How Is The Procedure Performed
MRI exams may be done on an outpatient basis.
You will be positioned on the moveable exam table. Straps and bolsters may be used to help you stay still and maintain your position.
Devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves may be placed around or next to the area of the body being scanned.
MRI exams generally include multiple runs , some of which may last several minutes.
Your exam may use an endorectal coil. If so, a nurse or doctor will place a disposable cover over the coil. They will lubricate the assembly and insert the coil a short distance into your rectum. After insertion, the doctor inflates the circular balloon that sits around the coil and holds it in place during the exam. When the exam is complete, the doctor deflates the balloon and removes the coil.
If a contrast material is used, a doctor, nurse or technologist will insert an intravenous catheter into a vein in your hand or arm that will be used to inject the contrast material.
You will be placed into the magnet of the MRI unit. The technologist will perform the exam while working at a computer outside of the room.
If a contrast material is used during the exam, it will be injected into the intravenous line after an initial series of scans. More images will be taken during or following the injection.
When the exam is complete, you may be asked to wait while the radiologist checks the images in case more are needed.
Your IV line will be removed after the exam is over.
Setting Your Browser To Accept Cookies
There are many reasons why a cookie could not be set correctly. Below are the most common reasons:
- You have cookies disabled in your browser. You need to reset your browser to accept cookies or to ask you if you want to accept cookies.
- Your browser asks you whether you want to accept cookies and you declined. To accept cookies from this site, use the Back button and accept the cookie.
- Your browser does not support cookies. Try a different browser if you suspect this.
- The date on your computer is in the past. If your computer’s clock shows a date before 1 Jan 1970, the browser will automatically forget the cookie. To fix this, set the correct time and date on your computer.
- You have installed an application that monitors or blocks cookies from being set. You must disable the application while logging in or check with your system administrator.
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Having An Mri Scan Before A Biopsy
Advantages
- It can give your doctor information about whether there is cancer inside your prostate, and how quickly any cancer is likely to grow.
- Its less likely than a biopsy to pick up a slow-growing cancer that probably wouldnt cause any problems in your lifetime.
- It can help your doctor decide if you need a biopsy if theres nothing unusual on the scans, this means youre unlikely to have prostate cancer that needs to be treated. You may be able to avoid having a biopsy, and its possible side effects.
- If you do need a biopsy, your doctor can use the scan images to decide which parts of the prostate to take samples from.
- If your biopsy finds cancer, you probably wont need another scan to check if it has spread, as the doctor can get this information from your first MRI scan. This means you can start talking about suitable treatments as soon as you get your biopsy results.
Disadvantages
- Being in the MRI machine can be unpleasant if you dont like closed or small spaces.
- Some men are given an injection of dye during the scan this can sometimes cause mild side effects.
Don’t Miss: Is Cranberry Juice Good For Prostate
What Are The Limitations Of Mri Of The Prostate
High-quality images depend on your ability to remain perfectly still and follow breath-holding instructions while the images are being recorded. If you are anxious, confused or in severe pain, you may find it difficult to lie still during imaging.
A person who is very large may not fit into certain types of MRI machines. There are weight limits on the scanners.
Implants and other metallic objects can make it difficult to obtain clear images. Patient movement can have the same effect.
A very irregular heartbeat may affect the quality of images. This is because some techniques time the imaging based on the electrical activity of the heart.
MRI cannot always distinguish between cancer and inflammation or the presence of blood products within the prostate. Blood may sometimes appear due to a prostate biopsy. To avoid confusing any bleeding with cancer, your doctor may wait six to eight weeks after prostate biopsy to perform prostate MRI. This will allow any remnants of bleeding to resolve.
MRI typically costs more and may take more time to perform than other imaging methods. Talk to your insurance provider if you have concerns about the cost of MRI.
Use In Men Already Diagnosed With Prostate Cancer
The PSA test can also be useful if you have already been diagnosed with prostate cancer.
- In men just diagnosed with prostate cancer, the PSA level can be used together with physical exam results and tumor grade to help decide if other tests are needed.
- The PSA level is used to help determine the stage of your cancer. This can affect your treatment options, since some treatments are not likely to be helpful if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- PSA tests are often an important part of determining how well treatment is working, as well as in watching for a possible recurrence of the cancer after treatment .
