Pain As Symptom Of Prostate Cancer
Early diagnosis of prostate cancer is very difficult since the symptoms of the disease usually do not manifest until advanced stages. Pain is one of these symptoms and it can be experienced very differently from patient to patient. In earlier stages of prostate cancer, pain can occur during urination or ejaculation, which is related to the blockage caused by cancer growth in the prostate. The tumors start to pressure the nearby organs and tissues, causing the pain. In more advanced cases, the pain may spread to the pelvis, lower back, ribs, or upper thighs, and in the bones of those areas.
Approximately 70% to 85% of patients with advanced prostate cancer have associated clinically apparent bone metastases, while another 20% to 25% have metastatic liver lesions, explain the authors of the study Pain Management in Patients With Advanced Prostate Cancer.In addition to pelvic pain associated with primary tumor extension, these metastatic lesions cause pain that ranges from mild to very severe and may require extensive, highly individualized pain management. Pain is perhaps the one aspect of cancer that patients fear most, and effective pain control is a critical issue for patients and often a challenge for clinicians.
Eating Diet And Nutrition
Researchers have not found that eating, diet, and nutrition play a role in causing or preventing prostatitis. During treatment of bacterial prostatitis, urologists may recommend increasing intake of liquids and avoiding or reducing intake of substances that irritate the bladder. Men should talk with a health care provider or dietitian about what diet is right for them.
The Tension Headache Of The Groin
Prostatitis is a benign but painful condition that causes inflammation of the prostate or surrounding area. While half of all men will experience it, many dont know what it is.
When prostatitis happens to younger men, it can be alarming and a little scary.
We asked UNC Medical Center urologist Eric Wallen, MD, to explain prostatitis and what can be done to fix it.
Read Also: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Wednesday 4 October 2017
Hey guys, we know that talking about your prostate can be a little uncomfortable. You might not know where or what it is, or you might have only heard about it in stories about older men having difficulty peeing or the doctor sticking their finger up you know where to check on it.
Below, weve got all the details about what your prostate is, where it is and what it does. Well also discuss how it might change as you age, and any changes or symptoms you should keep an eye on and tell your doctor about.
When To Get Medical Advice
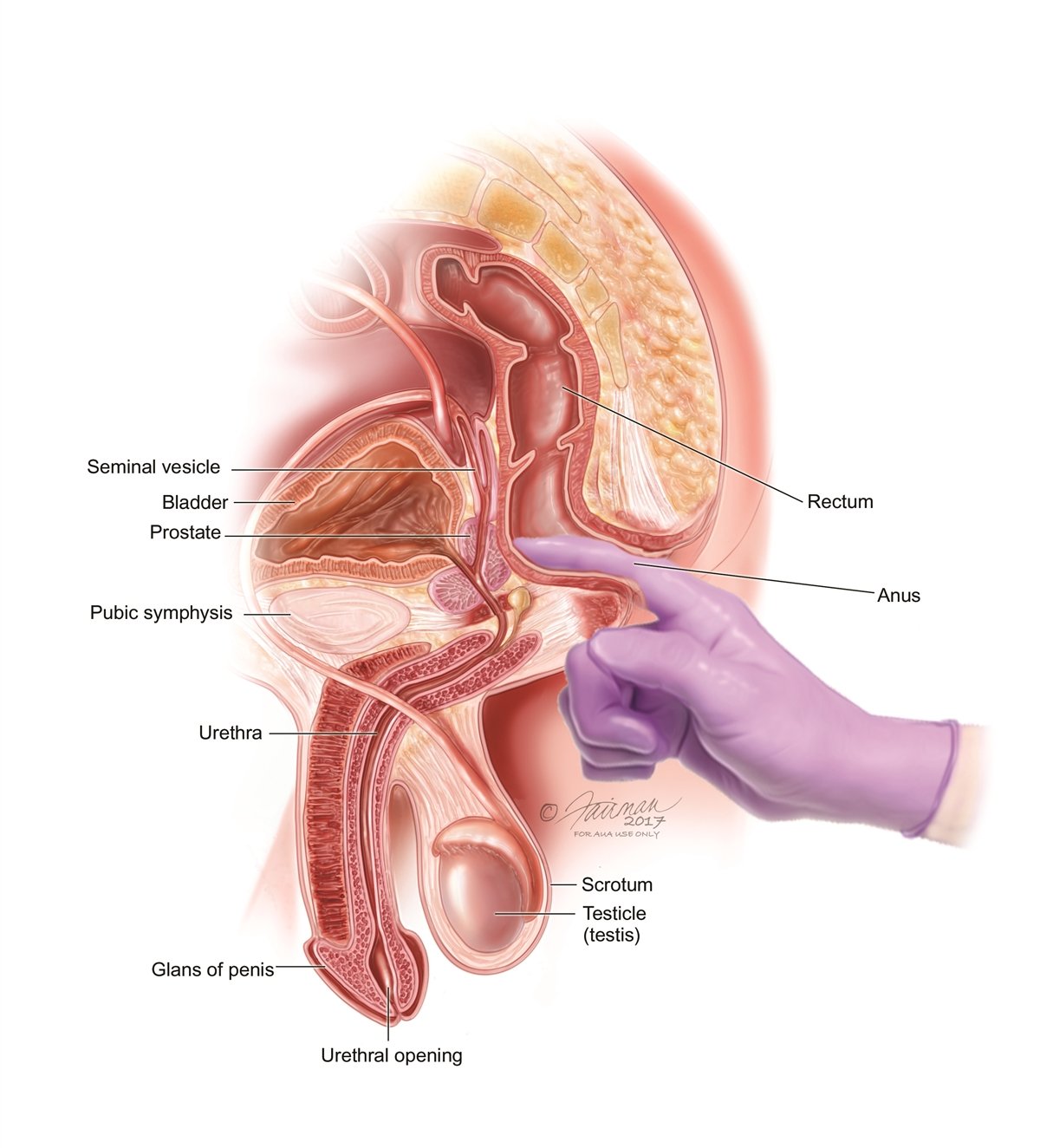
See a GP if you have symptoms of prostatitis, such as pelvic pain, difficulty or pain when peeing, or painful ejaculation.
They’ll ask about the problems you’re having and examine your tummy.
You may also have;a rectal examination. This is where a doctor inserts a gloved finger into your bottom to feel for anything unusual. You may have some discomfort during this examination if your prostate is swollen or tender.
Your urine will usually be tested for signs of infection, and you may be referred to a specialist for further tests to rule out other conditions.
