What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
If you have prostate cancer, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- Why did I get prostate cancer?
- What is my Gleason score? What is my Grade Group? What do these numbers mean for me?
- Has the cancer spread outside of the prostate gland?
- What is the best treatment for the stage of prostate cancer I have?
- If I choose active surveillance, what can I expect? What signs of cancer should I look out for?
- What are the treatment risks and side effects?
- Is my family at risk for developing prostate cancer? If so, should we get genetic tests?
- Am I at risk for other types of cancer?
- What type of follow-up care do I need after treatment?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Prostate cancer is a common cancer that affects males. Most prostate cancers grow slowly and remain in the prostate gland. For a small number, the disease can be aggressive and spread quickly to other parts of the body. Men with slow-growing prostate cancers may choose active surveillance. With this approach, you can postpone, and sometimes completely forego, treatments. Your healthcare provider can discuss the best treatment option for you based on your Gleason score and Group Grade.
Who Is More Likely To Have Prostate Cancer Recurrence
In general, the further your cancer has spread and the more aggressive it is, the more likely it is to recur. Specific factors include:
- Tumor size: In general, the larger the tumor, the more likely it is to recur.
- Gleason score: A higher Gleason score means a more aggressive cancer and a higher rate of recurrence.
- Cancer staging: Staging refers to how far the cancer has spread. Higher stage cancers have spread further at initial treatment and have higher rates of recurrence.
- Involvement of the lymph nodes: Prostate cancer that has entered the lymph nodes prior to treatment is more likely to recur.
Tools To Help You Decide
The Predict Prostate tool can help you decide between monitoring and more radical treatment. It is for men whose prostate cancer hasn’t spread.
It can’t tell you exactly what is going to happen in the future, but it gives you an idea about the differences in survival between the different treatment options. The tool works less well for men with a very high PSA or those with a fast growing or large tumour.
To be able to use the tool you need to know the following about your cancer:
- PSA level
Also Check: Prostate Cancer Perineural Invasion Radical Prostatectomy
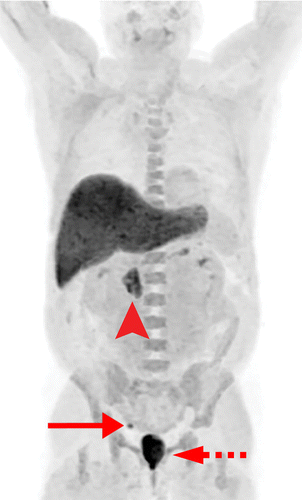
What Does It Mean For Prostate Cancer To Spread
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. If this occurs, doctors say the cancer has metastasized or spread.
Areas of the body to which prostate cancer can spread include:
- the bones
- the lungs
- the lymph nodes, usually those around the pelvis
A doctor will typically recommend imaging scans and tissue samples to test for the presence of cancerous cells.
According to the Prostate Cancer Foundation, age is the biggest contributing factor to the risk for prostate cancer. An estimated 65 percent of all prostate cancers are diagnosed in men older than 65 years of age.
Additional risk factors for prostate cancer include:
- Family history: Men who have a father or brother with prostate cancer are twice as likely to get prostate cancer as men who do not.
- Race: African-American men face the greatest risk of prostate cancer.
- Smoking: A history of smoking is associated with a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
Researchers are also studying a link between diet and increased prostate cancer risk. Diets low in vegetables or high in calcium have been linked to an increased risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
The prostate is very close to the point at which urine drains from the body. As a result, many prostate cancer symptoms affect the urination process. Examples of these symptoms include:
Some of these symptoms are associated with aging and an enlarged prostate. As a result, some men may ignore these symptoms instead of seeking medical attention.
B History Part : Prevalence:
-
Advancing age: Incidence in men age 65-75 is 35%, age 55-64 is 30%, age 45-54 is 10%, and age 35-44 is 1%.
-
In 2014, 233,000 new cases of prostate cancer were diagnosed and 29,480 prostate cancer related deaths were noted.
-
Family History: Men with a 1st-degree relative are two-times likely to develop prostate cancer, and men with two 1st-degree relatives are five-times likely.