Don’t Miss: Perineural Invasion Prostate Cancer Treatment
Standardized Reporting Of Prostate Mri: Comparison Of The Prostate Imaging Reporting And Data System Version 1 And Version 2
-
Affiliation Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
-
Affiliation Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Klinikum der Region Hannover, Hannover, Gehrden, Germany
-
Affiliation Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
-
Affiliation Clinic for Urology, Klinikum der Region Hannover, Hannover, Gehrden, Germany
-
Affiliation Department of Urology and Urologic Oncology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
-
Affiliation Clinic for Urology, Klinikum der Region Hannover, Hannover, Gehrden, Germany
-
Affiliation Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
-
Affiliation Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
-
Affiliation Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Klinikum der Region Hannover, Hannover, Gehrden, Germany
Introduction To Clinical Context And Proposed Utility Of Modality
MRI became the method of choice for detection and staging of prostate cancer . Adapted from breast imaging a Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System was published by the European Society of Urogenital Radiology : PI-RADS version 1 . This first guideline paper was based on a summary score for each lesion assessed in different sequences of mpMRI, consisting of T2w, DWI and DCE-MRI and spectroscopy facultatively. These guidelines have been updated recently by a steering committee including the American College of Radiology , ESUR and the AdMeTech Foundation to the PI-RADS v2 . In this version spectroscopy was omitted and DCE-MRI was attributed a minor role. In contrast to version 1 each lesion is attributed a single score based on findings of mpMRI. The objectives of these guidelines were to promote global standardisation of prostate imaging, to improve detection, localisation, characterisation, risk stratification of prostate cancer in treatment naïve prostate as well as to improve communication with referring urologists. The latest PI-RADS version assesses the likelihood of clinically significant prostate cancer on a 5-point scale for each lesion as follows:
-
PI-RADS 1 Very low
-
PI-RADS 2 Low
-
PI-RADS 3 Intermediate
-
PI-RADS 4 High
-
PI-RADS 5 Very high
For corresponding examples of findings see Fig. .
Fig. 1
You May Like: Perineural Spread Of Tumor
What Will I Experience During And After The Procedure
Most MRI exams are painless. However, some patients find it uncomfortable to remain still. Others may feel closed-in while in the MRI scanner. The scanner can be noisy. Sedation may be arranged for anxious patients, but fewer than one in 20 require it.
You may feel pressure while the doctor inserts the endorectal coil into your rectum. This is similar to that experienced during a digital rectal exam.
It is normal for the area of your body being imaged to feel slightly warm, but if it bothers you, notify the radiologist or technologist. It is important that you remain perfectly still while the images are being recorded, which is typically only a few seconds to a few minutes at a time. For some types of exams, you may be asked to hold your breath. You will know when images are being recorded because you will hear tapping or thumping sounds when the coils that generate the radiofrequency pulses are activated. You will be able to relax between imaging sequences, but will be asked to maintain your position as much as possible.
You will usually be alone in the exam room during the MRI procedure. However, the technologist will be able to see, hear and speak with you at all times using a two-way intercom. Many MRI centers allow a friend or parent to stay in the room as long as they are also screened for safety in the magnetic environment.
What Is Machine Learning And How Does It Work
There is a wide range of different methods that fall within the realm of machine learning some of them belong to the field of deep learning, but we will get to that in a next section. Let us first dive into the different types of methods that are machine learning, but not deep learning, to get an idea of the different problems machine learning can solve.
The difference between classification, regression, and clustering methods
Machine learning algorithms can assist us in many ways. To get a sensible grasp of how exactly they do so, this section explains three types of methods: classification algorithms, regression algorithms, and clustering algorithms.
Classification methods assign classes to the input they get. So, an algorithm that would tell whether a patient has prostate cancer based on, for example, PSA values and some other inputs such as age, estimated prostate volume, and other clinical variables, is considered a classification algorithm. In addition, an algorithm that provides a PI-RADS scoring for a prostate MRI falls within this category as well. A specific example of such a method is called a Support Vector Machine.
Regression methods determine a continuous value based on the input. Basically, it determines a function that outputs a value for the given input value . An example could be a risk score for prostate cancer based on the PSA value . Also, for regression problems, SVMs are often used.
Neural networks – how do these fit in?
Read Also: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
What Is The Prevalence Of Pi
The prevalence of prostate cancer and csPCa in published reports varies greatly . Several factors may influence the calculated prevalence, such as patient population, recruitment, definition of csPCa, and the diagnostic procedures. In MRI studies on prostate cancer, the prevalence of positive MRI varies comparably .
However, the prevalence of the maximal PI-RADS 3 score for the whole prostate is not clearly studied in the literature. For this review we initiated an explorative search to get insight into the prevalence of PI-RADS category 3 lesions. We identified relevant manuscripts published in the period 2014 to 2017. We summarized the results of each study and categorized the multiparametric MRI data into PI-RADS 12, 3, 4 and 5, and separately into a PI-RADS 45 group . In addition a sub classification was made within the patient groups of first biopsies, previously negative biopsies, and active surveillance biopsies for the PI-RADS 3 lesions.
