Lifestyle Changes For Bph
- Limit the amount of fluids you drink in the evening, 1 to 2 hours before bed, to help avoid frequent nighttime urination.
- Urinate when you need to and schedule regular bathroom breaks double voiding .
- Limit caffeine and alcohol, which can worsen symptoms.
- Lose weight if needed, and exercise daily. Obesity is associated with BPH.
- Avoid drugs that have “anticholinergic” properties, such as decongestants , or first generation antihistamines like diphenhydramine . These drugs may prevent muscle relaxation in the prostate, worsen urinary symptoms, and can make it harder to urinate.
- Stay warm: Cold temperatures can cause you to retain urine and increase frequent urination.
- Pelvic floor muscle training
How To Diagnose And Treat Bph
Diagnosis of this condition starts with a physical examination and medical history review wherein urologists will ask questions about the symptoms. A medical history review will provide a clear analysis about the specific conditions that can mimic BPH, such as urethral stricture, bladder cancer or stones, or abnormal bladder/pelvic floor function or pelvic floor muscle spasms. Diagnosis tests include urine test, blood tests and scans. Urine tests are done to measure how well urine is released, and check whether the urethra is blocked or obstructed. Urine tests include Urinalysis, Post-void residual volume , Uroflowmetry and Urodynamic pressure flow study. Prostate-specific antigen blood tests are used to screen for prostate cancer and check the level of PSA . BPH scans like Transrectal Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography and Cystoscopy are performed to see the size and shape of the prostate. If the condition is more complex, urologists may recommend biopsy wherein tissue samples of the prostate are sent for diagnosis to check for chances of prostate cancer. Treatment depends on the size of the prostate, severity of symptoms, age of the patient and his/her overall health condition. Treatment modalities include a combination of medications, minimally invasive therapies and surgery.
Donât Miss: Risk Of Dying From Prostate Cancer
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia With Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms N401
The ICD10 code for the diagnosis Benign prostatic hyperplasia with lower urinary tract symptoms is N40.1. N40.1 is a VALID/BILLABLE ICD10 code, i.e it is valid for submission for HIPAA-covered transactions.
- N40.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM N40.1 became effective on October 1, 2018.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N40.1 other international versions of ICD-10 N40.1 may differ.
Donât Miss: Prostate Artery Embolization New York
Read Also: What Is Prostate Gland In Male
What Is The Icd 10 Code For History Of Bph
What is the ICD 10 code for History of BPH? Rest of the detail can be read here. People also ask, what is the diagnosis code for enlarged prostate? N40.1 Beside above, what is the ICD 10 code for family history of AAA? ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z83 Z83. 1 Family history of other infectious and parasi Z83.
Men with BPH may experience these symptoms:
- frequent need to urinate
- blood in the urine
- urinary tract infections
When the prostate enlarges, not all men have significant symptoms. Several different conditions can lead to symptoms comparable to an enlarged prostate, such as inflammation of the prostate , kidney or bladder stones, prostate cancer, or narrowing of the urethra. If you experience any of these symptoms, be sure to consult with your doctor.
BPH is not a form of prostate cancer but symptoms can be similar. Having BPH does not increase your risk for prostate cancer, but they can occur at the same time.