-
Race: Highest worldwide incidence in African Americans. African-Americans have higher mortality and are diagnosed at a younger age than Caucasians.
-
Geographical: The highest risk for prostate cancer occurs in Scandinavia, while the United States and Europe have intermediate risk, and the risk for prostate cancer is lowest in Asia though risk in Asian men who immigrate to US increases to that of US men.
Genetic and environmental factors have been linked to prostate cancer. The HPC-1 gene on Chromosome 1 has been associated with familial prostate cancer. Environmental factors that render an increased risk include prostatitis, STDs, Western diet and androgens. Vitamin D may have a protective effect. Finasteride and dutasteride have been shown to reduce rates of low-grade prostate cancer compared to placebo. These drugs cause erectile dysfunction and reduce PSA levels, but they have not been FDA approved for cancer prevention. Trials of Vitamin E and selenium showed no preventative benefit.
Don’t Miss: Do Girls Have Prostate Glands
Types Of Prostate Cancer
Almost all prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas. These cancers develop from the gland cells .
Other types of cancer that can start in the prostate include:
- Small cell carcinomas
- Neuroendocrine tumors
- Transitional cell carcinomas
- Sarcomas
These other types of prostate cancer are rare. If you are told you have prostate cancer, it is almost certain to be an adenocarcinoma.
Some prostate cancers grow and spread quickly, but most grow slowly. In fact, autopsy studies show that many older men who died of other causes also had prostate cancer that never affected them during their lives. In many cases, neither they nor their doctors even knew they had it.
How Common Is Prostate Cancer
About one in nine men will receive a prostate cancer diagnosis during his lifetime. Prostate cancer is second only to skin cancer as the most common cancer affecting males. Close to 200,000 American men receive a diagnosis of prostate cancer every year. There are many successful treatments and some men dont need treatment at all. Still, approximately 33,000 men die from the disease every year.
Recommended Reading: Describe The Effect Of An Enlarged Prostate Gland On The Urinary Function Of A Male
Role Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Endorectal coil magnetic resonance imaging is gradually gaining a foothold in staging prostate cancer. The accuracy of endorectal coil MRI in determining extraprostatic extension is far greater than that of TRUS.88 DâAmico and colleagues108,109 reported that endorectal coil MRI findings correlate with surgical outcome. Given the improved accuracy of endorectal coil MRI in defining prostate anatomy and in identifying suspicious intraprostatic areas,111 extracapsular extension, and seminal vesicle invasion,112-114 treatment planning using three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy or intensity-modulated radiation therapy should be enhanced. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy permits the visualization of choline-rich areas, which are related to bulky tumor regions identified at pathology examination.115 Dose-painting techniques that use IMRT to focally escalate the dose per fraction in choline-rich areas are being developed.116,117 Functional imaging methods have tremendous promise in radiation treatment planning for prostate cancer and will undoubtedly become more commonplace over time.
David G. Bostwick, Isabelle Meiers, in, 2008
Benefits Of Early Detection And Treatment
The goal of screening for prostate cancer is to identify high-risk, localized prostate cancer that can be successfully treated, thereby preventing the morbidity and mortality associated with advanced or metastatic prostate cancer.
Adequate evidence from randomized clinical trials shows that PSA-based screening programs in men aged 55 to 69 years may prevent approximately 1.3 deaths from prostate cancer over approximately 13 years per 1000 men screened.3, 4 Screening programs may also prevent approximately 3 cases of metastatic prostate cancer per 1000 men screened.3 Current results from screening trials show no reductions in all-cause mortality from screening. There is inadequate evidence to assess whether the benefits for African American men and men with a family history of prostate cancer aged 55 to 69 years are different than the benefits for the average-risk population. There is also inadequate evidence to assess whether there are benefits to starting screening in these high-risk groups before age 55 years.
Adequate evidence from RCTs is consistent with no benefit of PSA-based screening for prostate cancer on prostate cancer mortality in men 70 years and older.