Table 1
In men with respectively first biopsies, previously negative biopsies, and active surveillance biopsies, prostate MRIs were classified as PI-RADS 3 in 22% , 32% and 22% . In two large cohorts of men with mixed first and previously negative biopsies, the prevalence of maximal PI-RADS 3 score was 31% and 32% .
What Are The Risks Of A Prostate Mri
A very small number of people have an allergic reaction to the gadolinium contrast medium. Most reactions are mild, such as a rash or hives .
If you have very poor kidney function, you will not be given contrast medium, as there is a small risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis see Contrast Medium: using gadolinium or iodine in patients with kidney problems.
If an endorectal coil is used for the scan, there is also a very small risk of damage to the rectum from the balloon. If you have any concerns, please contact the MRI facility.
Read Also: Prostate Cancer Perineural Invasion Radical Prostatectomy
What Is An Mri Scan Of The Prostate
A magnetic resonance imaging scanner uses strong magnetic fields to create an image of the prostate and surrounding tissues.
The prostate gland is a small soft structure about the size and shape of a walnut, which lies deep in the pelvis between the bladder and the penis, and in front of the rectum .
Its function is to help liquefy semen .
Why Does An Mri Scan Cost So Much
Overhead costs can help explain why hospitals charge so much for MRI scans. The hospital must buy the MRI equipment, and MRI scanners are especially expensive. Typically, a new MRI machine costs upwards of $1 million.
In addition to that, emergency room and intensive care unit overhead costs are notoriously expensive. These overhead costs are due to various labeled facility fees, which are typically not disclosed to patients. Some hospitals up-charge patients for radiology procedures, among others, to help offset those other expenses.
Clinics, hospitals, and imaging centers also need to pay for maintenance and administration fees. These costs are generally pushed to the patients.
Also Check: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
When Can I Expect The Results Of My Prostate Mri
The time that it takes your doctor to receive a written report on the test or procedure you have had will vary, depending on:
- the urgency with which the result is needed
- whether more information is needed from your doctor before the examination can be interpreted by the radiologist
- whether you have had previous X-rays or other medical imaging that need to be compared with this new test or procedure
- how the report is conveyed from the practice or hospital to your doctor .
Please feel free to ask the private practice, clinic or hospital where you are having your test or procedure when your doctor is likely to have the written report.
It is important that you discuss the results with the doctor who referred you, either in person or on the telephone, so that they can explain what the results mean for you.
Biopsy Vs Prostate Mri
A prostate biopsy is a procedure performed to remove samples of suspicious tissue from the prostate and is used to detect prostate cancer. The most common way of performing a prostate biopsy is passing the needle through the wall of the rectum in a procedure known as a transrectal biopsy. Stereotactic Transperineal Prostate Biopsy is performed by comprehensively sampling the prostate through the perineum while the patient is under general anesthesia. The benefits of STPB include:
- An increased ability to identify hiding cancers
- No hospital stay necessary
- Minimally invasive
- Very low level of discomfort
- Virtually no risk of infection from the procedure
The prostate biopsy diagnosis has been around for a while and has proven results, some patients might choose to opt for a more non-invasive alternative such as a prostate MRI.
The main difference between the procedures stems from an MRIs use of magnetic waves to produce an image, as opposed to needle insertion of a prostate biopsy. The prostate MRI can also help find prostate cancer if you previously had elevated or rising PSAs. MRI is comparable in accuracy to prostate biopsy and it can be essential to help determine the extent of the prostate cancer by helping Doctors find out if the cancer has spread. We recommend you talk to your Doctor for more information on whether a prostate MRI or a prostate biopsy is better for your treatment.