You May Like: Living With Metastatic Prostate Cancer
How Common Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
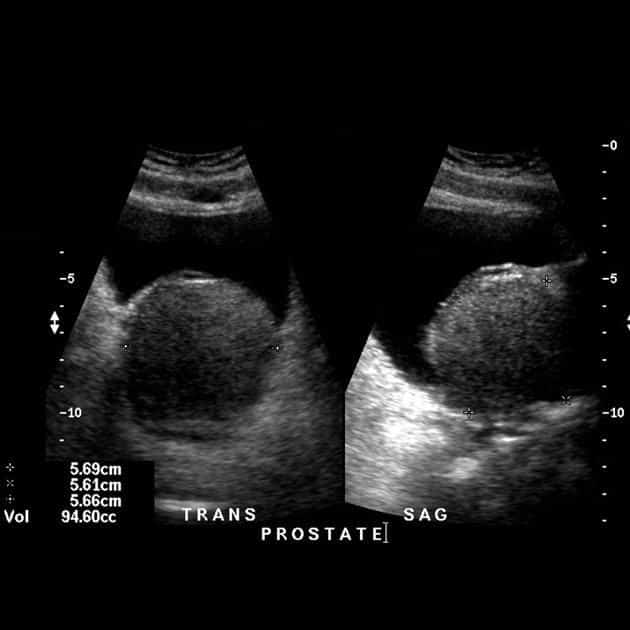
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is the most common prostate problem for men older than age 50. In 2010, as many as 14 million men in the United States had lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia.1 Although benign prostatic hyperplasia rarely causes symptoms before age 40, the occurrence and symptoms increase with age. Benign prostatic hyperplasia affects about 50 percent of men between the ages of 51 and 60 and up to 90 percent of men older than 80.2
Don’t Miss: What Is Gleason 6 Prostate Cancer
What Is The Icd 10 Code For Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
ICD-10 Code: N40.1 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. ICD-Code N40.1 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 600.01. Billable: Yes. ICD-9 Code Transition: 600.01.
The Initial Causes Benign Prostate Hypertrophy Icd 10
One of the first symptoms of prostate issues is pain or tenderness in the groin or lower back. This can be the result of a noncancerous condition called enlarged prostatic tissue, or it could be an infection of the bladder. In either case, its important to see a doctor as soon as possible. If youre suffering from prostate pain, you may want to consider reducing your caffeine intake.
Another symptom of a potentially enlarged prostate is difficulty starting a stream of urine, leaking, or dribbling. These symptoms are not serious, but theyre still alarming. Most men put up with an enlarged prostate for years before seeking medical attention, but they typically seek treatment as soon as they notice symptoms. Even if you dont have symptoms, its worth getting checked to determine if you have any prostate issues.
If you experience nightly bathroom runs, you may be experiencing an enlarged prostate. You may be having difficulty starting a stream of urine, or you may even be dribbling or leaking during the day. These problems arent life-threatening, but can become a nuisance. You should not ignore these signs and seek treatment as soon as you notice them. If you feel any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Recommended Reading: Sleeping Pills And Enlarged Prostate
Recommended Reading: Cyberknife Side Effects Prostate Cancer
What You Need To Know About The Prostate Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia With Urinary Obstruction Icd 10
A enlarged prostate can also cause blockages in the urethra. A blocked urethra can also damage the kidneys. A patient suffering from an enlargement of the prostate may have pain in his lower abdomen and genitals. If pain is present, a digital rectal examination will reveal hard areas. A doctor may prescribe surgery or perform an endoscopic procedure. If the enlarged prostate is not completely removed, it will shrink.
While the size of an enlarged prostate will influence the extent of urinary symptoms, men may experience a range of urinary symptoms. Some men have minimal or no symptoms at all. Some men will have a very enlarged prostate, whereas others will have a mild enlargement. Generally, the symptoms can stabilize over time. Some men may have an enlarged prostate but not notice it. If they have an enlarged colon, their physician can perform a TURP procedure.
Read Also: Prostate Cancer Psa Level 200
How Is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treated
Treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia may include
- lifestyle changes
- minimally invasive procedures
A health care provider treats benign prostatic hyperplasia based on the severity of symptoms, how much the symptoms affect a mans daily life, and a mans preferences.
Men may not need treatment for a mildly enlarged prostate unless their symptoms are bothersome and affecting their quality of life. In these cases, instead of treatment, a urologist may recommend regular checkups. If benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms become bothersome or present a health risk, a urologist most often recommends treatment.
- pain while peeing
Recommended Reading: Is It Ok To Ejaculate After Prostate Biopsy
What Causes Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The cause of benign prostatic hyperplasia is not well understood however, it occurs mainly in older men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia does not develop in men whose testicles were removed before puberty. For this reason, some researchers believe factors related to aging and the testicles may cause benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Throughout their lives, men produce testosterone, a male hormone, and small amounts of estrogen, a female hormone. As men age, the amount of active testosterone in their blood decreases, which leaves a higher proportion of estrogen. Scientific studies have suggested that benign prostatic hyperplasia may occur because the higher proportion of estrogen within the prostate increases the activity of substances that promote prostate cell growth.
