About The Prostate And Prostate Cancer
The prostate gland, which grows during puberty, is considered an organ and is made up of several dozen lobules or saclike glands, held together with connective prostate tissue and muscle between them. The glands are called exocrine glands, because they secrete liquid to outside the body.
An enlarged prostate, called benign prostatic hyperplasia , is common in men over the age of 40 and may obstruct the urinary tract. The abnormal prostate cell growth in BPH is not cancerous and doesnt increase your risk of getting prostate cancer. However, symptoms for BPH and prostate cancer can be similar.
A condition called prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia , where prostate gland cells look abnormal when examined under a microscope, may be connected to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Prostate cancer is often caught by a doctor performing a digital rectal exam , through a prostate-specific antigen blood test, through a prostate biopsy or with a CT scan.
Another condition, prostatitis, is the inflammation of the prostate. While not cancerous, it may cause higher PSA levels in the blood.
When prostate cancer is found, pathologists stage the disease using a Gleason score, which grades the extent and arrangement of the cell mutations. For instance, a Gleason score of 6, the lowest possible, indicates a low-grade tumor, while cancers with scores of 9 or 10 are considered high-grade or the most aggressive and most likely to spread.
What Are Other Common Diagnostic Tests
Imaging tests such as MRI scans, CT scans, and ultrasounds can also be used to aid the detection of prostate cancer. These methods, some of them new or under development, can often help determine the presence of prostate cancer and help doctors minimize the risk of side effects.
An ultrasound may be used to look for suspicious areas in the prostate. This involves inserting a small ultrasound probe into the rectum. The ultrasound uses sound waves to take pictures of the inside of the body, in this case the prostate and surrounding areas.
Magnetic resonance imaging uses a magnetic field to produce clear images that may not be seen clearly with an X-ray or pictures derived from ultrasounds. It is painless and usually takes about 45 minutes to complete. After prostate cancer has been confirmed by a biopsy, an MRI is useful in enabling doctors to determine malignant areas. Some research has even suggested MRIs can help predict prostate cancer recurrence.
Most MRI machines place the patient into a tube-like tunnel for the test. This is called a closed MRI. Some people, particularly those with claustrophobia, find it difficult to have the test in the closed machine and can seek to have an open MRI. If an open MRI is not accessible and the test must be done, ask your doctor for medication to help reduce anxiety before the test.
Medical History And Physical Exam
If your doctor suspects you might have prostate cancer, you will be asked about symptoms you are having, such as any urinary or sexual problems, and how long you have had them. You might also be asked about possible risk factors, including your family history.
Your doctor will also examine you. This might include a digital rectal exam , during which the doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into your rectum to feel for any bumps or hard areas on the prostate that might be cancer. If you do have cancer, the DRE can sometimes help tell if its only on one side of the prostate, if its on both sides, or if its likely to have spread beyond the prostate to nearby tissues. Your doctor may also examine other areas of your body.
After the exam, your doctor might then order some tests.
Recommended Reading: Home Urine Test For Prostate Cancer
How Do I Prepare For A Prostate Biopsy
Before your prostate biopsy, your urologist works closely with you to ensure you avoid any medications that can increase your chances of bleeding, like blood thinners, certain herbal supplements, and over-the-counter drugs like aspirin and ibuprofen.
Your urologist also recommends an enema to make sure your bowels are completely empty before your biopsy.
