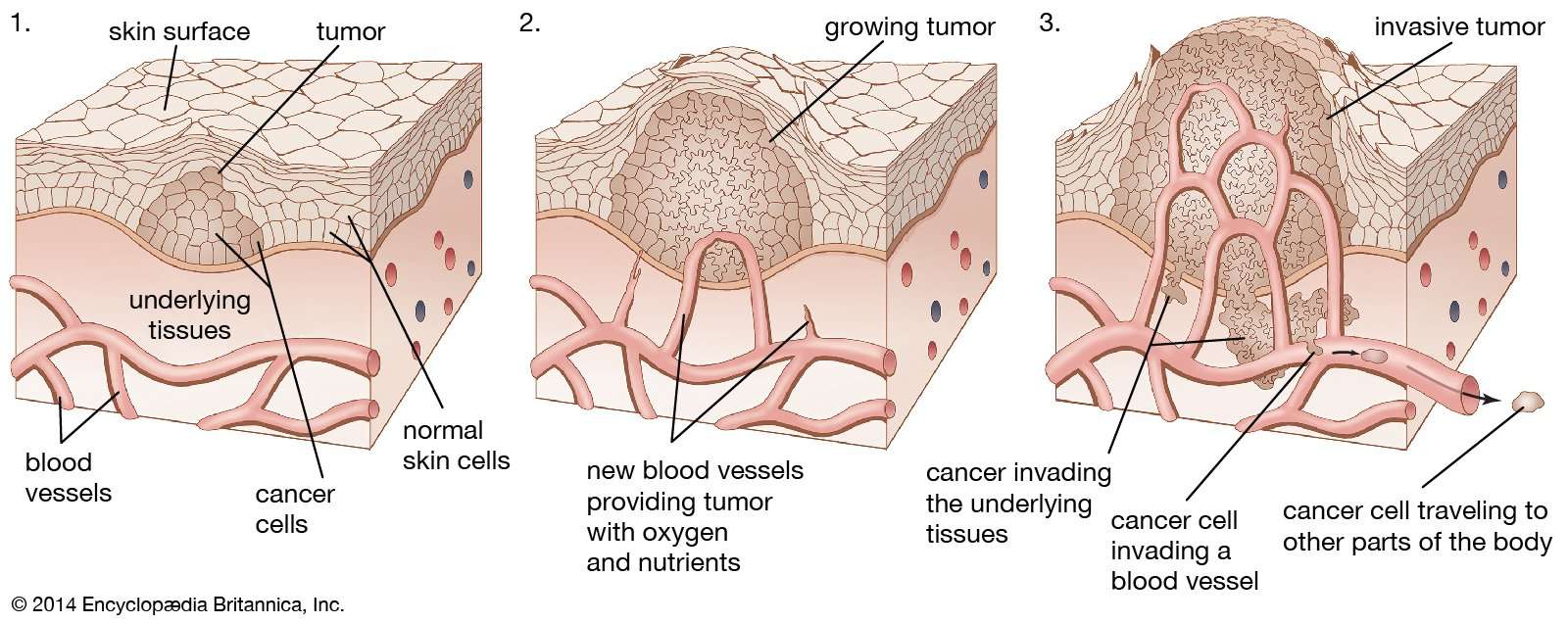
Characteristics Of Malignant Neoplasm
A neoplasm or tumor can be either benign or malignant. If the tumor is benign, it doesnt exhibit much activity, but a malignant neoplasm is highly active and has certain important characteristics that may be helpful in its identification. However, it must be remembered that these features of malignant neoplasia arent usually visible from the outside and can be determined only via clinical tests. The important features that a malignant tumor usually exhibits are as follows:
- Malignant tumors undergo a fast increase in their size.
- The cell mass that forms undergoes very little or no differentiation at all, thereby forming a big lump of cells that are totally useless.
- Malignant cells have a tendency to attack nearby cells and either destroy them or make them malignant.