Read Also: How Effective Is Chemotherapy For Prostate Cancer
Internal And External Radiation Therapy For Prostate Cancer
By | Submitted On August 23, 2010
Prostate cancer, being one of the common cancers that happen in men, has indeed caused an alarm to those who are and who will be affected. Knowledge about prostate cancer treatment is indeed important so that possible patients will know about the methods that will be used in order to treat this kind of cancer. The use of radiation is one of the methods being adapted by experts to cure and alleviate not only that of prostate cancer symptoms but also other types of cancer.
Radiation therapy can be delivered in two ways, internally or externally. It depends upon the choice of the patient and the decision of the doctor when it comes to the severity of the tumor that needs to be treated with radiation. During delivery, the personnel must be protected. The amount of exposure to harmful radiation effects is directly proportional to the length of time of exposure, the distance from the radiation source, and the use of shields containing lead like the walls, aprons or movable shields which absorb the radioactive rays and decrease exposure to their harmful effects.
Lastly, the linear accelerators or sometimes called the supervoltage machines use protons, neutrons, or electrons as the radiation source. The radiation dose penetrates below the skin surface, varying in depth from several millimeters to several centimeters, therefore sparing of the skin is significant. This has also expanded the use of radiation as a treatment modality.
Pathological Stage: A Look At The Actual Cancer Cells And Their Distribution Within The Pelvic Area
This system assesses how pervasive the cancer cells are within and around the prostate. These stages begin at T2.
T2: The tumor is located in the prostate only.T3: The tumor has breached the prostate border on 1 or more sides.T3b: The tumor has begun to grow in the seminal vesicles.T4: The tumor has grown into other neighboring structures, like the bladder, the rectum, or the pelvic wall.
You May Like: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Looking For More Survivorship Resources
For more information about cancer survivorship, explore these related items. Please note that these links will take you to other sections of Cancer.Net:
-
ASCO Answers Cancer Survivorship Guide:Get this 44-page booklet that helps people transition into life after treatment. It includes blank treatment summary and survivorship care plan forms. The free booklet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
-
Cancer.Net Patient Education Video:View a short video led by an ASCO expert that provides information about what comes after finishing treatment.
-
Survivorship Resources: Cancer.Net offers an entire area of this website with resources to help survivors, including those in different age groups.
The next section offers Questions to Ask the Health Care Team to help start conversations with your cancer care team. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
This is the end of Cancer.Nets Guide to Prostate Cancer. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
Treatment By Stage Of Prostate Cancer
Different treatments may be recommended for each stage of prostate cancer. Your doctor will recommend a specific treatment plan for you based on the cancers stage and other factors. Detailed descriptions of each type of treatment are provided earlier on this same page. Clinical trials may also be a treatment option for each stage.
Early-stage prostate cancer
Early-stage prostate cancer usually grows very slowly and may take years to cause any symptoms or other health problems, if it ever does at all. As a result, active surveillance or watchful waiting may be recommended. Radiation therapy or surgery may also be suggested, as well as treatment in clinical trials. For those with a higher Gleason score, the cancer may be faster growing, so radical prostatectomy and radiation therapy are often recommended. Your doctor will consider your age and general health before recommending a treatment plan.
ASCO, the American Urological Association, American Society of Radiation Oncology, and the Society of Urologic Oncology recommend that patients with high-risk early-stage prostate cancer that has not spread to other areas of the body should receive radical prostatectomy or radiation therapy with hormonal therapy as standard treatment options.
Locally advanced prostate cancer
Watchful waiting may be considered for older adults who are not expected to live for a long time and whose cancer is not causing symptoms or for those who have another, more serious illness.
You May Like: How To Massage A Man’s Prostate
Radical Retro Public Prostatectomy
A nerve-sparing radical retro pubic prostatectomy is a modification of this operation. During this procedure, the surgeon carefully preserves the small bundles of nerves on either side of the prostate gland. If the cancer has not spread to these nerves, the surgeon will not remove them. Because these are the nerves that are needed for erections, leaving them intact lowers the risk of impotence following surgery.
Treatment Options For Stage 4 Cancer
Stage 4 cancer is challenging to treat, but treatment options may help control the cancer and improve pain, other symptoms and quality of life. Systemic drug treatments, such as targeted therapy or chemotherapy, are common for stage 4 cancers.
Often, a clinical trial may be an option, offering new treatments to help you fight stage 4 cancer.
