Additional Treatment After Surgery
Additional treatment can come with one of two approaches: treatment given as adjuvant therapy , or as salvage therapy . In the modern era, most additional treatment is given as salvage therapy because firstly this spares unnecessary treatment for men who would never experience recurrence, and secondly because the success rates of the two approaches appear to be the same.
Regardless of whether an adjuvant or salvage therapy approach is taken, the main treatment options following biochemical recurrence are:
- Radiotherapy this is the commonest approach. Because scans dont show metastatic deposits until the PSA is more than 0.5 ng/ml and because radiotherapy is more effective when given before this level is reached, the radiotherapy energy is delivered to the prostate bed. This is because we know that this is the commonest site of recurrence in most men, and that 80% of men treated in this way will be cured.
- Active surveillance this is appropriate for a very slowly-rising PSA in an elderly patient who has no symptoms.
- Hormonal therapy in many ways this is the least appealing option as it causes symptoms but does not cure anyone, although it does control the recurrence and lower the PSA.
Treatments For Recurrent Prostate Cancer
Recurrent prostate cancer is cancer that comes back after it has been treated. Recurrent prostate cancer is also diagnosed when theprostate-specific antigen level starts to rise quickly after initialtreatment but there are no other signs of cancer. This is called a biochemicalrecurrence or PSA failure.
The following aretreatment options for recurrent prostatecancer. Your healthcare teamwill suggest treatments based on your needs and work with you to develop atreatment plan. The type of treatment that you receive will depend on:
- the treatments youve already had
- where the cancer comes back
- whether the cancer has spread
- your overall healthand whether you have other illnesses
- your age and life expectancy
- your personal preferences
Also Check: Is Prostate Cancer Genetically Inherited
Side Effects From Radiation
Urinary symptoms from radiation treatment for prostate cancer are different from those caused by prostate surgery. Its more like a urinary tract infection-increased urgency and frequency, and men may some have bleeding or pain when they urinate, Calvaresi said. These problems often go away once treatment is complete.
Radiation also may cause bowel changes, such as constipation, loose stools or both. These can be managed by over-the-counter medication. Men may also see some blood in their stool during treatment-if so, let your health care provider know about this.
Men undergoing radiation are likely to have ED, but not immediately. It slowly sets in after radiation treatment, Calvaresi said. Treatments for radiation-related ED are the same as ED caused by prostate cancer surgery.
Also Check: Steps To Prevent Prostate Cancer
You May Like: Can Locally Advanced Prostate Cancer Be Cured
Cvaccine Plus Radiation Therapy
Many patients with clinically localized prostate cancer develop biochemical failure despite excellent local therapy, perhaps due to occult metastatic disease. Thirty patients were randomized into vaccine plus radiotherapy or radiotherapy-only arms . Thirteen of 17 patients in the combination arm had increases in PSA-specific T cells of at least 3-fold versus no detectable increases in the radiotherapy-only arm . There was also evidence of de novo generation of T cells to well-described prostate-associated antigens not found in the vaccine, providing indirect evidence of immune-mediated tumor killing . Another study in men with localized prostate cancer investigated whether the vaccination with rV-PSA/rV-B7.1 prime and rF-PSA boosters induced immune responses to additional TAAs. Western blotting revealed treatment-associated autoantibody responses in 15 of 33 patients treated with vaccine + radiotherapy versus 1 of 8 treated with radiation alone.
BSBrock R. Baker, MD, MPHRonald C. Chen, in, 2016
Also Check: What Does It Mean When Your Prostate Is Enlarged
Life Expectancy And Localized Prostate Cancer
So how do these treatments affect life expectancy? In one study, researchers in Switzerland examined the treatment and outcomes of 844 men diagnosed with localized prostate cancer. They compared men who had been treated with prostatectomy, radiotherapy and watchful waiting and found that at five years from diagnosis, the type of treatment made little difference to survival. When the researchers went to 10 years from diagnosis, they did find a difference in survival based on treatment, but it was fairly small.
After 10 years, 83 percent of the men who had gotten a prostatectomy were still living, compared to 75 percent who had undergone radiotherapy and 72 percent who took a watchful waiting approach.
