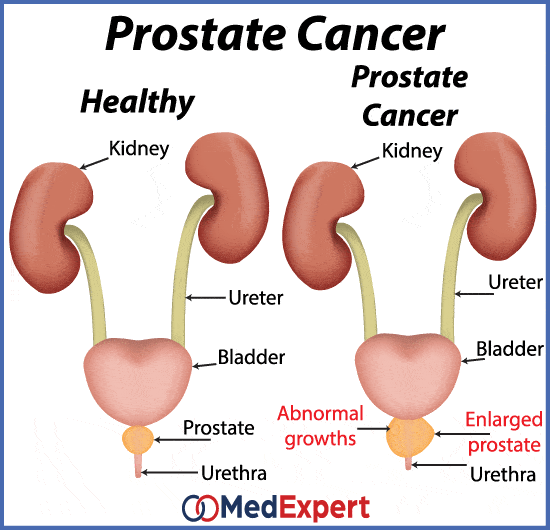
Why Does Prostate Cancer Happen
The causes of prostate cancer are largely unknown. However, certain things can increase your risk of developing the condition.
The chances of developing prostate cancer increase as you get older. Most cases develop in men and anyone with a prostate aged 50 or older.
For reasons not yet understood, prostate cancer is more common in men and anyone with a prostate of African-Caribbean African descent. It’s less common in men and anyone with a prostate of Asian descent.
Men and anyone with a prostate who have first-degree male relatives affected by prostate cancer are also at a slightly increased risk.
Read more about the causes of prostate cancer
Malignant Neoplasm Of Prostate
- 201620172018201920202021Billable/Specific CodeMale Dx
- C61 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM C61 became effective on October 1, 2020.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C61 â other international versions of ICD-10 C61 may differ.
- C61 is applicable to male patients.
âuse additional codeâ
-
- 2017 â New Code2018201920202021Billable/Specific CodePOA Exempt
Applicable To
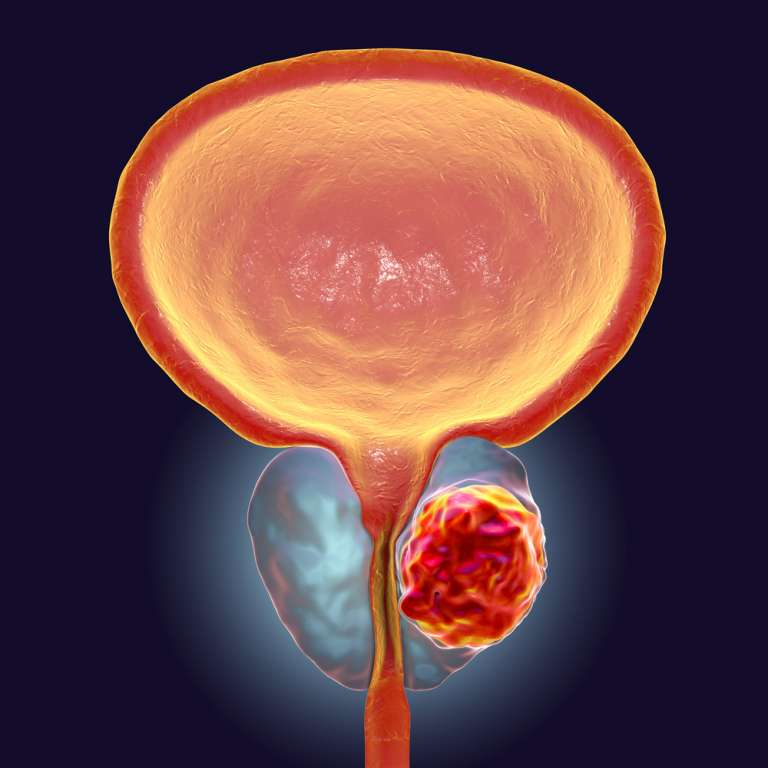
You Have Abnormal Growth Of Tissue In Your Prostate The Abnormal Tissue Tumor Can Be Benign Or Malignant
When there is abnormal growth of tissue, then this is also referred to as a tumor. The tissue in the body is made up of cells. A tumor disorder involves the cells multiplying more than normal. This results in abnormal or excess tissue forming. A tumor can be benign or malignant.