How Do You Prepare For A Prostate Biopsy
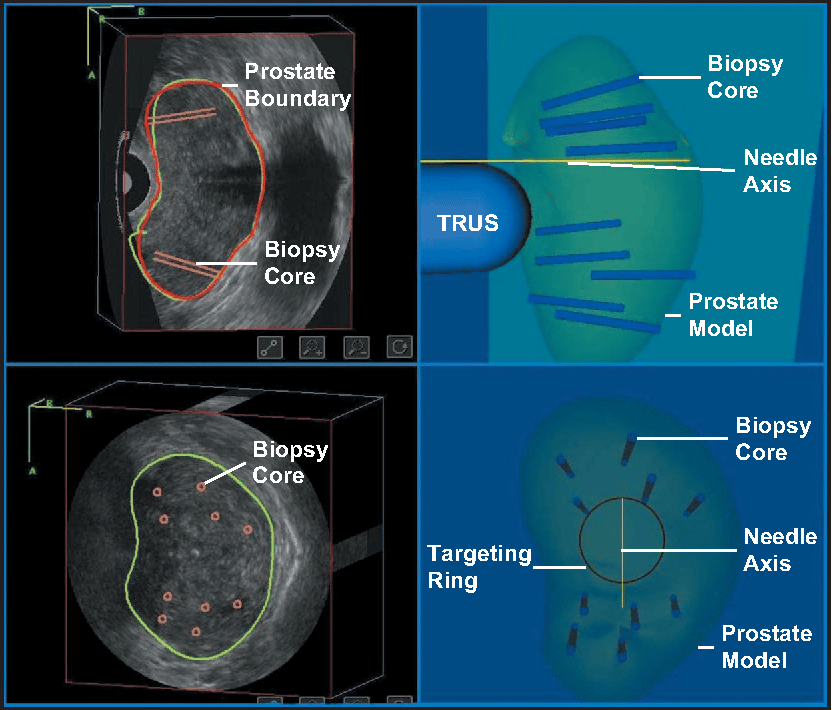
Your doctor will get you tested for urinary tract infections . If UTI is detected, the biopsy will be postponed till the infection clears with antibiotics.
You need to stop taking blood-thinning medications such as aspirin and warfarin and any other medications as advised by your doctor several days before the surgery.
Your doctor or nurse may instruct you to take an enema before the procedure. This helps to keep the bowels clean during the surgery.
Recommended Reading: What Age For Prostate Screening
Role Of Multiparametric Mri In Prostate Biopsy
Recent advances in imaging techniques including multi-parametric MRI have enabled non-invasive assessment of the prostate for suspicious lesions. mpMRI is a MRI technique that involves conjunctive use of multiple MRI sequences to more accurately characterize lesions. mpMRI reporting has been standardized by the European Society of Urogenital Radiology through the development of the Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System , which was updated to version 2 in 2015. Park et al. demonstrated in a retrospective study of patients who underwent both mpMRI and radical prostatectomy that PI-RADS2 score greater than 4 was 77% and 73.8% sensitive for detection of clinically significant cancer for each of the two readers with excellent inter-reader agreement. A recent meta-analysis by Woo et al. assessing the diagnostic performance of PI-RADS2 included 3857 patients and found a pooled sensitivity of 89% and specificity of 73% for cancer detection. Lesions with PI-RADS2 scores of 4 or 5 indicate a high or very high likelihood of clinically significant cancer, respectively, and should be biopsied.
Currently, the AUA suggests that mpMRI-based screening should be considered purely investigational and awaiting results of PROMIS and PRECISION trials before making a statement on the change in adoption, but it will be intriguing to see how rapidly it will change clinical practice.
Pros And Cons Of Transperineal Prostate Biopsy
In addition to potentially eliminating the need for antibiotics altogetheras the needle does not pass through the rectal wallthe newer method saves time instead of requiring separate appointments for both a pre-biopsy rectal swab and a subsequent biopsy once culture results are known, as is done using the TRUS system, the transperineal prostate biopsy can be completed in one in-office visit using only local anesthetic.
Duke began offering the transperineal prostate biopsy option in the clinic in October 2019, but Polascik has been performing the procedure in the operating room for the past 25 years using a cryotherapy grid. This larger transperineal prostate biopsy is done under anesthesia for the purpose of obtaining prostate tissue systematically every 5 mm, the results of which can be reconstructed into a 3-D framework of the prostate itself. Polascik gives two common reasons for why patients may opt for this larger 3-D transperineal mapping biopsy: to map out the exact size, number, and location of cancers within the prostate if interested in targeted ablation/focal therapy, and to confirm for patients in which there is still strong suspicion of having the disease, despite several rounds of conventional biopsies that have not detected prostate cancer.
Read Also: What Are The Side Effects Of Super Beta Prostate
When Do I Need A Biopsy
Your doctor may order a biopsy if your prostate-specific antigen level in your blood work is elevated or there is an abnormal lump found during a digital rectal exam. During a digital rectal exam, your doctor inserts a finger up your bottom to feel if your prostate is enlarged or has bumps. Another option before a biopsy is an ultrasound. Instead of a finger, a small probe is inserted to take pictures of the prostate.