Read Also: How Do Surgeons Remove Prostate
Prostate Cancer Treatment Health Professional Version
On This Page
The median age at diagnosis of carcinoma of the prostate is 66 years. Prostate cancer may be cured when localized, and it frequently responds to treatment when widespread. The rate of tumor growth varies from very slow to moderately rapid, and some patients may have prolonged survival even after the cancer has metastasized to distant sites, such as bone. The 5-year relative survival rate for men diagnosed in the United States from 2010 to 2016 with local or regional disease was greater than 99%, and the rate for distant disease was 30% a 98% survival rate was observed for all stages combined. The approach to treatment is influenced by age and coexisting medical problems. Side effects of various forms of treatment should be considered in selecting appropriate management.
Many patientsespecially those with localized tumorsmay die of other illnesses without ever having suffered disability from the cancer, even if managed conservatively without an attempt at curative therapy. In part, these favorable outcomes are likely the result of widespread screening with the prostate-specific antigen test, which can identify patients with asymptomatic tumors that have little or no lethal potential. There is a large number of these clinically indolent tumors, estimated from autopsy series of men dying of causes unrelated to prostate cancer to range from 30% to 70% of men older than 60 years.
Also Check: Is Testicular Cancer The Same As Prostate Cancer
General Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
According to the American Cancer Society:
- The relative 5-year survival rate is nearly 100%
- The relative 10-year survival rate is 98%
- The 15-year relative survival rate is 91%
Note: Relative survival rate means the percentage of patients who live amount of years after their initial diagnosis.
Keep in mind, however, that because the compiled list figures are of cancers diagnosed up to 15 years ago, you may have an even greater chance of survival than these indicate due to advances in prostate cancer treatment technology
Also Check: What Causes Enlarged Prostate At Young Age
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
19 July 2019
Sairam Tabibu, P. K. Vinod & C. V. Jawahar
13 January 2022
Wouter Bulten, Kimmo Kartasalo, the PANDA challenge consortium
volume 2, Article number: 64
Recurrence Of Prostate Cancer Life Expectancy
According to the table above, when the prostate cancer recurrence rate is low, then life expectancy generally is 10 years or higher. When calculating life expectancy to a prostate expectancy too.
Meanwhile, if the recurrence rate is high, then most probably the tumor will involve the adjacent areas. And often the recurrence seems to occur after 6-8 years of radical prostatectomy.
In cases of metastastasis, it is difficult to assess the period of relapse. This is actually considered as very high risk zone.
Sometimes, the actual cause is not the prostate cancer, but some other associated problems. Thats why, it is highly recommended regular annual check-ups not only to tackle prostate cancer, but also a scheduled check-up to detect its recurrence and related problems too.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Prostate Medicine Over The Counter
Life After Prostate Cancer Treatment
Adjusting to life after prostate cancer treatment can take time. For some men, the emotional impact of what they have been through may not hit them until they have finished treatment. For others, working through the physical side effects is their immediate focus.
Although prostate cancer treatment can be lifesaving, it can also take a toll on the body. This can result in a disruption to normal urinary, bowel and sexual function.
Whether you have surgery, radiation or hormone therapy, you are likely to have side effects.
Its important to talk with your health care provider about these side effects before you start treatment, so you can learn about the range of options to treat them, says Anne Calvaresi, DNP, CRNP, RNFA, Urology Nurse Practitioner at the Kimmel Cancer Center, Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
Study Identifies Death Risk Predictors Among Men With Recurrent Prostate Cancer
Readilyavailable clinical variables can predict the long-term risk of death fromprostate cancer and other causes among men who experience biochemicalrecurrence of PCa following radical prostatectomy , according to study datapresented during the American Urological Association 2020 Virtual Experience.
Using a statistical method called recursive partitioning, investigators found that men at highest risk for PCa-specific mortality are those with a PSA doubling time of less than 9 months and those who preoperatively had high-risk tumors according to DAmico criteria. Men at highest risk of other-cause mortality are those aged 70 years and older with any major comorbidity, lead investigator Timothy J. Daskivich, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles, said during a virtual presentation. The study also demonstrated that the 10-year cumulative incidences of PCSM and OCM are low, even among men with high-risk tumors.
Potentialapplications of this data include individualizing prognosis for men withbiochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy by readily availableclinical variables, Dr Daskivich said.