- These cells may also travel to other parts of the body via lymph or blood vessels and affect other normal tissues, thus causing secondary cancer at the other site.
Not only do cancer cells differ in their activities from normal cells, but their cytological differences are also quite prominent which help differentiate them from normal cells. The main cytological features that malignant neoplastic cells possess are as follows:
All About Prostate Cancer
FACTS: Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men. Fortunately, prostate cancer primarily impacts older men and as many prostate cancers are slow-growing, monitoring and observation can often suffice until mortality arrives via senescence.
But even though prostate cancer is rare in younger men, those with close relatives who have had the disease particularly at a young age are at elevated risk, as are black men, whose incidence rate is up to 50% higher than Caucasians.
The exact causes of prostate cancer are unknown, though environment, diet, activity levels, and heredity undoubtedly contribute.
Physical warning signs of prostate cancer include urination difficulties such as increased frequency or difficulties starting or stopping, as well as the presence of blood in the urine. Pain in the back can also be indicative, if the cancer has spread.
Elevated prostate-specific antigen levels in blood tests can also provide a warning indicator before any symptoms occur. However, PSA levels can be affected by the non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate that many men experience as they age as well as certain medications so false positives and false negatives from testing are not uncommon. Where appropriate, follow-up biopsies can be performed to provide a more definitive diagnosis.
| Cure | Treatment varies with each individual, but most people undergo a combination of treatments, such as surgery with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. |
|---|
Prognosis: Disease Course Often Hard To Predict
In the United States, improved cancer screening and treatment have reduced the number of people who die from certain cancers, such as colon cancer. However, your chances of survival are generally decreased if a cancer has spread beyond its primary location.
Malignant tumors can vary in their aggressiveness, so it is difficult to predict how rapidly they will grow. A medical oncologist can recommend appropriate testing and treatment to give you the best chance of survival.
Recommended Reading: Chemo Drug For Prostate Cancer
Can Prostate Cancer Be Prevented
There are no clear prevention strategies for prostate cancer. There is some conflicting evidence that a healthy diet composed of low fat, high vegetables and fruits may help reduce your risk of prostate cancer. Routine screening, with PSA blood test and physical exam, is important to detect prostate cancer at an early stage. A healthy diet and regular exercise are also critical in maintaining good health and preventing disease in general.
Read Also: How To Stimulate Prostate Gland
Neoplasm Of Uncertain Behavior Of Skin
Neoplasm of uncertain behavior is a term used by Dr. Chris Rouse when he is not sure what the spot is on the skin but is concerned it could be skin cancer. Basal Cell Carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. Dr. Rouse is looking for pimples that will not go away, especially after 3 months. Another common type of skin cancer is Squamous Cell Carcinoma. For this type of skin cancer, Dr. Rouse is also looking for pink or red warts, especially in adults.
Neoplasm of uncertain behavior and these types of skin cancers are much less likely than melanoma to go inside the body and hurt you, but they can still grow very large and can cause internal spread if left alone too long. To learn about more skin cancer services offered at Northland Dermatology be sure to visit our pages about Pre-cancers and Mole Removal.
Read Also: Tamsulosin Ejaculation
Stages Of Malignant Neoplasm
Once a malignant neoplasm has been detected, it is important to determine its stage so that proper treatment can be started immediately. Though different staging methods exist, the TNM classification is most commonly and widely used to categorize the level of the malignant tumor. The T value indicates the extent and/or size of the tumor. The N value refers to the level of involvement of the lymph node while the M value shows whether remote metastases are absent or present. Based on the data collected from clinical tests, the staging of neoplasms is done as below:
TX impossible to evaluate the primary tumor
Tis the tumor is non-invasive and in-situ
T1 the neoplasm is small in size and shows minimal invasion at the primary location.
