Proton Therapy Vs Other Prostate Cancer Treatments
Is proton therapy superior to hormone therapy or chemotherapy? The answer might not be that simple because it depends on what you need.
Each treatment method has its pros and cons. They also have specific applications, and using them or not in a determined patient depends on comprehensive studies that evaluate what works better for most.
However, for educative purposes, lets make a brief comparison between proton therapy and other prostate cancer treatments:
What To Expect From Proton Therapy
The proton therapy process is very similar to conventional radiation therapy. With both, well start with a consultation and then a planning session, Dr. DeNunzio says. Patient treatment times are generally similarabout 2030 minutes per appointment.
Both types of therapy are painless during treatment and similar in the types of side effects that may arise. However, proton therapy can often reduce the chance of these side effects from developing during treatment or in the months or years following.
Many people are living more years after cancer treatment, Dr. DeNunzio says. Trying to mitigate the long-term impact of cancer therapy is incredibly importantwe are not just thinking about what we are trying to do now, but five, 10, even 20 or more years down the line.
Da Vinci Robotic Prostatectomy/robotic
The surgery is performed by a trained and skilled surgeon through the use of a computer-enhanced robotic surgical system. Instead of the large incision used in open surgery, da Vinci surgeons make just a few small incisions similar to traditional laparoscopy. The da Vinci System also features a magnified 3D high-definition vision system and special wristed instruments which precisely translates the hand movements of the surgeon.
Pros:
- Catheter removed in just 5-7 days
- More maneuverability and precision for the robotic surgeon
- More visibility of prostate and surrounding tissue/organs
- Prostate cancer is removed with a higher cancer cure rate when performed by a skilled robotic surgeon
Cons:
- Possible erectile and urinary side effects post surgery when procedure is performed by a less-skilled and inexperienced surgeon
Read Also: Cold Medicine For Enlarged Prostate
Who Is A Good Candidate
In most cases, you will be a good candidate for proton therapy if you were initially offered radiotherapy as an option. Patients who receive radiotherapy usually have no problems being a candidate for proton treatment. They are usually patients in an early stage or those with localized prostate cancer. It is also useful to keep advanced cancer under control for as long as possible and treat recurrent prostate cancer cases.
However, some patients may not benefit from proton therapy if they have one of these problems :
- In patients with hip replacements, because proton beams often cant reach beyond the prosthesis. In some proton therapy centers, these patients can still get a session when a hip replacement is limited to one side. But bilateral replacement makes it impossible to treat the patient with proton beam therapy.
- In patients with advanced prostate cancer in which treating the pelvic lymph nodes is fundamental. Since proton beam radiation is less likely to reach other tissues than the prostate, it is not applicable when treating surrounding lymph nodes.
- In overweight patients, because the proton beam can only go through a determined depth. This depth depends on the beams energy, and some centers may have a higher energy device that solves the problem.
More Than 10000 Prostate Patients Treated With Proton Therapy At Llumc Proton Treatment Center
![[Full text] Proton beam therapy: clinical utility and current status in ... [Full text] Proton beam therapy: clinical utility and current status in ...](https://img.healthyprostateclub.com/wp-content/uploads/full-text-proton-beam-therapy-clinical-utility-and-current-status-in.jpeg)
The James M. Slater, MD Proton Therapy Treatment and Research Center has treated more than 10,000 prostate patients with proton therapy since it opened in 1990. No other proton treatment center in the world has such a contribution to health. And as proton research continues, the proton treatment will continue to improve the quality of life in men with prostate cancer.
Also Check: How To Check If Prostate Is Enlarged
Literature Search Results And Characteristics
Our searches of four databases yielded 6,378 articles. After 413 duplication records were removed, titles and abstracts of these records were screened for inclusion. Full texts of 46 records were read, and 33 studies met the inclusion criteria .
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the literature screening process and results.