Another theory focuses on dihydrotestosterone , a male hormone that plays a role in prostate development and growth. Some research has indicated that even with a drop in blood testosterone levels, older men continue to produce and accumulate high levels of DHT in the prostate. This accumulation of DHT may encourage prostate cells to continue to grow. Scientists have noted that men who do not produce DHT do not develop benign prostatic hyperplasia.
You May Like: Enlarged Prostate Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
How Do You Code Bph
4.7/5codein-depth answer
N40.1
Furthermore, what is male BPH? Benign prostatic hyperplasia also called prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. An enlarged prostate gland can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. It can also cause bladder, urinary tract or kidney problems.
Besides, what is benign prostatic hyperplasia with lower urinary tract symptoms?
About half of men with BPH develop an enlarged prostate gland, called benign prostatic enlargement , and among these, about half develop bladder outlet obstruction . BOO and/or changes in smooth muscle tone and resistance that can accompany BPH often result in lower urinary tract symptoms .
What are lower urinary tract symptoms?
Lower urinary tract symptoms include voiding or obstructive symptoms such as hesitancy, poor and/or intermittent stream, straining, prolonged micturition, feeling of incomplete bladder emptying, dribbling, etc, and storage or irritative symptoms such as frequency, urgency, urge incontinence, and nocturia.
You May Like: Urinary Tract Infection Go Away On Its Own
Don’t Miss: Can A Enlarged Prostate Cause Sciatic Nerve Pain
Nodular Prostate With Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific CodeAdult Dx Male Dx
- N40.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N40.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N40.3 other international versions of ICD-10 N40.3 may differ.
- N40.3 is applicable to adult patients aged 15 124 years inclusive.
- N40.3 is applicable to male patients.
use additional code
The Male Urogenital System
A benign tumor is not cancerous. It will not spread to other parts of the body. In many older men, the prostate enlarges in this benign way, called benign prostatic hypertrophy .
Cancer cells, though, divide and damage tissue around them. They can enter the bloodstream and spread to other parts of the body. This can be life threatening. Prostate cancer produces local symptoms by producing pressure on the bladder, urethra, and surrounding tissues. It also has a tendency to spread beyond the prostate gland to the bones.
Read Also: What Are The 5 Early Signs Of Prostate Cancer
About The Turquoise Health Ms
We build tools and machine learning systems that simplify healthcare revenue cycle operations.We were frustrated with the formatting of the MS-DRG rules, so we built our own solution.
MS-DRG rules and ICD-10 CM/PCS codes are automatically parsed from CMS’s MS-DRG data files. All content is provided strictly AS IS and may contain parsing errors. If you spot an error, .
We have converted the MS-DRG logic into fully structured, machine-readable data. If you need structured data versions of the MS-DRG manuals, .
N403 Nodular Prostate With Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
NEC Not elsewhere classifiableThis abbreviation in the Tabular List represents other specified. When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the other specified code.
NOS Not otherwise specifiedThis abbreviation is the equivalent of unspecified.
This note further define, or give examples of, the content of the code or category.
List of terms is included under some codes. These terms are the conditions for which that code is to be used.The terms may be synonyms of the code title, or, in the case of other specified codes, the terms are a list of the various conditions assigned to that code.The inclusion terms are not necessarily exhaustive. Additional terms found only in the may also be assigned to a code.
Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology.For such conditions, the ICD-10-CM has a coding convention that requires the underlying condition be sequenced first, if applicable, followed by the manifestation.Wherever such a combination exists, there is a use additional code note at the etiology code, and a code first note at the manifestation code.These instructional notes indicate the proper sequencing order of the codes, etiology followed by manifestation.
