further evaluation.
A physician can recommend a number of treatments to address an enlarged prostate. An enlarged prostate will require surgery to relieve the symptoms. In most cases, surgical treatment for an enlargement of the penis is enough. Moreover, a doctor may recommend a course of treatment based on symptoms. A TURP procedure is not painful and requires less recovery time than open surgery. The recovery period will be shorter and less traumatic.
Does Prostatitis Cause Cancer
Although prostatitis can cause you trouble, it does not cause cancer. There is a blood test some doctors use for prostate cancer called the prostate-specific antigen test . If you have prostatitis, your PSA level might go up. This does not mean you have cancer. Your doctor will treat your prostatitis and may check your PSA level again.
Read the full article.
- Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
- Choose a single article, issue, or full-access subscription.
- Earn up to 6 CME credits per issue.
You May Like: Is Cranberry Juice Good For The Prostate
Drugs To Treat Cancer Spread To Bone
If prostate cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it almost always goes to the bones first. These areas of cancer spread can cause pain and weak bones that might break. Medicines that can help strengthen the bones and lower the chance of fracture are bisphosphonates and denosumab. Sometimes, radiation, radiopharmaceuticals, or pain medicines are given for pain control.
Side effects of bone medicines
A serious side effect of bisphosphonates and denosumab is damage to the jaw, also called osteonecrosis of the jaw . Most people will need to get approval from their dentist before starting one of these drugs.
The Basics: How An Erection Occurs
At its most basic level, an erection is a matter of hydraulics. Blood fills the penis, causing it to swell and become firm. But getting to that stage requires extraordinary orchestration of body mechanisms. Blood vessels, nerves, hormones, and, of course, the psyche must work together. Problems with any one of these elements can diminish the quality of an erection or prevent it from happening altogether.
Nerves talk to each other by releasing nitric oxide and other chemical messengers. These messengers boost the production of other important chemicals, including cyclic guanosine monophosphate, prostaglandins, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide. These chemicals initiate the erection by relaxing the smooth muscle cells lining the tiny arteries that lead to the corpora cavernosa, a pair of flexible cylinders that run the length of the penis .
Figure 1: Anatomy of the penisThe penis is made up of three cylindrical bodies, the corpus spongiosum which contains the urethra and includes the glans of the penisand two corpora cavernosa , that extend from within the body out to the end of the penis to support erection. Blood enters the corpora cavernosa through the central arteries. |
Recommended Reading: How To Shrink Prostate Mayo Clinic Naturally
Infection By Germs That Normally Live In Your Bowel
This is the usual cause. Some bacteria that live harmlessly in the bowel commonly get on to the skin near to the anus when we pass stools . In some people they may then multiply. Some of these bacteria may then travel up the urethra and cause infection anywhere in the urinary tract – that is, the kidneys, bladder, prostate, or urethra. This is called a ‘urinary tract infection‘.
A prostate infection may also occur with or without other parts of the urinary tract being infected. Some conditions that cause pooling or blockage of urine increase the risk of a urinary tract infection. For example, having an enlarged prostate or kidney stones. This is because bacteria often thrive and multiply quickly in pooled urine.
Can Prostate Infections Make Me Infertile
Infections of the prostate can cause swelling and block off part of the reproductive passage that goes through the prostate. This can also stop sperm from being ejaculated.
Because the prostate and seminal vesicles create most of the fluid that you ejaculate, a blockage near the prostate can sometimes lower the amount of semen ejaculated. Infected cells can also be passed from the prostate and seminal vesicles into the semen, which can damage the sperm.
You May Like: Perineural Invasion Prostate Cancer Treatment
> > > This Simple Morning Test Will Fix Your Prostate
Another type of prostate issue is chronic prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome. This condition causes pain in the lower back and groin area, and may cause urinary retention. Symptoms include leaking and discomfort. In severe cases, a catheter may be required to relieve the symptoms. If the problem is unresponsive to other treatments, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure. If these do not work, your symptoms could progress and become chronic.
An acute bacterial infection can cause a burning sensation. Inflammation of the prostate can affect the bladder and result in discomfort and other symptoms. This is the most common urinary tract problem in men under 50, and the third most common in men over 65. The symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis are similar to those of CPPS. Patients may experience a fever or chills as a result of the infection.
A bacterial infection can also lead to prostate issues. Acute bacterial infections can be hard to treat. Some men with a bacterial infection may need to take antibiotics to prevent or treat symptoms. Symptoms of the disease include fever and chills, pain in the lower back and the tip of the penis. Some men may have blood in the urine, frequent urination, and blood in the urine. If you suffer from acute bacterial prostatitis, a medical professional should be able to prescribe you the appropriate treatments to prevent the disease.
What Is The Prognosis For A Prostate Infection
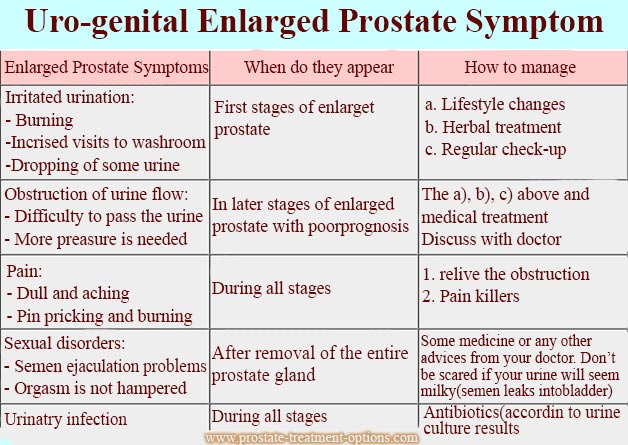
The prognosis for acute bacterial prostatic infections is usually good if treated appropriately with effective antibiotics. The prognosis for chronic bacterial prostatic infections is less or only fair because the recurrent disease is difficult to cure, and the cure rate is less than the acute type.