Read Also: Prostate Definition Medical
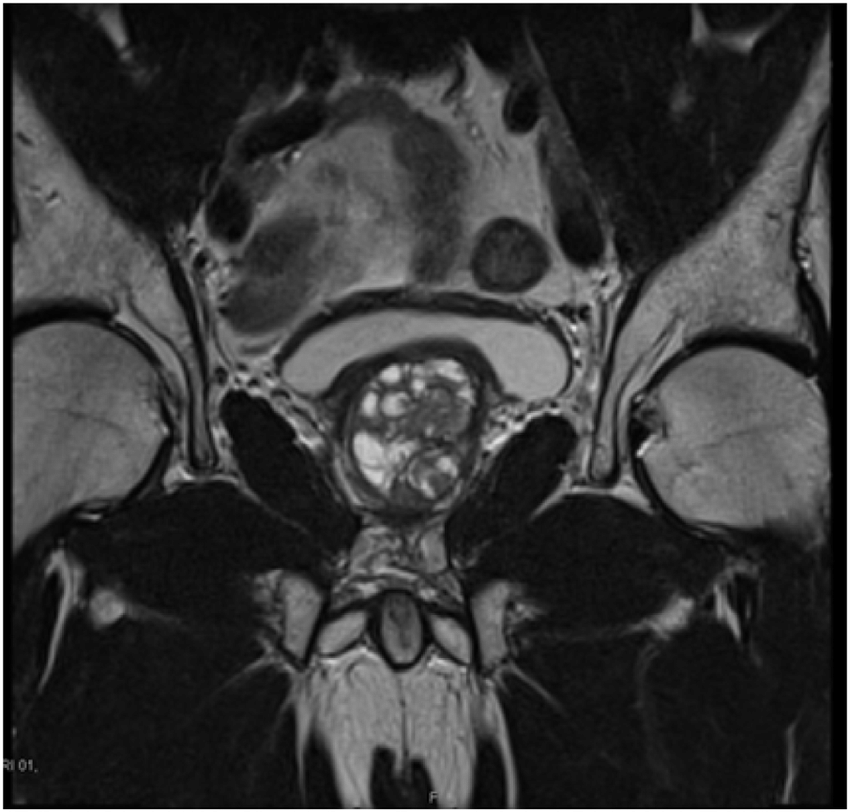
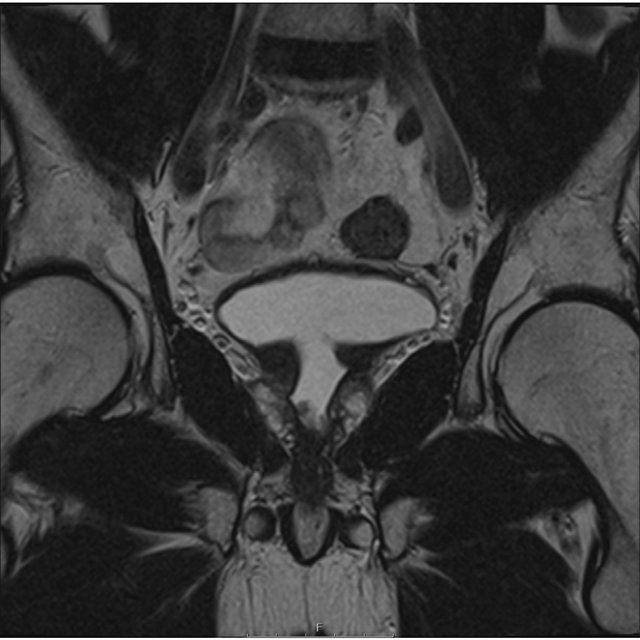
Prostate Adenocarcinoma With A Large Right Seminal Vesicular Cyst
Malignancy associated with cystic lesions of the prostate is rare. Both benign and malignant prostate neoplasms may contain cystic components. In this case, histology post-radical prostatectomy revealed Gleason score 5+4=9 prostate adenocarcinoma with involvement of both seminal vesicles. The large right-sided cystic structure was identified as arising from the right seminal vesicle which was invaded by the adenocarcinoma, leading to obstruction and distention. Due to the cystic nature of the lesion, there was no avidity within it on PSMA PET. When the cystic component grows as large as in this case, it can be associated with lower urinary tract symptoms. Other tumours of the prostate gland which can have cystic components include papillary cystadenocarcinoma and combined transitional cell/ adenocarcinoma and leiomyoma or liposarcoma can also show this although are much rarer . The aspirate of the cystic component is usually haemorrhagic and contains malignant cells with a high concentration of prostate specific antigen and Y-seminoprotein .
Fig. 9
Cystic prostate adenocarcinomaac Axial T2W images demonstrate multiple large high T2 signal lesions in keeping with cysts surrounding the prostate with small fluid-fluid levels likely due to internal haemorrhage
First How Does Artificial Intelligence Work
AI supports, or, in some cases, even replaces humans in performing certain tasks. There are many examples throughout society, also in the field of healthcare, the applications are abundant. Then how should we understand AI in this context? How can we define AI in healthcare?
AI concerns computers copying human behavior, or, at least, aiming to simulate humans in their intelligent tasks. In a healthcare context, we could then phrase a definition something like this:
Artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science concerning the simulation of intelligent human behavior in computers to solve problems in the healthcare space.
The applications can vary widely. AI algorithms can dig through patient databases figuring out patterns and predicting the course a disease will take, or even act as surgical robots that perform surgeries all by themselves. But these systems can also do other things like help send out reminders to people who might otherwise forget about their appointments, or support education of medical specialists keep them up to date with the latest developments in a medical field.
A concrete AI example: rule based engines
Figure 2: An example of an artificial intelligence algorithm: a rule-based engine.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Definition Of Prostate Gland