Comparedwith men who had low-risk tumors by DAmico criteria, those with high-risktumors had 4.1-fold and 3.3-fold increased risks for PCSM and metastasis,respectively. A PSADT less than 9 months was significantly associated withnearly 2.5-fold and 2.3-fold increased risks for PCSM and metastasis,respectively.
Recommended Reading: Enlarged Prostate Blocking Urine Flow
Stage Iv Prostate Cancer Prognosis
Prostate cancers detected at the distant stage have an average five-year survival rate of 28 percent, which is much lower than local and regional cancers of the prostate. This average survival rate represents stage IV prostate cancers that have metastasized beyond nearby areas to lymph nodes, organs or bones in other parts of the body.
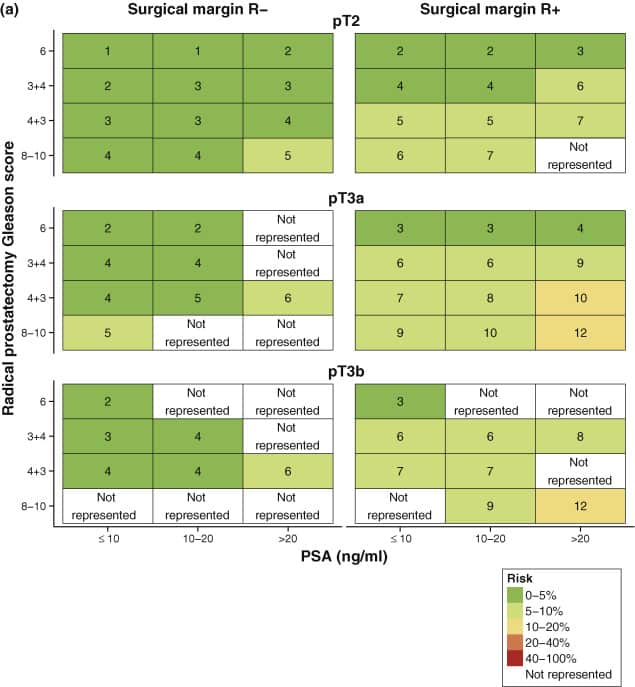
Table : Predictors Of Biochemical Recurrence At Time Of Diagnosis
Although a number of clinical factors contribute to your risk of relapse after treatment, the parameters below provide a simpler assessment of your chances of biochemical recurrence, based on your clinical profile at the time of diagnosis. For more sophisticated estimates, based on specific risk factors, see Figures 1 through 3.
Low risk Gleason score less than or equal to 6and Cancer stage T2c or more
Recommended Reading: Is There Ejaculation After Prostate Removal
Differences Among Risk Groups
Men with PCa have been classified into low-, intermediate- and high-risk Groups for tumor recurrence and disease specific mortality, based on PSA level, clinical or pathological staging and GS. High-risk patients have PSA level 20ng/mL or GS 8 or clinical/pathological stage T2c . Lymph-node positive and PSM have also been reported as poor prognosis factors.
Risk Group classification predicts biochemical and clinical progression as well as PCa specific mortality and overall survival. The risk of disease progression in these groups has been validated for patients submited to RP in many studies. In patients from Mayo Clinic, BCR rates were 2.3 and 3.3-fold greater in high and intermediate-risk in comparison with low-risk patients, respectively. In those patients, mortality rates in high and intermediate-risk patients were greater than 11 and 6-fold over low-risk men .
Therefore, it is crutial to understand the role of each clinical and pathologic feature in PCa BCR and disease progression.
Dont Miss: Can You Be Asleep During A Prostate Biopsy
How To Handle A Relapse After Treatment For Prostate Cancer
Am I going to die? This is the first question a patient usually asks me when a follow-up blood test reveals that his prostate-specific antigen level has risen after he has already undergone treatment for prostate cancer . The fear is understandable: When PSA levels rise to a certain threshold after prostate cancer treatment, the patient has suffered what is known technically as a biochemical recurrence, sometimes also referred to as a biochemical relapse or stage D1.5 disease. Whatever term is used, it means that prostate cancer remains within the after radiation therapy, that it survived outside the excised area after radical prostatectomy, or that it has reappeared in metastatic form in other tissues and organs. In most cases the cancer remains at a microscopic level, and many years will pass before any physical evidence of it is detectable on a clinical exam or any abnormalities are seen on a bone scan or CT scan.