The prostate forms part of the male genital organs. The prostate sits below the bladder and encircles the urethra. The prostate is also known as the prostate gland. Some of the seminal fluid is formed in the prostate.
Also Check: Will Removal Of Prostate Cause Impotence
What Is The Prognosis Of Malignant Neoplasm Of Prostate
The overall prognosis of a patient with Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate depends on the age, overall health of the patient, and stage of the disease process. In majority of the cases where the disease is diagnosed early the prognosis is extremely good. Since this is a slow growing tumor, even if the diagnosis is made a bit late with adequate treatments the prognosis for the patient overall is fair to good post treatment of Malignant Neoplasm of the Prostate.
Faqs Malignant Neoplasm Cancer
Can you Smoke Cigar instead of a Cigarette?
In short, no! The tobacco present in cigar undergoes a long aging process, thereby increasing the concentration of nitrogenous compounds like nitrites and nitrates which emit some of the most active carcinogens known to mankind.
Can you use Tobacco Products that do not Emit Smoke?
Though tobacco, when chewed or taken as snuff, doesnt produce the harmful smoke, yet this doesnt eliminate the intake of harmful carcinogens as they contain TSNAs, PAHs, radioactive substances, etc. which are directly absorbed and can lead to different types of cancer.
Can you use e-cigs?
Though e-cigs brands claim that e-cigarettes can be used instead of actual cigarettes or cigars without any harm, yet the reality is quite different. The liquid used in the e-cigs contain synthetic flavors, addictive nicotine and several other chemical compounds that are classified as carcinogens.
Can Losing Body Weight help Lower Cancer Risk?
Though there are indications that maintaining an optimal body weight helps in curbing cancer menace in certain cases, yet there isnt enough proof to establish this as a fact. However, cutting down excess body weight does bring about certain changes in the body functionality that may have a direct impact on susceptibility to cancer.
Why is Remission Different from a Cure?
Are Seniors Prone to Cancer?
Also Check: How Many Cc’s Is A Normal Prostate
Malignant Tumor Of Prostate
Check Related conditions for additional relevant tests.
-
Also known as: AIS, AR8, DHTR, HUMARA, HYSP1, KD, NR3C4, SBMA, SMAX1, TFM, ARSummary: androgen receptor
-
Also known as: BRCC2, BROVCA2, FACD, FAD, FAD1, FANCD, FANCD1, GLM3, PNCA2, XRCC11, BRCA2Summary: BRCA2 DNA repair associated
-
Also known as: Arc-1, BCDS1, CD324, CDHE, ECAD, LCAM, UVO, CDH1Summary: cadherin 1
-
Also known as: CDS1, CHK2, HuCds1, LFS2, PP1425, RAD53, hCds1, CHEK2Summary: checkpoint kinase 2
-
Also known as: BCD1, CBA1, COPEB, CPBP, GBF, PAC1, ST12, ZF9, KLF6Summary: KLF transcription factor 6
-
Also known as: MAD1, PIG9, TP53I9, TXBP181, MAD1L1Summary: mitotic arrest deficient 1 like 1
-
Also known as: MAD2, MXD2, MXI, bHLHc11, MXI1Summary: MAX interactor 1, dimerization protein
-
Also known as: 10q23del, BZS, CWS1, DEC, GLM2, MHAM, MMAC1, PTEN1, PTENbeta, TEP1, PTENSummary: phosphatase and tensin homolog
-
Also known as: ATBF1, ATBT, C16orf47, ZFH-3, ZNF927, ZFHX3Summary: zinc finger homeobox 3
Politics Of Psa Testing: The Us Preventive Services Task Force
Policymakers consider screening at the population level, while clinicians are trained to view PSA testing at the individual-patient level.62 Most physicians have little knowledge of the USPSTF, the processes under which it operates, or that reform of the process continues to be a legislative priority.63,64
The USPSTF was created in 1984, as an advisory committee to Medicare. It consists of 16 volunteers serving 4-year terms and is funded from the Agency for Health Research and Quality. Its mission is to evaluate the benefits and harms of health services and make recommendations for primary care physicians. The USPSTF panel is composed of internists, pediatricians, family physicians, obstetricians, gynecologists, and nurses, but no urologists, radiation oncologists or medical oncologists.61 It is allowed to select the studies it deems most relevant to review and typically weighs RCTs most heavily.62