T2 the tumor is large in size and shows comparatively more invasion at the primary location
T3 the tumor is large, and the invasion has gone beyond the perimeters of the primary location
T4 large tumor with extreme invasion and has spread to the nearby organs as well
NX It is impossible to evaluate the regional lymph nodes
N0 the lymph node is not at all involved
N1 the closest lymph node is involved
N2 the regional lymph node is involved
N3 remote lymph nodes are also involved
MX the occurrence of remote metastases cannot be determined
M0 No occurrence of remote metastases
M1- remote metastases are present
Also Read: Pancoast Tumor Cancer
External Beam Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation therapy uses radiation produced by a machine called a linear accelerator. Short bursts of x-rays are fired from the machine at your cancer. The x-rays come out in square shapes the radiation oncologist designs special blocks or special collimators within the machine to shape the radiation beam so that it treats the cancer and as little normal tissue as possible.
There are several newer techniques that may be used in treating your prostate cancer, including conformal treatment planning and intensity modulated therapy . These techniques allow a more precise delivery of radiation to the tumor area and may be used alone or in combination with surgery, hormonal therapy, or brachytherapy .
Dont Miss: How To Avoid Getting Prostate Cancer
You May Like: Female Prostate Equivalent
A Detailed Introduction About Malignant Neoplasm Cancer
Over the centuries, mankind has been faced with numerous diseases and ailments that have caused immense suffering and even, have proved to be fatal. With medical and technological advancement, humans have been able to diagnose and find a cure to most common diseases and ailments that prevail in the present times. But amidst all these advancements, a disease remains that, though being very common, cannot always be completely cured and even if cured, has serious repercussions on the patient. That ailment is malignant neoplasm, more commonly known as cancer.
Risk Factors You Can Control
Diet seems to play a role in the development of prostate cancer, which is much more common in countries where meat and high-fat dairy are mainstays. The reason for this link is unclear. Dietary fat, particularly animal fat from red meat, may boost male hormone levels. And this may fuel the growth of cancerous prostate cells. A diet too low in fruits and vegetables may also play a role.
6
Recommended Reading: Prostate Fiducial Marker Placement
Looking For More Of An Introduction
If you would like more of an introduction, explore these related items. Please note that these links will take you to other sections on Cancer.Net:
-
ASCO Answers Fact Sheet:Read a 1-page fact sheet that offers an introduction to prostate cancer. This free fact sheet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
-
ASCO Answers Guide:Get this free 44-page booklet that helps you better understand the disease and treatment options. The booklet is available as a PDF, so it is easy to print.
-
Cancer.Net Patient Education Video:View a short video led by an ASCO expert in prostate cancer that provides basic information and areas of research.
-
Cancer.Net En Español: Read about prostate cancer in Spanish or read a 1-page ASCO Answers Fact Sheet in Spanish. Infórmase sobre cáncer de próstata en español o una hoja informativa de una página, Respuestas sobre el cáncer.
The next section in this guide is Statistics. It helps explain the number of people who are diagnosed with prostate cancer and general survival rates. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
Screenings are the most effective way to catch prostate cancer early. If you are at average cancer risk, youll probably have your first prostate screening at age 55. Your healthcare provider may start testing earlier if you have a family history of the disease or are Black. Screening is generally stopped after age 70, but may be continued in certain circumstances.
Screening tests for prostate cancer include:
- Digital rectal exam: Your provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum and feels the prostate gland, which sits in front of the rectum. Bumps or hard areas could indicate cancer.
- Prostate-specific antigen blood test: The prostate gland makes a protein called protein-specific antigen . Elevated PSA levels may indicate cancer. Levels also rise if you have BPH or prostatitis.
- Biopsy: A needle biopsy to sample tissue for cancer cells is the only sure way to diagnose prostate cancer. During an MRI-guided prostate biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging technology provides detailed images of the prostate.
Don’t Miss: How To Shrink Prostate Mayo Clinic
What Is A Malignant Neoplasm
If your doctor says you have a malignant neoplasm, you may be wondering what that is and what to do next.