Twenty PBT-related studies involved 48,765 patients with a median mean age of 66 years old. Median follow-up across all studies was 43.4 months . The included studies were published from 2010 to 2020. Most of the studies were from the USA , five from Japan , and one from Korea . For the trials from the USA, most of the studies set irradiation dose at 7082 GyE delivered in 544 fractions. For the five trials from Japan, the irradiation dose was usually set at 6380 GyE delivered in 2039 fractions. For one trial from Korea, they set irradiation dose at 3560 GyE delivered in 520 fractions. The basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Basic characteristics of included studies.
Physical Comparison Of Protons And Imrt
To have a fair assessment of the dosimetric trade-offs between protons and photons, one must compare proton therapy to the most conformal type of photon therapy currently available, which is intensity-modulated radiation therapy . With IMRT, more beams are used than in conventional three-dimensional radiation therapy, and the fluence of each beam is modulated to create a highly target-conformal dose distribution capable of bending around critical normal structures such as the anterior rectal wall. In the United States, IMRT is becoming the dominant method of delivering external-beam radiation to the prostate.
Trofimov et al recently performed a dosimetric comparison of 10 patients whose treatment was planned with both protons and photon IMRT to a total dose of 79.2 Gy . The proton therapy was planned using two lateral parallel opposed beams, while the photon IMRT was planned with seven coplanar beams . This study found that IMRT actually yielded better dose conformality , reflecting the fact that a greater volume of nontarget tissue received the prescription dose of 79.2 Gy with proton therapy than with IMRT. Correspondingly, the V70 of the bladder was 50% higher with proton therapy than with IMRT, although the V70 of the rectum was not significantly different.
FIGURE 1
Protons vs Photons
FIGURE 2
Dose Difference Between IMRT and Proton Plans
Also Check: What Is The Main Cause Of Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer Treatment Near Me
Proton therapy and CyberKnife are both options for prostate cancer treatment. But the experts at CyberKnife Miami recommend getting a second opinion and a consultation to see which treatment is right for you from a lifestyle and cost perspective.
We are happy to be your second opinion and answer any questions you may have about all prostate cancer treatment options, and which one is right for your particular case.
If you are diagnosed with prostate cancer, call CyberKnife Miami for a consultation. Our goal is to get you back to your life cancer free with minimal to no downtime.
If you would like to find out more about prostate cancer treatment with CyberKnife, call us at 305-279-2900 or go to our prostate cancer website now for more information.
With The Beam of Life, CyberKnife Miami is giving thousands of people new hope in treating various cancers where there was none. Visit the CyberKnife Center of Miami located in Miami, Florida.
Treatment And Analysis Of Data
The value of the PSA at the time of failure was kept as the last PSA record for that patient, discarding subsequent PSA values, because they would be influenced by androgen deprivation.
The cases confirmed as loss in the follow-up were censored on the date referring to the last follow-up recorded in the medical record. Patients who died due to causes unrelated to prostate cancer or its treatment were censored at the date of death.
The cases were stratified according to risk classification proposed by DAmico,2121 DAmico AV. Combined-modality staging for localized adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Oncology . 2001 15:1049-59 discussion 1060-2,1064-5,1069-70,1073-5.considering: low risk as patients with PSA 10ng/mL, a Gleason score 6 and staging T2a intermediate risk as patients with staging of T2b or PSA between 10 and 20ng/mL, or Gleason score of 7 and high risk as patients with PSA > 20ng/mL or Gleason score 8 or staging T2c.1414 Comploj E, Pycha A. Experience with radical perineal prostatectomy in the treatment of localized prostate cancer. Ther Adv Urol. 2012 4:125-31.,2121 DAmico AV. Combined-modality staging for localized adenocarcinoma of the prostate. Oncology . 2001 15:1049-59 discussion 1060-2,1064-5,1069-70,1073-5.
We used the Epi Info 2000 program for input and descriptive analysis of the data and Stata version 9.0, for survival analysis and prognostic factors.
The study was authorized by the ethics committee of the Federal University of Juiz de Fora .