Recommended Reading: Does Prostate Cancer Spread Fast
The Initial Causes Neoplasm Of Uncertain Behavior Of Prostate
One of the first symptoms of prostate issues is pain or tenderness in the groin or lower back. This can be the result of a noncancerous condition called enlarged prostatic tissue, or it could be an infection of the bladder. In either case, its important to see a doctor as soon as possible. If youre suffering from prostate pain, you may want to consider reducing your caffeine intake.
Another symptom of a potentially enlarged prostate is difficulty starting a stream of urine, leaking, or dribbling. These symptoms are not serious, but theyre still alarming. Most men put up with an enlarged prostate for years before seeking medical attention, but they typically seek treatment as soon as they notice symptoms. Even if you dont have symptoms, its worth getting checked to determine if you have any prostate issues.
If you experience nightly bathroom runs, you may be experiencing an enlarged prostate. You may be having difficulty starting a stream of urine, or you may even be dribbling or leaking during the day. These problems arent life-threatening, but can become a nuisance. You should not ignore these signs and seek treatment as soon as you notice them. If you feel any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
When Should Clinic Follow Up Be Arranged And With Whom
If the hospitalist is concerned for a new diagnosis of prostate cancer, follow up should be arranged with the PCP for investigation within 2-4 weeks. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then the patient should be sent to a urologist for staging. If the patients hospitalization was related to the prostate cancer, then the patient should follow up with urology. If the patient has metastatic disease, the patient should be set up to see a urologist and an oncologist.
Don’t Miss: What Does It Mean When Your Prostate Hurts
Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment
Prostate cancer represents a wide spectrum of disease. Some prostate cancers progress and need treatment, while others grow slowly, if at all, and can be managed conservatively with a system of careful monitoring called active surveillance. It is important to learn the characteristics of your cancer before making treatment decisions. There are many ways to determine prostate cancer risk, most of which incorporate information from several parameters, including the PSA, Gleason score and tumor extent .
Prostate Cancer Caregiver Podcast Series
We are proud to announce a new podcast series geared toward helping give support, hope and guidance to prostate cancer caregivers. The goal of this Prostate Cancer Caregiver Podcast Series is to help others connect with a diverse group of people who have felt the impact of prostate cancer in their lives and empower them on their journey.
Read Also: Can Prostate Cancer Cause Erectile Dysfunction
Genetic And Genomic Tests For Localized Prostate Cancer
Genetic testing
A man’s inherited genes predict his prostate cancer risk. For a long time, we have known that there is a family risk in prostate cancer. If your father or brother has prostate cancer, or your mother or sister has breast or ovarian cancer, you are at higher risk of being diagnosed with prostate cancer. To partially quantify that genetic risk, a germline test can be performed before a biopsy. This test of DNA from healthy cells can determine whether you have inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, known to increase prostate cancer risk. If the test shows you’re low risk, you may be able to avoid a biopsy even if you have a slightly elevated PSA, while still being actively monitored for prostate cancer.