An MRI-guided prostate biopsy may be used in patients who have a rising PSA level, yet a negative ultrasound-guided biopsy. It also may be used in situations where a diagnostic prostate MRI performed because of rising PSA demonstrates a very small abnormality that may not be easily targeted by ultrasound. An MRI image to guide a biopsy can improve the ability to detect prostate tumors which may require treatment.
What Are The Symptoms Of Prostate Problems
The symptoms of prostate problems may include
- urinary retentionthe inability to empty the bladder completely
- urinary frequencyurination eight or more times a day
- urinary urgencythe inability to delay urination
- urinary incontinencethe accidental loss of urine
- nocturiafrequent urination at night
- trouble beginning a urine stream
- weak or interrupted urine stream
- blockage of urine
- urine that has an unusual color or odor
Different prostate problems may have similar symptoms. For example, one man with prostatitis and another with BPH may both experience urinary urgency. Sometimes symptoms for the same prostate problem differ among individuals. For example, one man with BPH may have trouble beginning a urine stream, while another may experience nocturia. A man in the early stages of prostate cancer may have no symptoms at all. Because of this confusing array of symptoms, a thorough medical exam and testing are vital.
You May Like: What Happens If Your Prostate Is Removed
Risks And Side Effects
The risks associated with a biopsy are small, but its important to know that all medical procedures have some risk involved. The most common prostate cancer biopsy side effects and complications include:
- Blood in the urine
- Light rectal bleeding
If something doesnt feel right after your biopsy, call your medical team as soon as possible to get advice.
Tests To Diagnose And Stage Prostate Cancer
Most prostate cancers are first found as a result of screening. Early prostate cancers usually dont cause symptoms, but more advanced cancers are sometimes first found because of symptoms they cause.
If prostate cancer is suspected based on results of screening tests or symptoms, tests will be needed to be sure. If youre seeing your primary care doctor, you might be referred to a urologist, a doctor who treats cancers of the genital and urinary tract, including the prostate.
The actual diagnosis of prostate cancer can only be made with a prostate biopsy .
On this page
Read Also: What Happens If Prostatitis Is Not Treated
Lymph Node Biopsy As A Separate Procedure
A lymph node biopsy is rarely done as a separate procedure. Its sometimes used when a radical prostatectomy isnt planned , but when its still important to know if the lymph nodes contain cancer.
Most often, this is done as a needle biopsy. To do this, the doctor uses an image to guide a long, hollow needle through the skin in the lower abdomen and into an enlarged node. The skin is numbed with local anesthesia before the needle is inserted to take a small tissue sample. The sample is then sent to the lab and looked at for cancer cells.
Types Of Prostate Cancer
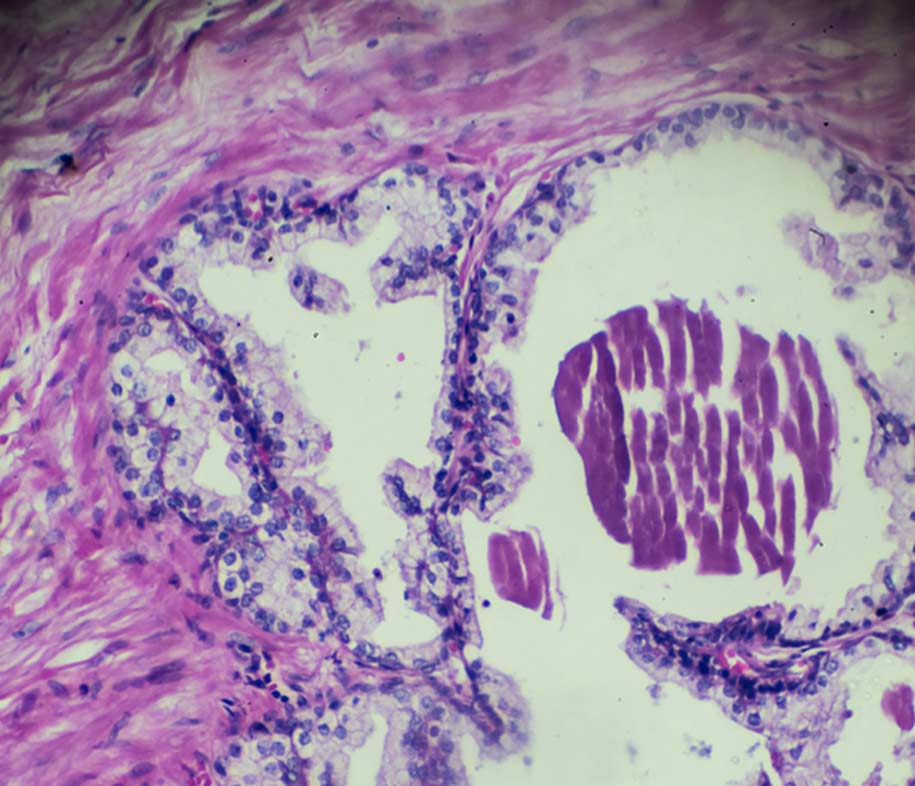
The type of prostate cancer tells you which type of cell the cancer started in. There are different types of prostate cancer. The most common type is adenocarcinoma of the prostate.