Read Also: Can The Prostate Grow Back After Surgery
Association Between Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia And Suicide In South Korea: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study
-
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing original draft
Affiliation Department of Mental Health Research, National Center for Mental Health, Seoul, Republic of Korea
-
Roles Conceptualization, Validation, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Department of Urology, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
-
Roles Investigation, Validation, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Department of Mental Health Research, National Center for Mental Health, Seoul, Republic of Korea
-
Roles Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Department of Psychiatry, Kangwon National University, School of Medicine, Chunchon, Republic of Korea
-
Roles Investigation, Validation, Writing review & editing
Affiliation College of Nursing, Woosuk University, Wanjoo, Republic of Korea
-
Roles Investigation, Validation, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
> > > All Natural Technique Fixes Enlarged Prostate Watch Here< <
Surgical procedures to remove the diseased prostate are usually necessary. Surgical procedures are not always necessary. If the disease is caused by bacterial infections, a doctor can treat the symptoms using alpha-blockers or surgery. Physical therapy, relaxation exercises, and warm baths are all recommended. A physician may also prescribe antibiotics to cure the infection. A bacterial infection can also cause a recurrence of the condition.
An enlarged prostate can be uncomfortable for both men and women. Some of the symptoms of an enlarged male reproductive organ include a weakened urine stream, urgent need to urinate, and urinary tract infections. BPH can also cause damage to the kidneys. A sudden inability to urinate can be life-threatening, as it can lead to bladder and kidney damage. Unfortunately, most men with enlarged prostrates put up with the symptoms for years before they seek treatment. However, many of the men with symptoms finally decide to go to a doctor for proper gynecological evaluation and to begin enlarged prostatic therapy.
Recommended Reading: Prostate Hormone Treatment Side Effects
Tabular List Of Diseases And Injuries
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized âhead to toeâ into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code N40.1:
Inclusion Terms
Also Check: What Should My Prostate Feel Like
Voiding Or Obstructive Symptoms
- Overflow incontinence
- Episodes of near retention
As the symptoms are common and non-specific, LUTS is not necessarily a reason to suspect prostate cancer. Large studies of patients have also failed to show any correlation between lower urinary tract symptoms and a specific diagnosis. Also, recently a report of lower urinary tract symptoms even with malignant features in the prostate failed to be associated with prostate cancer after further laboratory investigation of the biopsy.
Also Check: Can A Prostate Biopsy Spread Cancer
You May Like: Prostate Md By 1md Reviews
What Is The Icd 10 Code For Bph With Obstruction
3.9/5symptomsdiagnosis
Likewise, what is the ICD 10 CM code for benign prostatic hyperplasia with urinary retention?
N40. 1 Benign prostatic hyperplasia with lower urinary tract symptoms. ICD10CM.
Also Know, what are lower urinary tract symptoms? Lower urinary tract symptoms include voiding or obstructive symptoms such as hesitancy, poor and/or intermittent stream, straining, prolonged micturition, feeling of incomplete bladder emptying, dribbling, etc, and storage or irritative symptoms such as frequency, urgency, urge incontinence, and nocturia.
Similarly, you may ask, what is benign prostatic hyperplasia with lower urinary tract symptoms?
About half of men with BPH develop an enlarged prostate gland, called benign prostatic enlargement , and among these, about half develop bladder outlet obstruction . BOO and/or changes in smooth muscle tone and resistance that can accompany BPH often result in lower urinary tract symptoms .
What is male BPH?
Benign prostatic hyperplasia also called prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. An enlarged prostate gland can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. It can also cause bladder, urinary tract or kidney problems.
What Are The Symptoms Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia may include
- urinary frequencyurination eight or more times a day
- urinary urgencythe inability to delay urination
- trouble starting a urine stream
- a weak or an interrupted urine stream
- dribbling at the end of urination
- nocturiafrequent urination during periods of sleep
- urinary incontinencethe accidental loss of urine
- urine that has an unusual color or smell
Symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia most often come from
- a blocked urethra
- a bladder that is overworked from trying to pass urine through the blockage
The size of the prostate does not always determine the severity of the blockage or symptoms. Some men with greatly enlarged prostates have little blockage and few symptoms, while other men who have minimally enlarged prostates have greater blockage and more symptoms. Less than half of all men with benign prostatic hyperplasia have lower urinary tract symptoms.3
Also Check: What Is The Most Common Cause Of Prostatitis
