Survival Statistics For Prostate Cancer
Survival statistics for prostate cancer are very general estimates and must be interpreted very carefully. Because these statistics are based on the experience of groups of people, they cannot be used to predict a particular person’s chances of survival. In general, most men diagnosed with prostate cancer do not die from the disease itself and will die from other causes.
There are many different ways to measure and report cancer survival statistics. Your doctor can explain the statistics for prostate cancer and what they mean to you.
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of prostate cancer is 90%, it means that men who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as men who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Overview Of The Staging System
After a thorough assessment by your oncologist, your cancer will be assigned a stage between I and IV. Prostate cancer stages are based on the American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM system. Using the TNM system, your oncologist:
- Examines the tumor
- Determines if the cancer has spread to any lymph nodes
- Assesses whether the cancer has metastasized
- Considers the prostate-specific antigen level from blood testing
- Assigns a grade group based on how abnormal the cancer appears under a microscope
With this information in mind, you can better understand how stages are assigned and what they mean for patients in general.
Read Also: Surgical Options For Enlarged Prostate
Understanding Prostate Cancers Progression
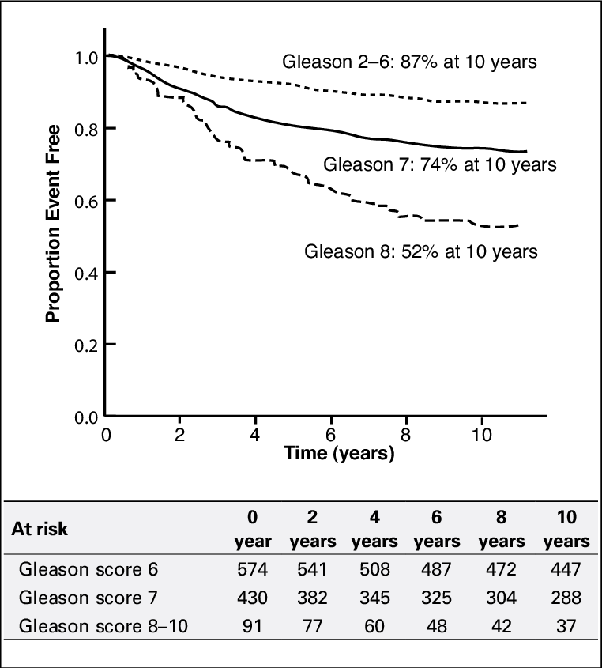
To determine the appropriate treatment, doctors need to know how far the cancer has progressed, or its stage. A pathologist, the doctor trained in analyzing cells taken during a prostate biopsy, will provide two starting pointsthe cancers grade and Gleason score.
- Cancer grade: When the pathologist looks at prostate cancer cells, the most common type of cells will get a grade of 3 to 5. The area of cancer cells in the prostate will also be graded. The higher the grade, the more abnormal the cells.
- Gleason score: The two grades will be added together to get a Gleason score. This score tells doctors how likely the cancer is to grow and spread.
After a biopsy confirms prostate cancer, the patient may undergo additional tests to see whether it has spread through the blood or lymph nodes to other parts of the body. These tests are usually imaging studies and may include a bone scan, positron emission tomography scan or computed tomography scan.
Prostate cancer treatment: The care you need is one call away
Your multidisciplinary team will work with you to develop a personalized plan to treat your prostate cancer in a way that fits your individual needs and goals.
Psa Levels After Treatment
A continuous rise in your PSA level can be the first sign that your cancer has come back. This should be picked up by your regular PSA tests.
The exact change in PSA level that suggests your cancer has come back will depend on which treatment you had. Speak to your doctor or nurse about your own situation.
Your PSA level should drop so low that its not possible to detect it at six to eight weeks after surgery. This is because the prostate, which produces PSA, has been removed. A rise in your PSA level may suggest that you still have some prostate cancer cells.
After radiotherapy or brachytherapy, your PSA should drop to its lowest level after 18 months to two years. Your PSA level wont fall to zero as your healthy prostate cells will continue to produce some PSA.
Your PSA level may actually rise after radiotherapy treatment, and then fall again. This is called PSA bounce. It could happen up to three years after treatment. It is normal, and doesnt mean that the cancer has come back.
If your PSA level rises by 2 ng/ml or more above its lowest level, this could be a sign that your cancer has come back. Your doctor will continue to check your PSA level and will talk to you about further tests and treatment options.
Also Check: Prostate And Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
Don’t Miss: What Causes A Man’s Prostate To Enlarge
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
Stage 4 prostate cancer is the final stage in the development of prostate tumors. By this stage, cancer cells have spread to parts of the body that are distant from the prostate gland. Once again, stage 4 prostate cancer branches into 2 subcategories.