Doctors use the information about your prostate cancer type along with:
- how abnormal the cancer cells look under the microscope. This is the grade of the cancer
- the size of the cancer and whether it has spread. This is the stage
This helps your doctor decide which treatment you need. Another way doctors may describe your cancer is as localised, locally advanced or advanced.
Read Also: Questions To Ask Doctor About Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer: What You Can Do
Often with no early symptoms, prostate cancer can be difficult to self-diagnose. However, with annual screening and testing options widely available, prostate cancer is often caught before it spreads and can be treated. The common risk factors for prostate cancer include family history, race, diet, and, most commonly, age. About 60% of prostate cancer cases occur in men aged 65 and older, and it is rare before age 40. While there are many risk factors, the survival rates are very high. To learn more about your risk of prostate cancer, screening options, as well as other preventative measures you can take, talk with your health care provider.
Urologist Weighs In On Risks And Benefits Of Multiple Methods Offered At Duke
Duke urologists recently adopted a newer, minimally invasive approach for performing a prostate biopsy in the clinica transperineal procedure that is linked to lower risk of biopsy-associated infection and may be associated with a higher prostate cancer detection rate than the conventional transrectal ultrasound system. The transperineal biopsy system avoids the transfer of potentially harmful rectal bacteria by creating two needle punctures through the perineum, enabling clinicians to obtain tissue samples from either side of the prostate.
Even though TRUS has been the most common system for performing prostate biopsies for the past 30 years, Thomas J. Polascik, MD, urologic oncologist, says it poses serious risks, even for relatively healthy men. The hospitalization rate for sepsis after prostate biopsy around the world is about 3%, but with 3 out of 100 patients, thats like rolling the dicehealthy men who come in for a biopsy can possibly end up in the ICU due to sepsis, he says.
Also Check: Who Do You See For A Prostate Exam
Description Of The Procedure
There are different types of surgery. The choice is made based on your health goals and where the growth is. Choices include:
- Transrectal biopsy A needle is sent through the rectum wall into the prostate. It will draw out a sample of tissue. A small ultrasound wand will be placed in the rectum. It will help to guide the needle.
- Perineal biopsyA small incision will be made in the area between the scrotum and the rectum. A small needle will be passed through the cut into the prostate gland. A sample will be drawn out with the needle.
Genetic Testing For Some Men With Prostate Cancer
Some doctors now recommend that some men with prostate cancer be tested to look for certain inherited gene changes. This includes men in whom a family cancer syndrome is suspected, as well as men with prostate cancer that has certain high-risk features or that has spread to other parts of the body. Talk to your doctor about the possible pros, cons, and limitations of such testing.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Removal After Radiation Therapy
Positron Emission Tomography Scan
A PET scan is similar to a bone scan, in that a slightly radioactive substance is injected into the blood, which can then be detected with a special camera. But PET scans use different tracers that collect mainly in cancer cells. The most common tracer for standard PET scans is FDG, which is a type of sugar. Unfortunately, this type of PET scan isnt very useful in finding prostate cancer cells in the body.
However, newer tracers, such as fluciclovine F18, sodium fluoride F18, and choline C11, have been found to be better at detecting prostate cancer cells.
Other newer tracers, such as Ga 68 PSMA-11, 18F-DCFPyl , and Ga 68 gozetotide , attach to prostate-specific membrane antigen , a protein that is often found in large amounts on prostate cancer cells. Tests using these types of tracers are sometimes referred to as PSMA PET scans.