Thats usually of small comfort to the patient whose PSA has risen. Its emotionally traumatic to go through treatment for prostate cancer, thinking it is cured, and then learn that it might have come back. For many men, its as if theyre dealing with another diagnosis of cancer, except this time its much worse because there is less likelihood of getting cured. A mans confidence and sense of safety may be shattered, especially because the popular misconception is that when prostate cancer recurs, it is deadly.
Recommended Reading: Who Do You See For Prostate Problems
How Will I Know That My Hormone Therapy Is Working
Doctors cannot predict how long hormone therapy will be effective in suppressing the growth of any individual mans prostate cancer. Therefore, men who take hormone therapy for more than a few months are regularly tested to determine the level of PSA in their blood. An increase in PSA level may indicate that a mans cancer has started growing again. A PSA level that continues to increase while hormone therapy is successfully keeping androgen levels extremely low is an indicator that a mans prostate cancer has become resistant to the hormone therapy that is currently being used.
Cancer That Is Thought To Still Be In Or Around The Prostate
If the cancer is still thought to be just in the area of the prostate, a second attempt to cure it might be possible.
After surgery: If youve had a radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, sometimes along with hormone therapy.
After radiation therapy: If your first treatment was radiation, treatment options might include cryotherapy or radical prostatectomy, but when these treatments are done after radiation, they carry a higher risk for side effects such as incontinence. Having radiation therapy again is usually not an option because of the increased potential for serious side effects, although in some cases brachytherapy may be an option as a second treatment after external radiation.
Sometimes it might not be clear exactly where the remaining cancer is in the body. If the only sign of cancer recurrence is a rising PSA level , another option for some men might be active surveillance instead of active treatment. Prostate cancer often grows slowly, so even if it does come back, it might not cause problems for many years, at which time further treatment could then be considered.
Factors such as how quickly the PSA is going up and the original Gleason score of the cancer can help predict how soon the cancer might show up in distant parts of the body and cause problems. If the PSA is going up very quickly, some doctors might recommend that you start treatment even before the cancer can be seen on tests or causes symptoms.
You May Like: How Long Does Prostate Surgery Take
Comparisons With Other Studies
Loeb et al presented evidence for low risk of cancer related morbidity and mortality within 20 years after radical prostatectomy if PSA was undetectable 10 years after radical prostatectomy. Ahove et al, with 10 years of follow-up, showed that it is unlikely for patients with Gleason score 6 to develop late biochemical recurrence if PSA was undetectable 5years after radical prostatectomy. In the present study with median follow-up of 24 years, men without biochemical recurrence 5years after radical prostatectomy still had a rather high probability of future biochemical recurrence, while the probability of metastases and prostate cancer death varied. Gleason score was the strongest predictor of outcomes. Among men with Gleason score 4+3=7the long-term probability of biochemical recurrence was about two times higher than for men with Gleason score 3+4=7 while the probabilities of metastasis and prostate cancer death were about 20 and 15 times higher, respectively. In all, 7 of 157 men with biochemical recurrence after more than 5years were later diagnosed with metastatic disease and six of them died from prostate cancer. Only one of these men was in the favourable Gleason score-group.
Outcomes 20 Years After Radical Prostatectomy Conditioned On 10 Years Without Biochemical Recurrence
The probability of biochemical recurrence 20years after radical prostatectomy for all patients without biochemical recurrence 10 years after radical prostatectomy was 17%. Among patients without biochemical recurrence 10 years after radical prostatectomy none was diagnosed with metastases or died from prostate cancer . The 20-year probabilities of future biochemical recurrence were 9% for Gleason score 3+4=7and 52% for Gleason score 4+3=7 10% for pT2 and 34% for pT3 and 12% for those with a negative and 34% for those with positive surgical margins. Among men with Gleason score 4+3=7 without biochemical recurrence 10 years after radical prostatectomy, 3 out of 20 received hormonal treatment and none underwent salvage radiotherapy.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Treatment For Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Talk with your doctor about how these numbers may apply to you, as he or she is familiar with your situation.
Read Also: Prostate Biopsy Cost In Usa