Shutterstock
The term “malignant neoplasm” means that a tumor is cancerous. A doctor may suspect this diagnosis based on observation such as during a colonoscopy but usually a biopsy of the lesion or mass is needed to tell for sure whether it is malignant or benign .
Types Of Prostate Cancer

Almost all prostate cancers are adenocarcinomas. These cancers develop from the gland cells .
Other types of cancer that can start in the prostate include:
- Small cell carcinomas
- Neuroendocrine tumors
- Transitional cell carcinomas
- Sarcomas
These other types of prostate cancer are rare. If you are told you have prostate cancer, it is almost certain to be an adenocarcinoma.
Some prostate cancers grow and spread quickly, but most grow slowly. In fact, autopsy studies show that many older men who died of other causes also had prostate cancer that never affected them during their lives. In many cases, neither they nor their doctors even knew they had it.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Perineural Invasion
Functional Outcomes And Quality Of Life After Treatment For Localized Prostate Cancer
At 15 years after treatment of localized prostate cancer diagnosed in 1994-1995, declines in urinary, sexual, and bowel function were common. These functional declines in quality of life occur to a significantly greater extent among those that undergo treatment for prostate cancer as compared to a normative aging population without a diagnosis of prostate cancer, and symptom distress is more common among men with prostate cancer that are treated compared to those not treated. In a contemporary study of quality of life after treatment for localized prostate cancer, the authors reported that a substantial proportion of men did not return to baseline function in the domains of bowel, sexual, and urinary function that changes in quality of life domains were treatment specific and that patient and partner outcome satisfaction were closely associated with changes in quality of life after treatment. Thus, treatment for prostate cancer commonly results in quality of life changes that affect both the patient and his partner.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Prostate Cancer That Has Spread To Bones
What Is Neoplasm Definition
The term neoplasm is derived from a combination of the Greek words neo meaning new and plasma meaning formation. The term neoplasm refers to an abnormal growth of tissue caused by the rapid division of cells that have undergone some form of mutation. Neoplasia refers to various types of growths including non-cancerous or benign tumors, precancerous growths, carcinoma in situ and malignant or cancerous tumors.
Read Also: How To Stimulate Prostate Gland
Don’t Miss: Expressed Prostatic Secretion
What Are My Treatment Options
Most localised prostate cancer often grows slowly and might not need treatment. You may be able to have your cancer monitored with regular check-ups instead. If you decide to have treatment, it will usually aim to get rid of the cancer.
The two ways of monitoring localised prostate cancer are:
You might also be offered high-intensity focused ultrasound or cryotherapy, but they are less common.
Your doctor or nurse will talk you through your treatment options and help you choose the right type of monitoring or treatment for you. You might not be able to have all of the treatments listed. Theres no overall best treatment for localised prostate cancer, and each one has its own advantages and disadvantages. Read more about choosing a treatment.
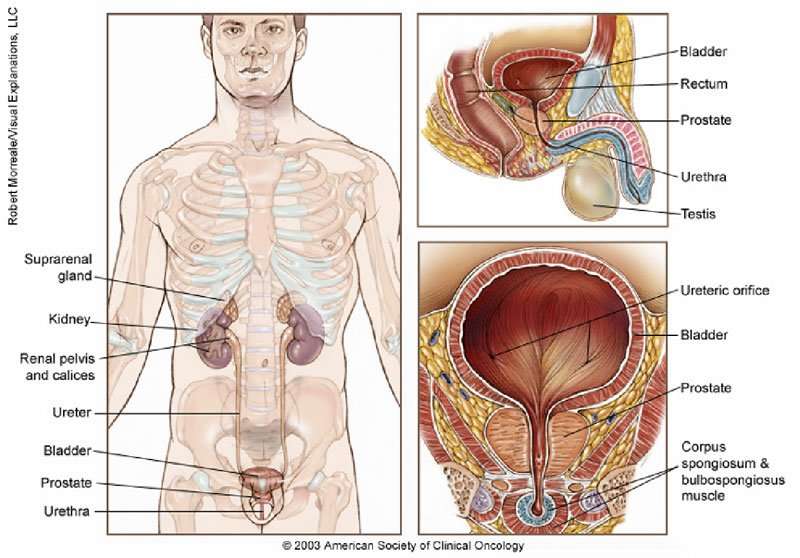
What Is Malignant Neoplasm Of Prostate
The prostate gland is a small gland found in males that is located between the urethra and the bladder. It is basically a male reproductive organ which secretes and propels semen ejaculated during sexual intercourse. Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate which is commonly known as prostate cancer is a type of cancer usually found in the elderly population and one of the most common type of cancer found in men.
Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate usually is found in people above the age of 70 although there have been cases of people getting it much before as well. People below the age of 40 rarely get this condition. Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate is found more in African-Americans that Native Americans. An individual with a family history of Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate is more likely to get this condition than others.
People involved in smoking and alcohol abuse are at increased risk for developing Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate. Overweight men and people who eat a lot of animal fat are also at an increased risk for Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate.
People who are exposed to Agent Orange and cadmium are also at risk for developing Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate. In some rare cases sexually transmitted diseases have also shown to increase the risk for Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate.
Don’t Miss: Urinozinc Prostate Plus
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
There are no obvious signs or symptoms of prostate cancer in its beginning stages. Many early stage prostate cancers are detected only through a digital rectal exam and prostate-specific antigen testing.
When the tumor becomes larger, symptoms may appear. They may include:
- Frequent urination, including the need to get up often during the night to urinate
- Hesitancy in starting the flow of urine or inability to urinate
- Loss of force of the stream of urine
- Pain or discomfort while urinating
- Impotence
You May Like: Prostate Cancer Statistics By Age
How Prostate Cancer Spreads
Cancer cells sometimes break away from the original tumor and go to a blood or lymph vessel. Once there, they move through your body. The cells stop in capillaries â tiny blood vessels â at some distant location.
The cells then break through the wall of the blood vessel and attach to whatever tissue they find. They multiply and grow new blood vessels to bring nutrients to the new tumor. Prostate cancer prefers to grow in specific areas, such as lymph nodes or in the ribs, pelvic bones, and spine.
Most break-away cancer cells form new tumors. Many others donât survive in the bloodstream. Some die at the site of the new tissue. Others may lie inactive for years or never become active.
Recommended Reading: External Prostate Massage Prostatitis
What Are Grade Groups
Grade Groups are a new way to grade prostate cancer to address some of the issues with the Gleason grading system.
As noted above, currently in practice the lowest Gleason score that is given is a 6, despite the Gleason grades ranging in theory from 2 to 10. This understandably leads some patients to think that their cancer on biopsy is in the middle of the grade scale. This can compound their worry about their diagnosis and make them more likely to feel that they need to be treated right away.
Another problem with the Gleason grading system is that the Gleason scores are often divided into only 3 groups . This is not accurate, since Gleason score 7 is made up of two grades , with the latter having a much worse prognosis. Similarly, Gleason scores of 9 or 10 have a worse prognosis than Gleason score 8.
To account for these differences, the Grade Groups range from 1 to 5 :
- Grade Group 1 = Gleason 6
- Grade Group 2 = Gleason 3+4=7
- Grade Group 3 = Gleason 4+3=7
- Grade Group 4 = Gleason 8
- Grade Group 5 = Gleason 9-10
Although eventually the Grade Group system may replace the Gleason system, the two systems are currently reported side-by-side.
There Are Different Types Of Treatment For Patients With Prostate Cancer
Different types of treatment are available for patients withprostate cancer. Some treatments are standard , and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
You May Like: Fiducials Prostate Cancer