Also Check: Is Weight Loss A Sign Of Prostate Cancer
Who Was In The Study
The study included 2,550 men from across the United States with localized prostate cancer. All the men started the study within six months of being diagnosed. Of these, 74 percent were white, and 26 percent were other races. The average patient age was 64, and all were younger than 80. Of the surgeries, 76 percent used a laparoscope, a small robotic instrument with a video camera that works through small cuts to the body. Among the men who chose radiation, 45 percent also took medicines to reduce male hormones.
Proton Therapy Advantages And Disadvantages
Proton radiation may represent an incremental improvement over IMRT due to the reduced exposure of surrounding normal body tissues to radiation. Therefore, in the situations outlined above where IMRT would normally be considered, men may prefer to choose proton radiation over IMRT. The purported advantages of proton radiation over IMRT remain theoretical and clinically unproven. No head to head studies comparing the IMRT and proton radiation exist.
Disadvantages associated with proton radiation are related to its high cost and the fact that not all insurance programs cover proton radiation. In addition, there are relatively few centers doing proton radiation, so geographic inconvenience can be a major factor considering that numerous visits are required over a 5 to 9-week period.
Men considering treatment for prostate cancer need to do their homework. Side effects from radiation can be irreversible. The selection of optimal radiation varies with patient circumstances. Many factors need to be considered when radiation is contemplated.
Recommended Reading: How Far Inside Is The Prostate
What Is Proton Therapy
Proton therapy is a branch of radiation treatment. It works like radiation therapy and can treat different types of cancer. Similar to radiation therapy, proton therapy can be a standalone therapy against cancer. However, in most cases, it is combined with additional methods to fight off cancer cells.
To understand proton therapy, it is essential to understand the basics of radiation therapy.
In conventional radiotherapy, you have high-energy X-rays passing through the body. The X-ray radiation is placed in the area where cancer is. Thus, it should destroy cancer tissue. But in doing so, normal tissue is also destroyed or similarly affected.
In prostate cancer, placing a radiation beam targeting the prostate gland exposes the rectum, the bladder, and other organs. As such, external beam radiation therapy complications include urinary symptoms, rectal bleeding, diarrhea, and more.
In an attempt to solve this problem, intensity-modulated radiation therapy was developed. It is known to cause less damage to surrounding tissues. Another option is using proton therapy treatment, which delivers radiation traveling in proton beams.
Benefits Of Proton Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Conventional radiation treatment is also known as photon treatment, which is different from proton therapy.
In conventional radiation treatment, high-energy X-rays are used to target and destroy cancer cells in the prostate. However, X-rays can damage healthy tissue as they pass through your body. This can lead to complications in nearby organs such as the bladder and rectum.
In proton therapy, radiation is delivered in proton beams. The key difference from X-rays is that proton beams stop once theyve delivered their energy to the target.
By using proton therapy, doctors can target prostate cancer more precisely and at great intensity with less risk of damaging surrounding tissue.
Recommended Reading: How To Have A Prostate Orgas
How Proton Therapy Works
A machine called a synchrotron or cyclotron speeds up protons. The high speed of the protons creates high energy. This energy makes the protons travel to the desired depth in the body. The protons then give the targeted radiation dose in the tumor.
With proton therapy, there is less radiation dose outside of the tumor. In regular radiation therapy, x-rays continue to give radiation doses as they leave the persons body. This means that radiation damages nearby healthy tissues, possibly causing side effects.
Recommended Reading: How Do I Know If I Have An Enlarged Prostate
Controversies In Proton Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Curtis Bryant, Randal H. Henderson, Bradford S. Hoppe, William M. Mendenhall, R. Charles Nichols, Zhong Su, Zuofeng Li, Nancy P. Mendenhall
Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Florida College of Medicine, Jacksonville, FL, USA
Contributions: Conception and design: C Bryant Administrative support: NP Mendenhall Provision of study materials or patients: C Bryant Collection and assembly of data: C Bryant Data analysis and interpretation: C Bryant Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Keywords: Particle therapy genitourinary cancer
Submitted Jul 26, 2016. Accepted for publication Aug 03, 2016.