See a GP straight away if you get sudden and severe symptoms of prostatitis.
You may have acute prostatitis, which needs to be assessed and treated quickly because it can cause serious problems, such as suddenly being unable to pee.
If you have persistent symptoms , you may be referred to a doctor who specialises in urinary problems .
Also Check: What Is Perineural Invasion In Prostate Cancer
If Youre The Receiving Partner
Youll want to be as relaxed and aroused as possible, because itll make the experience easier and more enjoyable.
The whole poop-comes-out-of-the-butt thing gives some people a case of the heebie-jeebies even when its their own butt.
Remedy this by taking a shower and paying a little extra attention back there to get it squeaky clean. Some people like to use an enema before engaging in butt play, but it isnt necessary.
Use the bathroom before getting started. Prostate stimulation can make you feel like you need to pee, and anal penetration can cause the sensation of needing to poop.
Even though you wont actually do either, worrying that you might can interfere with your ability to let go and enjoy yourself. Knowing your bladder and bowels are empty can help.
Getting used to the sensation of having your prostate touched can help, too. Practice with an anal sex toy, like a butt plug, or your fingers.
Be sure to set the mood so that youre turned on and primed for action. Light candles, watch porn, or engage in some good old-fashioned masturbation or foreplay to get there.
Finally, be sure to lube up real good. Applying a water-based lubricant will allow for easier penetration and make for some easy gliding if stimulating your prostate externally.
What To Do If You Suspect Prostatitis
Start with a self-examination. Ask yourself about stress in your life and think through ways you can easily decrease your stress.
Try over-the-counter anti-inflammatories and see if they help. If that doesnt solve the problem, talk to your doctor. Worrying about having a serious condition could worsen your symptoms.
Think you have prostatitis? Talk to your doctor. If you do not have a doctor, find one near you.
Recommended Reading: Perineural Tumor
Latest Men’s Health News
At the start, prostate cancer does not cause symptoms. As the cancer grows, you may have trouble urinating. Some men need to urinate often, especially at night. Others have pain or burning during urination, blood in the urine or semen, pain in the back, hips, or pelvis, and painful ejaculation.
To find out if these symptoms are caused by prostate cancer, your doctor will ask about your past medical problems and your family’s medical history. He or she will perform a physical exam. During the exam, your doctor will put a gloved finger into your rectum to feel your prostate for hard or lumpy areas.
Your doctor may also do a blood test to check the prostate-specific antigen level. PSA levels can be high in men with an enlarged prostate gland or with prostate cancer. You may also need an ultrasound exam that takes computer pictures of the prostate.
If tests show that you might have cancer, your doctor will want to confirm this with a biopsy. He or she will take out tiny pieces of the prostate to look for cancer cells. Your doctor may want to do a biopsy again to re-check the results.
Treatment for prostate cancer depends on whether cancer is in part or all of the prostate or if it has spread to other parts of the body. It also depends on your age and overall health. Talk with your doctor about the best treatment choice for you. You may want to ask another doctor for a second opinion.
Prostate Tests And Scans
Diagnostic tests for prostate abnormalities include physical examination, ultrasound examination, study of prostate biopsy samples and laboratory tests to detect the levels of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. To detect an enlargement of the prostate gland, a doctor may conduct a direct rectal examination of the prostate gland.
Ultrasound examination of the prostate gland through the rectal route can also detect an enlargement of the prostate gland. An increase in the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood occurs in both prostatic hypertrophy and prostate cancer. Prostate biopsy via the rectal route may then be done to rule out or confirm the presence of prostate cancer.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Va Disability Rating For Prostate Cancer
Testing Options For Prostate Cancer
There is no one age for prostate cancer testing, but the American Cancer Society makes recommendations about screenings. According to the ACS, patients in any of these groups should consider asking their doctor about testing:
- Men age 50 or older who have an average risk of prostate cancer and a life expectancy of at least 10 more years
- Men age 45 or older with a high risk, including African-American men and those with a first-degree relative who had prostate cancer before age 65
- Men age 40 or older who have a higher risk, such as more than one first-degree relative diagnosed with prostate cancer at an early age
Location Of Prostate Pain
Prostate pain is felt and described by patients in different ways. An individual suffering from prostate pain may describe the feeling as emanating from other structures in the pelvis and lower abdominal region. For example, a patient may describe prostate pain as pelvic pain, groin pain, bladder pain, lower back pain, pain in the testes, pain in the tailbone, and pain in the rectum.
In order to identify prostate pain as such, one must know the location of the prostate gland. The prostate gland lies in front of the rectum, below the urinary bladder, behind the pubic symphysis and above the levator ani muscles. Pain attributed to any of these surrounding structures may actually originate from the prostate gland.
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Pathophysiology Of Prostate Pain
Most commonly men who are affected with enlarged prostate donât exhibit particular symptoms. One important symptom of enlarged prostate is urine incontinence. Patient cannot sit for a long of period of time, especially without voiding. If we go through the anatomy of male, the flow of urine is from bladder through urethra. In case of prostate enlargement, extreme pressure will be on urethra. In this case, to overcome the situation of narrowing of urethra, the bladder tries to contract with more strength in order for it to push the urine out of the body. The bladder muscles will become sensitive, stronger and thicker. This will lead to altered function of the bladder in which condition it will void small quantity of urine.
Risk Factors For Prostatitis:

Many times, the exact cause for prostatitis is not fully determined or understood. However, there are certain risk factors that may increase your chance of acquiring prostatitis. The most common risk factors include:
- Risky sexual practices: As described above, a sexually transmitted disease may cause prostatitis. Therefore, practicing safe sexual practices can reduce a mans chances of acquiring prostatitis.
- Prostate stones
- Trauma to rectal/testicular area
You May Like: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
What Is The Outlook
It is difficult to give an outlook . Your symptoms may last a long time, although they may ‘come and go’ or vary in severity. Painkillers can keep discomfort to a minimum.
Most men diagnosed with chronic prostatitis/CPPS tend to have an improvement in their symptoms over the following six months. In one study, about a third of men had no further symptoms one year later. In another large study, one third of men showed moderate to marked improvement over two years.
Symptoms For Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
The symptoms of CPPS vary from man to man, but may include:
- pain in the area between your back passage and testicles
- pain in the lower part of your stomach area
- pain in your penis, especially the tip
- pain in your testicles
- pain in your back passage and lower back
- pain in your inner thighs
- sexual problems such as difficulty getting or keeping an erection, pain or burning when you ejaculate, and premature ejaculation
- urinary problems such as feeling like you havent emptied your bladder properly, needing to urinate more often or urgently, or mild discomfort or pain when you urinate
- bowel problems such as bloating or diarrhoea.
In rare cases, there can be blood in the semen. This can also be a sign that there is something else wrong, so always speak to your doctor if you have blood in your semen.
Speak to your GP if you have any of the symptoms listed here. You can also call our;Specialist Nurses;if you have any questions.
The chronic prostatitis symptom index
If you have CPPS, the chronic prostatitis symptom index can help you to explain your symptoms to your doctor and can help them to monitor your treatment. You might find it useful to download a copy of;these questions. You can use this to show your GP.
You May Like: Would You Expect A Male With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia To Have Difficulty With Ejaculation
What Is Prostate Pain
Prostatodynia is the medical term for prostate pain. It may also include other sensations like prostate discomfort and is a sign of prostate problems. Pain and discomfort may be seen in all three of the main conditions affecting the prostate gland prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer. The pain may vary in severity and nature radiating to surrounding structures and extending to the lower back or even the tip of the penis.