These newer types of PET scans are most often used if its not clear if prostate cancer has spread. For example, one of these tests might be done if the results of a bone scan arent clear, or if a man has a rising PSA level after initial treatment but its not clear where the cancer is in the body. PSMA PET scans can also be used to help determine if the cancer can be treated with a radiopharmaceutical that targets PSMA.
Doctors are still learning about the best ways to use these newer types of PET scans, and some of them might not be available yet in all imaging centers.
What Is The Research Team Doing
The research team is recruiting 1,302 patients who are having a prostate biopsy at one of 12 clinics and outpatient health centers across the United States. The team is assigning patients by chance to have either a transrectal or transperineal biopsy. Patients who are having a transrectal biopsy take an antibiotic before the biopsy to reduce their risk for infection.
Before the biopsy, right after, and a week later, the research team is surveying patients. Surveys ask about infections, pain, anxiety, and other adverse events. The team is looking at biopsy results to see if they detect cancer.
Prostate cancer survivors and staff from a national prostate cancer education organization are giving feedback on the study.
Also Check: Real Health Prostate Complete Walmart
Comparison Of Pain Scores Between Groups
There was no significant difference in the experience of pain at administration of block in our study. However, Urabe et al. reported a significantly higher average pain score of 2.9±2.1 in the CB+IRLA group than in the PPNB+IRLA group at the moment of administering the analgesia. This could have been as a result of the fact that in their study, IRLA was instilled prior to the administration of PPNB.
Table 4 Protocols, findings and conclusions of studies that compared CB with PPNB
Recommended Reading: How To Stop Leaking After Prostate Surgery
What Is The First Test For Detecting Prostate Problems
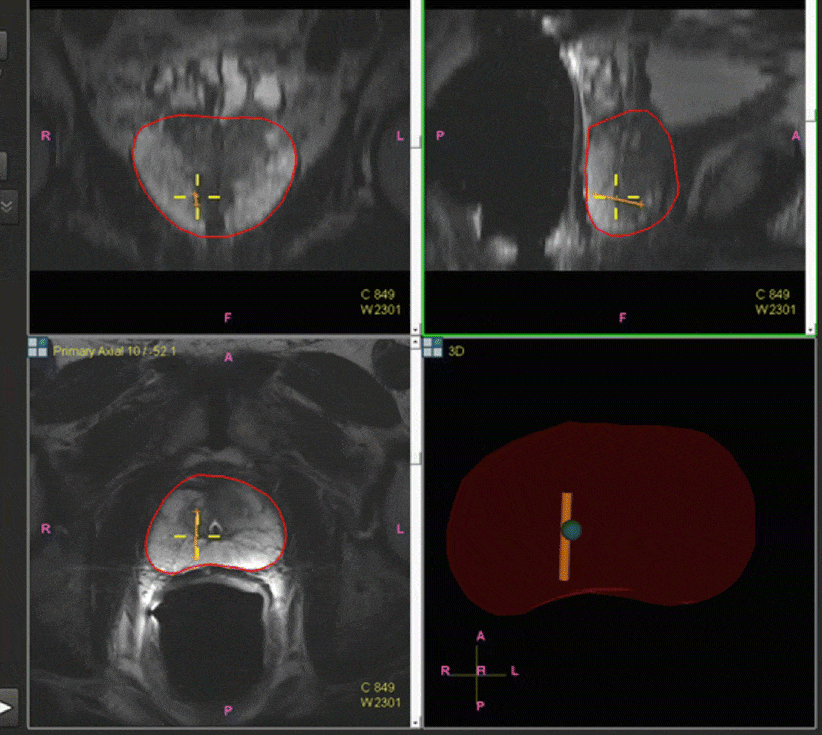
The first test for detecting prostate problems is a blood test to measure prostate-specific antigen , a protein made only by the prostate gland. This test is often included in routine physical exams for men older than age 50. Because African American men have higher rates of getting, and dying from, prostate cancer than men of other racial or ethnic groups in the United States, medical organizations recommend a PSA blood test be given starting at age 40 for African American men. Medical organizations also recommend a PSA blood test be given starting at age 40 for men with a family history of prostate cancer. Some medical organizations even recommend a PSA blood test be given to all men starting at age 40.
If urination problems are present or if a PSA blood test indicates a problem, additional tests may be ordered. These tests may require a patient to change his diet or fluid intake or to stop taking medications. If the tests involve inserting instruments into the urethra or rectum, antibiotics may be given before and after the test to prevent infection.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Enlarged Prostate