- No evidence suggests that any prostate infections increase the risk of urinalysis.
- Only a few men with acute bacterial prostatitis develop chronic bacterial prostatitis. After patients recover, their doctor should evaluate their upper urinary tract.
- Only half of the men with chronic bacterial prostatitis will be cured . Relapses are common and may lead to psychological problems, especially depression.
Also Check: Wellbutrin Ejaculation
Can Prostatitis Come Back
Men who have had prostatitis once are more likely to get it again. Antibiotics may not get into the prostate gland well. Small amounts of bacteria might hide in the prostate and not be killed by the antibiotic. Once you stop taking the antibiotic, the infection can get bad again. If this happens, you might have to take antibiotics for a long time to prevent another infection. Prostatitis that is not caused by infection is often chronic. If you have this kind of prostatitis, you might have to take medicine for a long time.
What Are Common Prostate Problems What Are The Symptoms And Signs
Here are some examples of non-cancer prostate problems:
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH, means your prostate is enlarged, but is not cancerous. It is very common in older men. An enlarged prostate may make it very difficult to urinate or cause dribbling after you urinate. You may feel the need to urinate a lot, often at night. See your family doctor for an exam. Treatments for BPH include:
- Watchful waiting, also called active surveillance. If your symptoms are not too bad, your doctor may tell you to wait before starting any treatment to see if the problem gets worse. Your doctor will tell you how often you need to return for checkups. You can start treatment later if your symptoms worsen.
- Medications. There are medicines that can help shrink the prostate or help relax muscles near your prostate to ease your symptoms. Talk with your doctor about possible side effects.
- Surgery. If nothing else has worked, your doctor may suggest surgery to help urine flow. There are many types of BPH surgery. Talk with your doctor about the risks. Regular checkups are important after surgery.
- Other treatments. Sometimes radio waves, microwaves, or lasers are used to treat urinary problems caused by BPH. These methods use different kinds of heat to reduce extra prostate tissue.
Don’t Miss: Fiducials Prostate Cancer
Acute Prostatitis: Causes Symptoms And Diagnosis
What is acute prostatitis?
Acute prostatitis happens when your prostate gland becomes suddenly inflamed. The prostate gland is a small, walnut-shaped organ located at the base of the bladder in men. It secretes fluid that nourishes your sperm. When you ejaculate, your prostate gland squeezes this fluid into your urethra. It makes up a large portion of your semen.
Acute prostatitis is usually caused by the same bacteria that cause urinary tract infections or sexually transmitted diseases . Bacteria can travel to your prostate from your blood. It can enter your prostate during or after a medical procedure, such as a biopsy. It can also be caused by infections in other parts of your genitourinary tract.
If you have acute prostatitis, you may develop:
- chills
- pain above your pubic bone
- pain in your genitals, testicles, or rectum
Any bacteria that causes UTIs can cause prostatitis. Bacteria that commonly cause UTIs and prostatitis include:
- Proteus species
- Klebsiella species
- Escherichia coli
Some bacteria that cause STDs, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can also cause acute bacterial prostatitis. Other conditions that can lead to acute bacterial prostatitis include:
Factors that increase your risk of UTIs, STDs, and urethritis also increase your risk of acute prostatitis. For example, these risk factors include:
- not drinking enough fluids
- having unprotected vaginal or anal intercourse
Other risk factors include:
Read Also: Flomax No Ejaculation
What To Do If Your Child Starts Sniffling
Looking ahead to the return to school after the winter break, the US is at a point where people need to treat cold or flu symptoms the same as Covid-19, Combs said.
When a family comes into her emergency room with a child that has sniffles and a sore throat and asks what it is, she is honest: She can’t know for sure without a test, said Combs.
Children are experiencing Omicron much in the same way adults are in that the symptoms are much more wide-ranging and often milder, like a cold, she said.
Getting a flu shot for your child is important to reduce the chance of adding another virus to the mix, Combs said. Children under 5-years-old are still waiting on Covid-19 vaccine approval from the US Food and Drug Administration, but those older can get vaccinated to reduce the risk of spread and serious disease.
As they go back to a school environment, testing is going to be essential to protecting against outbreaks, Combs said.
“If you’re looking to be really careful, if you’re looking at a child going back to a school environment is to spread to other people, I would say really the only way to know is taking that test,” Combs said.
The good news is we know how to manage infections when children return to school, Combs said. When it isn’t clear if your child was exposed or if their test is still pending, protocols like masking, sanitizing, distancing and reducing indoor gatherings are still believed to be effective in reducing spread, she added.
Don’t Miss: Side Effects Of Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
How Do I Know If My Prostate Is Enlarged
If your prostate is enlarged, it may not be a sign of cancer, but it is something that you should discuss with your doctor. Many of the symptoms of an enlarged prostate tend to relate to urination. If you are concerned about an enlarged prostate, here are 7 symptoms to look for:
