How Do I Know Which Treatment Is Right For Me
Your treatment choices depend on the type of prostate cancer you have, test results and the stage of the cancer. The goal of treatment may be to cure you, control the cancer and help ease problems caused by cancer. Your healthcare team will talk through treatment choices, the goals of treatment, and what the risks and side effects may be.
While there are various prostate cancer treatment options, the UC Cancer Center recently adapted a way to personalize treatment plans even further.
One of the exciting, new innovations that were offering is genomic analysis of tumors, said Timothy D. Struve, MD, radiation oncologist at the UC Cancer Center and assistant professor in the Department of Radiation Oncology at the UC College of Medicine.
What these tests allow us to do is to look at the genes whats driving that tumor and that allows us to tailor the treatment approach to that patient.
In addition to the new focal therapies discussed in this article, physicians consider treating prostate cancer with:
Focal Therapies Can Become A Cost
Prostate cancer therapy is costly. Comparing radical prostatectomy with watchful waiting shows that surgery costs are 34% higher. Radiotherapy and laparoscopic surgery are even more expensive.
The minimally-invasive nature of these therapeutic methods makes them suitable for a more cost-effective approach. They are not as expensive as whole-gland therapy but reduce the progression of cancer as well. The risks of adverse events are lower for less money.
Onclive: What Topics Will Be Covered In Psma
Albala: This is a timely panel that Neil Shore, MD, has put together to talk about recent advances in imaging and the hot topic right now is PSMA imaging. We are going to go over the indications for newly diagnosed patients with prostate cancer and those with recurrent prostate cancer discuss how one will incorporate that into the workflow of your practice.
Traditionally, we have used conventional imaging with bone scans and CT scans in these patients. This opens a new era of how we can look at these patients and make treatment decisions based on real data. have been disappointed with the conventional imaging that we have had and our panelists that are going to be talking about how we can incorporate it in our practices and workflow.
Recommended Reading: Focal Laser Ablation Prostate Cancer Results
Hifu And Clinical Trials
HIFU is not available in every hospital. Your doctor might offer you HIFU treatment as part of a clinical trial. Or you might need to travel to specialist centre for treatment.
-
Focal therapy using high-intensity focused ultrasound for localised prostate cancerNational Institute for Health and Care Excellence , 2012
-
A multicentre study of 5 year outcomes following focal therapy in treating clinically significant non metastatic prostate cancerS Guillaumier and others
How Do You Sign Up For A Clinical Trial
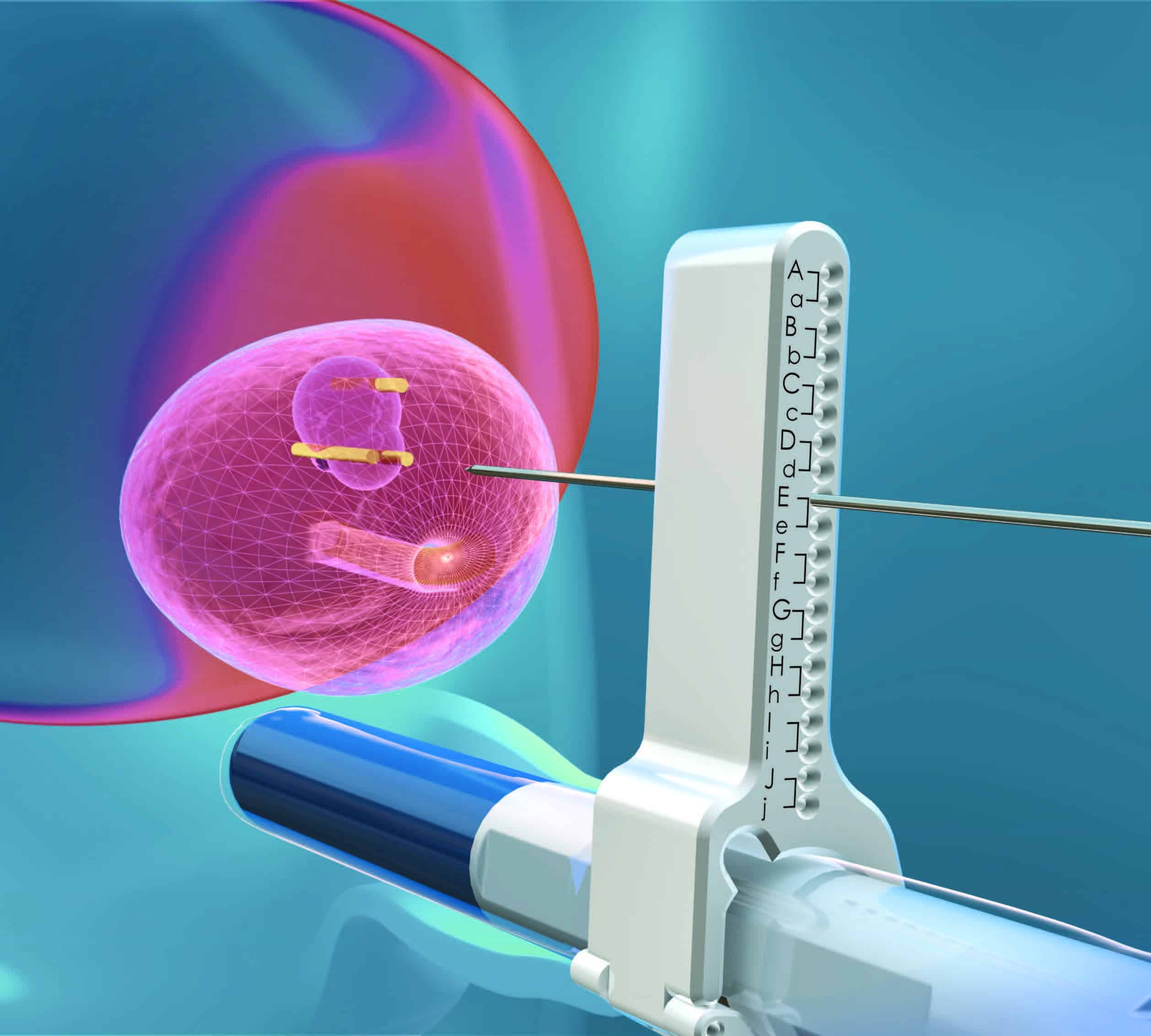
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network, a group assembled from the major comprehensive cancer centers of the U.S., considers that the best care for a cancer patients is afforded by their participation in a clinical trial. Patients with prostate cancer should always ask if there is a clinical trial option for them at any point in their therapy. Clinical trial participation assures you that your treatment has been considered by numerous cancer experts and is at least as good as a standard treatment that you may receive in a clinical trial. In addition, the results of your treatment will be carefully analyzed anonymously, and the results can be used to help others.
Also Check: How To Examine The Prostate
What Are The Types Of Focal Therapy
According to studies, around 40% of prostate cancer cases could be candidates for focal therapy.
Most of them have a Gleason score of 6 or 7. However, each one should be evaluated individually to assess the risk and other factors. Depending on each case, you could receive one of the following alternatives :
What Treatments Are Used In Focal Therapy For Localized Prostate Cancer
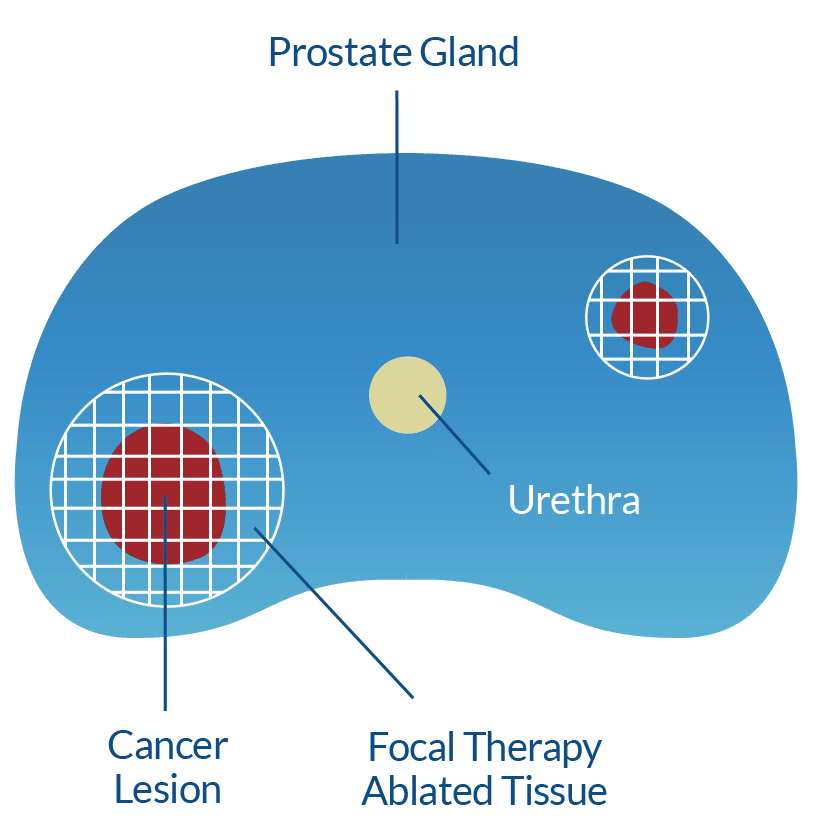
Focal therapy uses ablation, which is the use of extreme temperatures to destroy tissue. In focal ablation, the area of the prostate that contains the index lesion is targeted, rather than treating the entire prostate gland. Focal ablation techniques include:
- Cryotherapy: The use of very cold gases passed through needles to freeze and destroy cancer tissue.
- HIFU : The use of high-frequency sound waves directed at the tumor through an ultrasound probe inserted into the rectum. The high intensity waves cause the diseased tissue to heat up and die.
- : A drug called a photosensitizer is injected into the bloodstream. This drug then absorbs light rays directed at the tumor, and produces an active form of oxygen that destroys cancer cells.
- Laser ablation: The use of laser radiation energy pinpointed to a very small area to burn away cancerous tissue. Some laser ablation has the advantage of being able to be performed at the same time as magnetic resonance imaging , allowing very specific targeting and also real-time views of results.
Also Check: Can You Get An Erection If Your Prostate Is Removed
How Prostate Cancer Is Treated
In cancer care, different types of doctorsincluding medical oncologists, surgeons, and radiation oncologistsoften work together to create an overall treatment plan that may combine different types of treatments to treat the cancer. This is called a multidisciplinary team. Cancer care teams include a variety of other health care professionals, such as palliative care experts, physician assistants, nurse practitioners, oncology nurses, social workers, pharmacists, counselors, dietitians, physical therapists, and others.
The common types of treatments used for prostate cancer are described below. Your care plan may also include treatment for symptoms and side effects, an important part of cancer care.
Treatment options and recommendations depend on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, possible side effects, and the patients preferences and overall health.
Cancer treatment can affect older adults in different ways. More information on the specific effects of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy on older patients can be found another section of this website.
Because most prostate cancers are found in the early stages when they are growing slowly, you usually do not have to rush to make treatment decisions. During this time, it is important to talk with your doctor about the risks and benefits of all your treatment options and when treatment should begin. This discussion should also address the current state of the cancer:
General Recommendations On Inclusion Criteria Diagnostic Steps And Follow
The expert committee states that FT treats only a part of the prostate . In principle, FT of localized PCa is a minimally invasive procedure following the therapeutic concept of partial-gland treatment to treat only the region affected by cancer and a safety margin. Therefore, one tumor site or several closely located PCa foci are treated. FT has a curative goal. Multifocality and disease heterogeneity are limitations to the concept of partial or focal gland therapy. Success of FT is ultimately related to the accuracy of diagnosis and identification of tumor sites within the prostate.
The aim of FT in localized PCa is the eradication of all significant tumor tissue . This statement implies that FT intends to target and effectively treat all significant tumor foci within the gland. To achieve this, the region affected by PCa must be exactly localized and defined in order to be accessible for a FT modality with curative intention. Therefore, the authors defined tumor characteristics suitable for FT.
Especially, the latter is important to identify all significant PCa foci. Therefore, patients considering FT should undergo mpMRI, mpMRI fusion biopsy, and mandatorily accompanied by systematic biopsy . If MRI fusion biopsy is not possible, a template-based biopsy may be considered to be performed as an alternative .
Read Also: What Is The Best Mri For Prostate
What Is The Outlook For Patients Who Receive Focal Therapy
While the use of focal therapy for localized prostate cancer appears to be a promising development in a number of ways, it is still considered investigational and not yet part of standard therapy. There are a number of reasons for this, as follows:
- The criteria for selecting ideal candidates havent been fully agreed on. This is an important question because mistakenly using focal therapy in place of a more traditional treatment could allow a cancer to go under-treated.
- The criteria for defining an index lesion still need to be agreed on.
- The idea that the index lesion determines how the cancer will develop hasnt yet been proven.
- The factors that define treatment success or failure, and the triggers for re-treatment still need to be determined.
- The long-term effectiveness of focal therapy is unknown.
- It isnt clear that all side effects are eliminated by using focal therapy.
- Focal therapy doesnt allow for firsthand pathologic and biologic study of cancerous tissue, as can be done when using surgical treatment.
- Focal therapy sometimes leaves behind untreated cancer, which could possibly raise the risk of more serious problems in the future.
- The overall cost to the healthcare system may be greater for focal therapy than for standard treatments.
How Frequently Is Psma
The decay of the agent is in some respects the rate-limiting step. it is used, but there are a number of agents that now have been approved by the FDA. If you are living in a city such as Los Angeles, , you have 2 agents that are readily available. But, if you are living in rural upstate New York, , where these agents decay, getting the agents to the hospitals where the studies can be performed is more of a challenge. trying to understand how we can get these different agents spread out there are different agents, different half-lives, and different imaging quality .
You May Like: Has Anyone Survived Stage 4 Prostate Cancer
Focal Therapy For Localised Prostate Cancer
26 August 2021
Over 90% of patients present with cancer in multiple areas within the prostate and only 2040% have cancer in one area. Despite the multifocal nature of prostate cancer, many cancerous prostates have a single substantial lesion . It has been proposed that the characteristics of the index lesion predict the behaviour of disease in the rest of the prostate and its metastatic potential. So by targeting the index lesion in men with low and intermediate-volume prostate cancer it will provide satisfactory oncological outcomes. Patients should have a life expectancy a performance status of 0/1 and a Gleeson score < 8. High grade prostate cancer has to be excluded with a template guided prostate biopsy and the prostate is mapped with an MRI. For the procedure to be successful there should be at least a 3mm margin around the index lesion1.
Several energy modalities exist to target the cancer including irreversible electroporation, laser ablation, high intensity focused ultrasound , cryotherapy, and photodynamic therapy. The rest of this blog will discuss three modalities currently available in Australia: Irreversible electroporation, HIFU, and laser ablation.
Irreversible electroporation
HIFU
Uses ultrasonic waves to initiate cellular damage. ‘High-intensity’ refers to the power of these sound waves. The ultrasound probe is placed in the rectum allowing real-time visualization of prostatic tissue and also delivering energy to destroy the desired target
Are Focal Therapies The Future Of Prostate Cancer
In men, prostate cancer is the second-most deadly cancer accounting for more than 30,000 deaths a year in the United States. It is also very common, affecting 1 in 9 men, and decisions about treatment can sometimes be complex. Definitive treatment with surgery or radiation can bring side effects like incontinence and erectile dysfunction. On the other hand, while watchful waiting can often be a reasonable approach, there is always the chance that a cancer will progress.
For some men with lower-risk, localized types of prostate cancer, there is a middle-of-the-road option. With an approach called focal therapy, only those parts of the prostate that are cancerous are destroyed and other tissue is left unharmed.
Focal therapy is minimally-invasive treatment that can be delivered via cold, heat, or electrical impulses. Patients go home the same day with a urinary catheter they will use for only a day or so, rather than coping with longer-term incontinence that occurs after surgery. It can be repeated as needed, and definitive surgical or radiation treatment can also be subsequently performed, if necessary. In the meantime, nearby nerves and organs may be preserved, along with the patients quality of life.
Not everyone needs treatment, and , not everyone needs aggressive treatment, said Associate Professor of Urology Preston C. Sprenkle, MD, a pioneering advocate and practitioner of focal therapy.
You May Like: How To Diagnose An Enlarged Prostate
How Does A Clinician Determine When To Perform Psma
The largest experience with PSMA imaging has been with recurrent disease. Those patients that have had either definitive treatment with surgery or radiation and then they present back to the office or clinic with a rising prostate-specific antigen. In those patients, we have next generation imaging or a targeted type of imaging. We are going to be how we look at the historical perspective of using agents such as fluciclovine or sodium fluoride, even prior to that, and now we have migrated into PSMA testing. That is an exciting group of patients that has been around for quite some time and this type of imaging works quite nicely in.
We are also going to look at patients with intermediate-grade or high-grade prostate cancer that have not had definitive treatment and try to see if they have metastatic lesions before we recommend definitive treatment. There are patients who will present that way and treating them properly right out of the box makes a big differencethis type of imaging allows us to do that. That is the exciting area that we are going to see an extreme amount of growth in the next few years.
What Are Promising Treatments Under Study For Prostate Cancer
High-intensity focused ultrasound is an approach to therapy that is presently approved for use in Europe, and is under study in the U.S. It uses high-intensity sound waves focused on the prostate gland to heat and thereby kill cancer cells. It should only be used as part of a research study . The safety, side effects, and comparative effectiveness of surgery and radiation therapy must be established.
Clinical trials are research studies being conducted to evaluate new treatments for prostate cancer. These include approaches such as HIFU, as well as modifications of surgical and radiation techniques, and new drugs and immune therapy approaches.
You May Like: How Doctors Check For Prostate Cancer
Focal Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Video Transcript
Some men with early stage prostate cancer who previously had to choose between active surveillance and aggressive treatment with a greater risk for side effects, now have a new option for treatment: focal therapy.
Focal therapy is an overall term that refers to several minimally invasive treatments that target only the parts of the prostate gland where cancer is located. The goal of the treatment is to ablate, or destroy, the tumor and a safety margin within the prostate, while leaving the remainder of the gland intact.
The Benefits Of Focal Therapy
Traditionally, men with localized prostate cancer meaning it has not spread outside the prostate gland who do not opt for active surveillance are treated with surgery or radiation therapy. These approaches remove or radiate the prostate gland and can potentially damage nerves and urinary and bowel passages. As a result, they are often associated with side effects that impact sexual, urinary, and bowel function.
Focal therapy uses advanced imaging, such as ultrasound and MRI, to target the exact location of the tumor and minimize the impact of treatment on the surrounding, healthy prostate tissue and structures. As a result, it is less likely to cause erectile dysfunction, urinary incontinence, and bowel problems.
Because focal therapy does not treat the entire prostate, there is an increased risk that cancer may be left behind or may return. For this reason, regular follow-up appointments are required to monitor for cancer recurrence. If a tumor appears again, repeat focal therapy or another option may be recommended to treat the prostate cancer.
Read Also: Can A Man Get An Erection After Prostate Removal
Financial Support And Sponsorship
NIH and Philips have a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement. NIH has intellectual property in the field, including among other patents and patent applications, Patent: System, methods, and instrumentation for image-guided prostate treatment US Patent number: 8948845, with inventors/authors B.W. and P.P. NIH and Philips have a licensing agreement. NIH and authors B.W. and P.P. receive royalties for a licensing agreement with Philips/InVivo Inc. NIH does not endorse or recommend any commercial products, processes, or services. The views and personal opinions of authors expressed herein do not necessarily reflect those of the US Government, nor reflect any official recommendation nor opinion of the NIH nor National Cancer Institute.
If Treatment Does Not Work
Recovery from cancer is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or terminal.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for some people, advanced cancer may be difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment, including a hospital bed, can make staying at home a workable option for many families. Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss. Learn more about grief and loss.
Don’t Miss: Can Enlarged Prostate Be Cured