- Stage IVA: Any PSA value, any Gleason score. There are cancer cells around lymph nodes.
- Stage IVB: Any PSA value, any Gleason score. There are cancer cells around lymph nodes and other parts of the body, including organs far away from the prostate gland.
The metastatic prostate cancer survival rate drops to a 30% chance to survive in the first 5 years of their diagnosis. Treatment plans can include anything at this point, be it hormone therapy, chemotherapy, prostatectomy, external beam radiation, or a mixture of several of these options.
Read Also: Almond Milk And Prostate Cancer
What Can Affect My Outlook
No one can tell you exactly what will happen. How prostate cancer affects you will depend on many things.
- Your stage Whether your cancer is localised, locally advanced, or advanced.
- Your Gleason score or grade group The higher your Gleason score, the more aggressive the cancer, and the more likely it is to spread.
- Your treatment options You may be able to have treatment aimed at getting rid of the cancer. Or you may be able to have treatment to keep the cancer under control. Read more about choosing your treatment.
- Your health If you have other health problems, you may have fewer treatment options. And you may be more likely to die from another condition, such as heart disease.
- Your PSA level After youve been diagnosed, PSA tests are a good way of monitoring your prostate cancer and seeing how youre responding to treatment.
- How successful your treatment is Your treatment may be successful at getting rid of your cancer or keeping it under control. But for some men, treatment may not work as well as expected.
You May Like: Does An Enlarged Prostate Affect A Man Sexually
What Is Localized Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the prostate gland. Localized prostate cancer has not spread outside the gland. Early prostate cancer usually doesnt cause symptoms.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men. Most men who get it are older than 65. If your father, brother, or son has had prostate cancer, your risk is higher than average.
Men of African descent have the highest rates of both prostate cancer and deaths from it.
About 21,000 men are diagnosed with prostate cancer in Canada every year.footnote 1 In the United States, about 12 out of 100 men in the U.S. will be diagnosed with prostate cancer sometime in their lifetime.footnote 2 But most men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer dont die from prostate cancer.
Unlike many other cancers, prostate cancer is usually slow-growing. When prostate cancer is found earlybefore it has spread outside the glandit may be cured with radiation or surgery.
Prostate cancer that has grown beyond the prostate is called advanced prostate cancer. Treatment choices are different for that stage of cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can Prostatitis Go Away On Its Own
Castrate Refractory Prostate Cancer: A Wider Range Of Options
In this section, we explain the treatments available at Birmingham Prostate Clinic for patients once their disease becomes resistant to hormone treatment, called castrate refractory prostate cancer. Two types of treatments are needed to:
- Control the cancer and prevent further spread of cancer
- Control or prevent the symptoms caused by the spread of prostate cancer to the bones
Recommended Reading: When Do Guys Need A Prostate Exam
Prognosis For Prostate Cancer
It is not possible for a doctor to predict the exact course of a disease, as it will depend on each person’s individual circumstances. However, your doctor may give you a prognosis, the likely outcome of the disease, based on the type of prostate cancer you have, the test results, the rate of tumour growth, as well as your age, fitness and medical history.
Prostate cancer often grows slowly and even more aggressive types tend to grow more slowly than other types of cancer. If diagnosed early, prostate cancer has one of the highest five year survival rates.
Definition Of Patient Outcomes And Evaluation Metrics
The relatively long survival time and low mortality rate of localized prostate cancer pose a great challenge in risk estimation. To get a more accurate disease prognosis evaluation over a shorter and practical timescale, we define a composite outcome as our event of interest:
-
Metastatic diseases
-
Prostate cancer mortality.
The event time is the earliest date of any of these three events. The censoring time is 1 year after the last PSA test. In cases where patients died of other causes before censoring, the censoring time instead is the time of death.
For better insight into the model performances over time, we calculate the time-dependent concordance-index \\):
Here, \\) is the cumulative distribution function at time t, given input feature \. To account for the high censoring ratio, we adjust \\) with the inverse probability of censoring weights. Additionally, we test our models against the more conventional outcome, namely, prostate cancer mortality. In this study, we set the truncation time t to be 2, 5, and 10 years after diagnosis.
Depending if the input \ is time-dependent, we employ two DL models, RDSM and Deep Survival Machine . As a benchmark, we also consider two popular machine learning models, Random Survival Forest and Gradient Boosting Machine , along with the classical Cox model,,,. All three benchmark models are implemented using the scikit-survival package.