Below are the prevailing treatment options for the five most common cancers.
Treatment of stage 4 breast cancer: For cancer that has spread beyond the breast and nearby lymph nodes, systemic drug treatments are typically used. These include:
- Hormone therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy
They may be used alone or in combination, and they may also be determined by the hormone receptor and the HER2 status of the cancer.
Surgery and radiation may be treatment options in specific cases to help improve symptoms caused by a growing tumor, not to get rid of the cancer. The tumor may be removed with surgery or shrunk by radiation therapy if, for example, its:
- Blocking a blood vessel
- Causing a wound
- Affecting the spinal cord
Treatment of stage 4 lung cancer: In general, stage 4 lung cancer is also treated with systemic drug therapies.
Stage 4 lung cancer that has spread to one distant area tends to be treated differently than lung cancer that has spread more widely. For stage 4A cancers, treatment tends to focus on the one site where the cancer has spread.
There may also be clinical trials assessing new treatments for stage 4 melanoma.
You May Like: Does Enlarged Prostate Affect Ejaculation
Side Effects Of Cryosurgery
Freezing can damage nerves near the prostate and cause impotence and incontinence. These complications occur about as often after cryosurgery as they do after radical prostatectomy. In addition, freezing may damage the bladder and intestines to some extent, leading to pain, a burning sensation, and the need to empty the bladder and bowels often. About 50 percent of men notice swelling of their penis and scrotum after cryosurgery, usually lasting a couple of weeks.
Types Of Cancer That Are Treated With Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation therapy is used to treat many types of cancer.
Brachytherapy is most often used to treat cancers of the head and neck, breast, cervix, prostate, and eye.
A systemic radiation therapy called radioactive iodine, or I-131, is most often used to treat certain types of thyroid cancer.
Another type of systemic radiation therapy, called targeted radionuclide therapy, is used to treat some patients who have advanced prostate cancer or gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor . This type of treatment may also be referred to as molecular radiotherapy.
You May Like: Carboplatin Prostate Cancer
Keeping Personal Health Records
You and your doctor should work together to develop a personalized follow-up care plan. Be sure to discuss any concerns you have about your future physical or emotional health. ASCO offers forms to help keep track of the cancer treatment you received and develop a survivorship care plan when treatment is completed.
This is also a good time to talk with your doctor about who will lead your follow-up care. Some survivors continue to see their oncologist, while others transition back to the care of their family doctor or another health care professional. This decision depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, side effects, health insurance rules, and your personal preferences.
If a doctor who was not directly involved in your cancer care will lead your follow-up care, be sure to share your cancer treatment summary and survivorship care plan forms with them and with all future health care providers. Details about your cancer treatment are very valuable to the health care professionals who will care for you throughout your lifetime.
The next section in this guide is Survivorship. It describes how to cope with challenges in everyday life after a cancer diagnosis. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
The word survivorship means different things to different people. Common definitions include:
Recent Advances: Molecular Markers
Currently, risk stratification for men who have recently been diagnosed with prostate cancer by biopsy is accomplished with the combination of prostate-specific antigen level, clinical stage, and Gleason score or Grade Group. The limitation of using these parameters for risk stratification is that collectively they do not address specific biologic features of prostate cancer, specifically the aggressiveness of tumor cells. In addition, many studies have shown that localized prostate malignancy can vary in potential for progression in different patients, despite similar risk-stratifying characteristics.
This problem has sparked the advent of research and use of biological/genomic assays to help risk stratify men diagnosed with localized prostate cancer. The theory behind utilizing genomic assays is to identify genes in biopsy specimens that potentiate cellular proliferation.
Cooperberg et al aimed to validate the application of the cell cycle progression score in identifying men at risk for recurrent disease after radical prostatectomy. The CCP score identifies genes that promote cellular proliferation. In this study, the CCP score was compared with the Cancer of the Prostate Risk Assessment post-Surgical , which risk stratifies recurrence after prostatectomy based on pre-procedural PSA, Gleason score, and clinical staging, and has been shown to have good accuracy.
- Confirm MDx
- Oncotype DX
- Promark
References
Recommended Reading: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