doi: 10.21037/cco.2016.08.02
Recommended Reading: How To Slow Prostate Cancer
Clinical Efficacy And Safety Of Proton And Carbon Ion Radiotherapy For Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review And Meta
- 1Evidence-Based Medicine Center, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China
- 2Evidence-Based Social Science Research Center, School of Public Health, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Evidence-Based Medicine and Knowledge Translation of Gansu Province, Lanzhou, China
- 4Health Technology Assessment Center of Lanzhou University, School of Public Health, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China
- 5Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
- 6The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China
- 7The First School of Clinical Medicine, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China
- 8Institute of Modern Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou, China
- 9Lanzhou Heavy Ions Hospital, Lanzhou, China
Background: Carbon ion radiotherapy and proton beam therapy are promising methods for prostate cancer, however, the consensus of an increasing number of studies has not been reached. We aimed to provide systematic evidence for evaluating the efficacy and safety of CIRT and PBT for prostate cancer by comparing photon radiotherapy.
Communicate With Your Doctor
The most critical recommendation to reduce your risk is to keep in communication with your doctor. Your case is different from any other, and you deserve personalized treatment. These recommendations should adapt to your case, too. Thus, talk to your doctor and follow recommendations. If your doctor considers it appropriate to screen with PSA testing, talk about the pros and cons with him. And if you need treatment, discuss the benefits and drawbacks of your treatment options. Ask questions and inform yourself about prostate cancer and what to do about it.
Also Check: How To Lower The Risk Of Prostate Cancer
Protons For Dose Escalation: Evidence From Clinical Trials
No randomized trials have directly compared the efficacy of protons and photons in the treatment of clinically localized prostate cancer. Clinical experience with the use of protons in dose escalation comes from the combined Loma Linda/MGH trial mentioned above. In this study, all patients received 50.4 Gy in 1.8-Gy fractions to the prostate and seminal vesicles using conformal photon therapy in a four-field configuration. The randomization was to either a 19.8-GyE or 28.8-GyE prostate boost via protons in 1.8-GyE fractions, to a total dose of 70.2 or 79.2 GyE. Overall, treatment to the higher dose with protons was tolerable, but came at the cost of an increase in late grade 2 rectal morbidity .
However, new preliminary data from an analysis of patients in this trial who received a detailed validated quality-of-life questionnaire suggest that there is no significant difference in long-term patient-reported quality of life between the high-dose and conventional-dose arms. This evidence is a clear proof of principle that protons can be used to escalate dose without causing a significant difference in patient-reported quality of life, which is more relevant than physician-reported measures of toxicity.
How Are They Used
With photon radiation, we can minimize, but are not always able to eliminate, the radiation dose that a neighboring organ receives, says Hani Halabi, MD, Radiation Oncologist at Cancer Treatment Centers of America® , Atlanta.
Advanced technology allows radiation oncologists to better match the size and shape of the tumor and to follow a tumor as it moves while a patient is breathing. But radiation may still affect parts of the body other than the area being treated.
We can modify the beams, change the angles and modify the intensity of the radiation to make the normal organ get less radiation, and keep the radiation exposure to the organ within acceptable and tolerable levels, Dr. Halabi says. But it will not be zero.
Protons have physical mass and can be stopped at a certain depth inside tissue. Without the exit dose, protons improve the sparing of surrounding organs and normal tissues. This offers several potential advantages over photon therapy, including:
- It may result in fewer side effects because less healthy tissue is irritated by the radiation.
- Because of the enhanced ability to spare surrounding organs, proton therapy may allow for higher doses of radiation to be delivered to the cancer compared to photons.
With proton therapy, we can stop the radiation at a certain depth in the body, Dr. Halabi says. This can significantly improve our ability to spare the neighboring organs from receiving radiation.