Recommended Reading: Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
What Is The Most Effective Treatment For Prostate Cancer
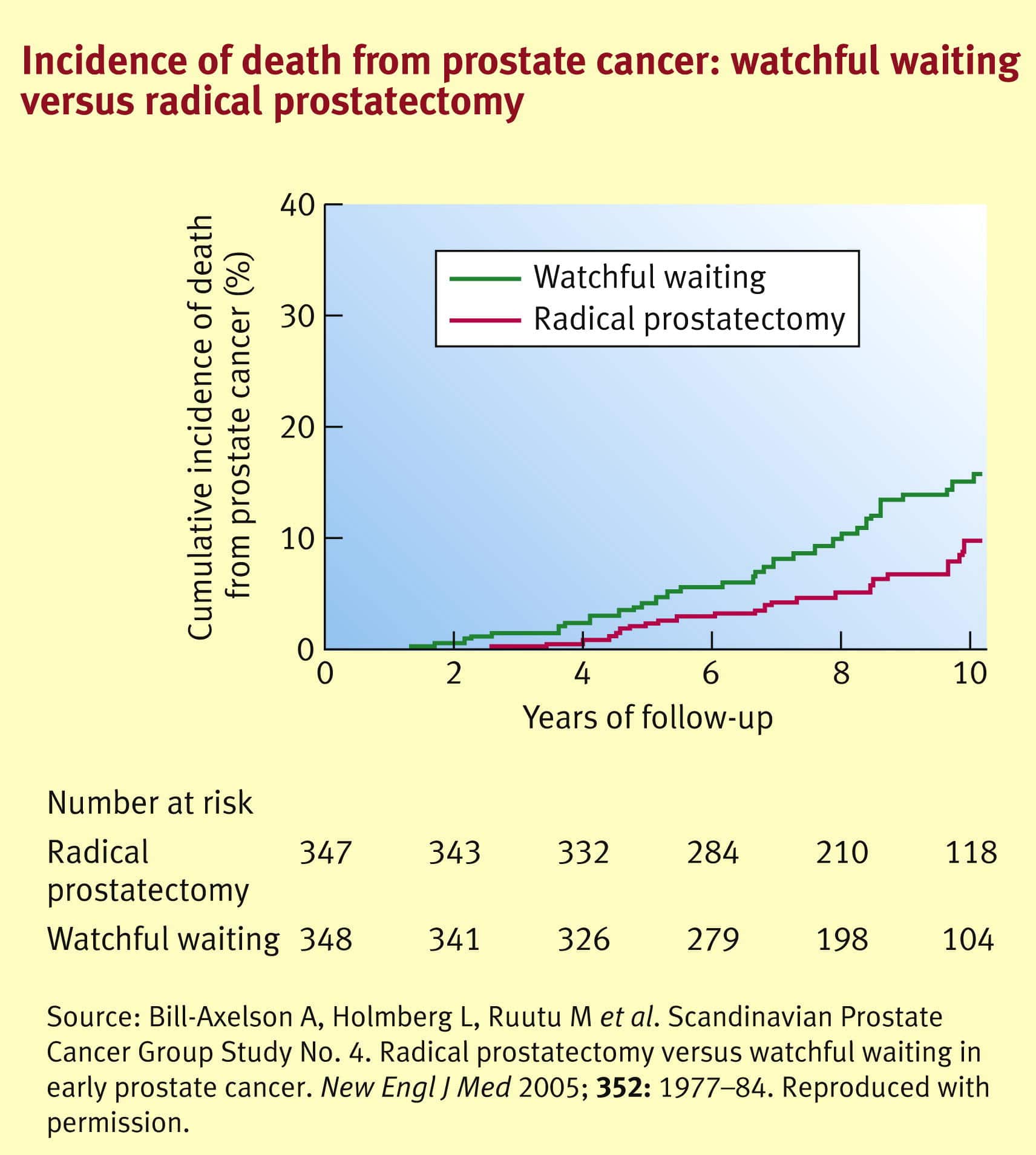
For most men with prostate cancer, the most effective treatment will be surgery to remove the tumor or the entire prostate. The different types of prostate cancer surgery include:
- Radiofrequency ablation A minimally invasive procedure, RFA uses ultrasound or another imaging technique to guide a needle electrode into the cancerous tumor. The electrode then emits high-frequency electrical currents to destroy cancer cells.
- Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy During this procedure, a surgeon will remove the entire prostate. The surgeon will make a few small incisions and insert special instrumentsone of which has a video camera attachedto complete the procedure.
- Robotic surgery For certain procedures, surgeons can use robotic assistance, which can improve precision.
Some patients may also undergo radiation therapy after their surgery to eliminate any lingering cancer cells.
As with other cancers, prostate cancer has the most favorable survival rates when patients are diagnosed early. When prostate cancer is detected before it has spread to the lymph nodes , it is most responsive to treatment and, therefore, more easily cured.