At times, prostate pain may involve a large area of the lower abdomen or the entire pelvis. It is not uncommon for no pain to be present, especially in mild BPH and chronic prostatitis, with discomfort or pain only being reported during acute exacerbation and a secondary prostate gland infection.
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Once a tumor causes your prostate gland to swell, or once cancer spreads beyond your prostate, you may have symptoms including:
- The need to pee often, especially at night
- Trouble starting or stopping a stream of urine
- A weak stream or one that starts and stops
- Leaking pee when you laugh or cough
- Not being able to pee standing up
- Pain or burning when you pee
- Pain or burning when you ejaculate
- Less fluid when you ejaculate
- Blood in your pee or semen
- Pressure or pain in your rectum
- Pain or stiffness in your lower back, hips, pelvis, or thighs
- New trouble getting an erection
These arenât symptoms of the cancer itself. They happen because the cancer growth is blocking your prostate.
Don’t Miss: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
Identifying Potential Prostate Problems
Natural Treatment Options For Prostate Pain
As prostate pain is associated with all three conditions like prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatitis so it is good to find some natural remedies for such prostate troubles. Although, medical science has developed several medications and treatment solutions for this condition but natural therapies are always the most trustworthy options. The major reason behind using home based remedies is that they do not lead to any side effect; so person can stay safe.
Read Also: What Are The Symptoms Of Perineural Invasion
Urinating Frequently During The Day
It may be more difficult to notice a change in frequency during the day than at night. Most of us dont go around counting how many times we use the washroom in a given day!
Besides, whats normal, anyway?
Normal urination during the day is considered to be within a range offour to seven times for most healthy adult men. If youre going more often than this, it could indicate a prostate issue.
It can be easy to miss this sign. Drinking more water or caffeinated beverages than usual can be an easy explanation for a few extra trips.
Even a night out for dinner with a few more glasses of beer than usual can cause several extra trips to the bathroom because alcohol is a diuretic, meaning it triggers anincrease in urine production.
Diuretics cause your kidneys to process more salt and water out into your urine, resulting in increased volume that makes you need to go more often.Source:WonderWhizKids.com
But like your nighttime routine, if you notice an ongoing pattern of having to go more often during the day, ask your doctor about it. A simple blood test and rectal examination is often the first diagnostic step, which is quick and painless.;
What Are The Different Types Of Pain In Prostate

Pain in prostate may be classified according to the location , and the cautions.
1 Painful prostate by location
Actually, pain cannot be described exactly where it is. Sometimes, you may feel it at the lower part of your tummy , and in sometimes you may feel only prostate back pain.
Some other times the pain is present while urinating or during orgasm. Keep in mind that pain location is also tightly related to various diseases and conditions of prostate.
2 Pain in prostate by causes
It is also called the inflammation of prostate and might have an infectious or non-infectious nature depending on the cause.
The pain is located in the pelvis and you may feel pain even during urination. In this case treating the principle cause of prostatitis and alpha-blockers, and some pain relievers would be effective.
In any case, do not hesitate to seek medical help.
Actually, at the;very first stages,;prostate cancer doesn’t have any clear symptoms. The most common problems would be related to urine flow and similar troubles.
Meanwhile in the;advanced stages, when the cancer has spread in the surroundings, then appear the pain depending on the invaded organ. So, you may feel leg pain, like not moving your leg, or back pain.
Recommended Reading: Is Viagra Good For Enlarged Prostate
How Is Prostatitis Treated
Treatment depends on the type of prostatitis.
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Treatment for chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome aims to decrease pain, discomfort, and inflammation. A wide range of symptoms exists and no single treatment works for every man. Although antibiotics will not help treat nonbacterial prostatitis, a urologist may prescribe them, at least initially, until the urologist can rule out a bacterial infection. A urologist may prescribe other medications:
- silodo
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors such as finasteride and dutasteride
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugsalso called NSAIDssuch as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen sodium
- glycosaminogly
- cans such as chondroitin sulfate
- muscle relaxants such as cyclobenzaprine and clonazepam
- neuromodulators such as amitriptyline, nortriptyline , and pregabalin
Alternative treatments may include
- warm baths, called sitz baths
- local heat therapy with hot water bottles or heating pads
- physical therapy, such as
- Kegel exercisestightening and relaxing the muscles that hold urine in the bladder and hold the bladder in its proper position. Also called pelvic muscle exercises.
- myofascial releasepressing and stretching, sometimes with cooling and warming, of the muscles and soft tissues in the lower back, pelvic region, and upper legs. Also known as myofascial trigger point release.