You May Like: What Is Removed During Prostate Surgery
Protons: A Different Mechanism
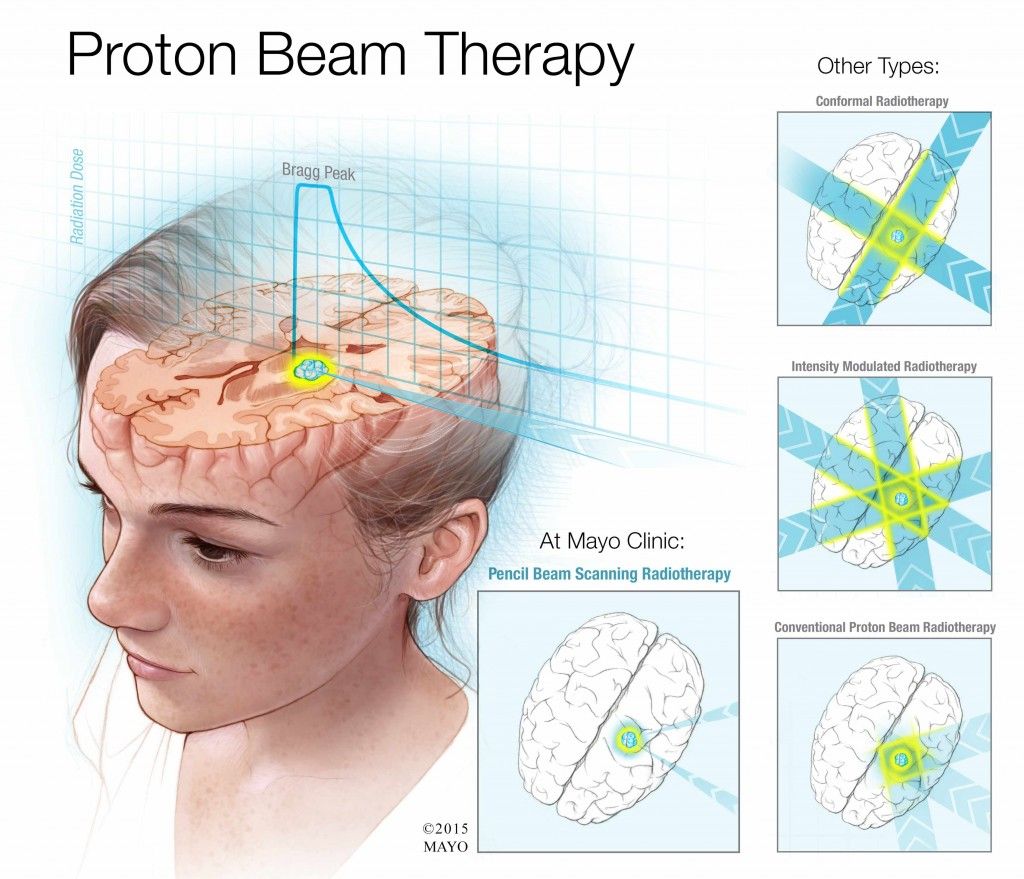
Protons can also be administered by two methods. The older method includes large beams of passively scattered protons that are shaped with the use of high-density blocks or apertures to shape the large beam as it exits the nozzle. Compensators are employed within the beam to alter the beam profile to better conform the SOBP to the actual tumor. A second, newer method employs a very narrow, pencil thin beam to paint the dose on the target, and no blocks or compensators are needed. The pencil beam is swept in a raster pattern back and forth across a target guided out of the nozzle by magnets . This allows the delivery of intensity-modulated proton beam therapy , with a greater ability to conform the dose to an irregularly shaped target. Although not widely available, many new facilities are being planned with pencil beam-only systems.
Pencil beam scanning. The pencil beam is swept in a raster pattern back and forth across a target. Reproduced with permission from Mayo Clinic News Network.
aAs determined by Phoenix criteria. bAs determined by American Society for Therapeutic Radiology Oncology criteria. c Determined by a rise in prostate-specific antigen to > 50% than the nadir and > 2 ng/mL.
2D, two-dimensional 3D, three-dimensional GI, gastrointestinal GU, genitourinary HD, high dose IMRT, intensity-modulated radiation therapy LD, low dose.