Learn More About Prostate Cancer Care At Rcca
If youve been diagnosed with prostate cancer or are concerned about potential symptoms, contact RCCA today. Our team of cancer care specialists will assess the stage of your cancer using the latest diagnostic methods and work with you to design a fully individualized care plan that includes advanced treatment options, the potential for clinical trials, and support that addresses physical and emotional well-being. To speak with a representative right away, please call .
Read Also: What Is A Prostate Scrape
What Is Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer develops in the prostatea small gland that makes seminal fluid. It is one of the most common types of cancer in men. Prostate cancer usually grows over time and, in the beginning, usually stays within the prostate gland, where it may not cause serious harm. While some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may need minimal or no treatment, other types are aggressive and can spread quickly.
Prostate cancer that is caught early has a better chance of successful treatment.
Prostate Cancer Statistics And Survival Rates
Prostate cancer is the second most prevalent cancer¹ among men in the United States.
The prostate gland plays an essential role in the production of seminal fluid. Cancer in the prostate often develops slowly and remains inside the gland. It can be more aggressive in some cases, which means it develops fast and can spread beyond the prostate.
Luckily, prostate cancer typically has a favorable prognosis. It is very curable in its early stages, and many people are treated effectively.
Also Check: Can You Feel Prostate Cancer
Gleason Prostate Cancer Score
1960s as a way to measure how aggressive your prostate cancer may be.
A pathologist determines your Gleason score by looking at a biopsy of your prostate tissue under a microscope. They grade the cells in the biopsy on a scale of 1 to 5. Grade 1 cells are healthy prostate, whereas grade 5 cells are highly mutated and dont resemble healthy cells at all.
The pathologist will calculate your Gleason score by adding together the number of the most prevalent type of cell in the sample and the second most prevalent type of cell.
For example, if the most common cell grade in your sample is 4 and the second most common is 4, you would have a score of 8.
A Gleason score of 6 is considered low-grade cancer, 7 is intermediate, and 8 to 10 is high-grade cancer.
Prognosis And Survival For Prostate Cancer
If you have prostate cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctor’s best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for prostate cancer.
Also Check: How To Massage Prostate Externally
Prostate Cancer Survival Trends Over Time
As with most cancers, survival for prostate cancer is improving. However, interpretation of prostate cancer survival trends is difficult as the case-mix on which they are based is likely to have changed over time with earlier diagnoses following the advent of TURP and PSA testing. The detection of a greater proportion of latent, earlier, slow-growing tumours in more recent time periods will have the effect of raising survival rates due to lead-time bias . Lead-time bias for prostate cancer is estimated to be between five and 12 years, varying with a mans age at screening. Data from the European Randomized Study of Prostate Cancer estimates that for a single screening test, mean lead times are 12 years at age 55 and six years at age 75. Some of the increase may also be attributed to genuine improvements in survival due to more effective treatment, for both early, aggressive prostate cancers and advanced cases.
One-year age-standardised net survival for prostate cancer has increased from 66% during 1971-1972 to 94% during 2010-2011 in England and Wales an absolute survival difference of 28 percentage points.
Prostate Cancer , Age-Standardised One-Year Net Survival, Men , England and Wales, 1971-2011
Prostate Cancer , Age-Standardised Five-Year Net Survival, Men , England and Wales, 1971-2011
Prostate Cancer , Age-Standardised Ten-Year Net Survival, Men , England and Wales, 1971-2011
Also Check: Cyberknife Prostate Cancer Side Effects
The Stages Of Prostate Cancer: What You Need To Know
After a prostate cancer diagnosis, your oncologist will refer to the stage of your cancer. All cancers are categorized into four distinct stages, each of which identifies the progress of the growth of cancerous cells within clinically defined standards. These stages help doctors determine the most appropriate care for each patient based on his or her condition, and can also provide easy-to-understand context for your diagnosis. Learn more about the stages of prostate cancer, how each stage will affect your treatment plan and the survival rates for each stage, then contact Regional Cancer Care Associates to schedule a consultation.
Recommended Reading: Do Over The Counter Prostate Meds Work
Radiation Therapy And Radiopharmaceutical Therapy
External-beam radiation therapy
Candidates for definitive radiation therapy must have a confirmed pathologic diagnosis of cancer that is clinically confined to the prostate and/or surrounding tissues . Staging laparotomy and lymph node dissection are not required.
Radiation therapy may be a good option for patients who are considered poor medical candidates for radical prostatectomy. These patients can be treated with an acceptably low complication rate if care is given to the delivery technique.
Long-term results with radiation therapy are dependent on stage and are associated with dosimetry of the radiation.
Evidence :
Evidence :
Brachytherapy