Genomic testing
If already diagnosed with prostate cancer, you may undergo another type of test for assessing your genetic risk. A genomic test of tissue from your biopsy or prostatectomy can look for somatic mutations, alterations in the DNA of the cancer cells themselves. Genomic tests measure expression of various genes that relate to how aggressive a cancer is likely to be. They indicate how rapidly cancer cells are growing and how genetically abnormal they are relative to normal cells.
Tissue Ablation And Focal Therapy
Tissue ablation treatments destroy the prostate cancer through freezing or heating. These treatments can be applied to all or just part of the prostate . Whereas whole gland ablation has largely fallen out of favor, focal ablation has gained popularity. The two most commonly used energy sources are as follows:
Cryosurgery kills cancer cells in the prostate by freezing them through special needles that are inserted into the gland. The needles are placed under ultrasound guidance. This method is effective in curing cancer but can’t treat lymph nodes and commonly causes erectile dysfunction if the entire prostate is treated. Urinary incontinence is a rare but possible side effect.
High-intensity focused ultrasound uses the high temperatures created by focused sound wave energy to kill cancer cells. While HIFU results over the years have been mixed, modern systems such the one used at UCSF allow real-time monitoring of tissue temperatures during treatment, improving outcomes.
Less commonly used ablation methods include interstitial laser ablation, electroporation , vascular targeted photodynamic therapy, gold nanoparticle therapy, and others under development. Focal radiation is used occasionally as well. Currently, there is little data comparing these technologies.
Read Also: High Intensity Ultrasound Prostate Cancer
Talk With Your Doctor
Prostate cancer is a risk for all men as they age, but if its caught and treated early, the outlook is generally very good. So as you get older, be sure to have open conversations with your doctor about your risk.
If you have any symptoms you think might be prostate cancer, talk to your doctor right away. And even if you dont have symptoms, consider adopting a healthy lifestyle to decrease your risk.
A Note About Sex And Gender
Sex and gender exist on spectrums. This article will use the terms male, female, or both to refer to sex assigned at birth. .
will depend on the cancer stage, among other factors, such as the Gleason score and PSA levels. It is also worth noting that many treatment options may be applicable, regardless of the stage of cancer.
In the sections below, we list some for prostate cancer and explore what treatment may mean for fertility.
Read Also: Why Does My Prostate Swell At Night
> > > One Crazy Prostate Trick All Men Over 40 Should Try
Symptomatic treatment of an enlarged prostate usually involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may be the best option if you suffer from chronic urination. It will help the body adjust to the increased size of the prostate. Also, taking regular urination intervals will help retrain the bladder to function properly. Inactivity also contributes to urine retention, and cold temperatures can increase the urge to urinate.
Invasive treatment of enlarged prostate includes medication that relieves the pressure on the urethra and bladder. However, if the condition is severe, it may require surgical intervention. If treatment is not successful, the enlarged prostate can become a potentially life-threatening disease. As the hormone levels in the body change, the enlarged prostate can lead to various complications, including urinary retention and even cancer. This is why it is critical to see a doctor for further evaluation.
Recommended Reading: Non Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer
Stages Of Malignant Neoplasm
Once a malignant neoplasm has been detected, it is important to determine its stage so that proper treatment can be started immediately. Though different staging methods exist, the TNM classification is most commonly and widely used to categorize the level of the malignant tumor. The T value indicates the extent and/or size of the tumor. The N value refers to the level of involvement of the lymph node while the M value shows whether remote metastases are absent or present. Based on the data collected from clinical tests, the staging of neoplasms is done as below:
TX impossible to evaluate the primary tumor
Tis the tumor is non-invasive and in-situ
T1 the neoplasm is small in size and shows minimal invasion at the primary location.
T2 the tumor is large in size and shows comparatively more invasion at the primary location
T3 the tumor is large, and the invasion has gone beyond the perimeters of the primary location
T4 large tumor with extreme invasion and has spread to the nearby organs as well
NX It is impossible to evaluate the regional lymph nodes
N0 the lymph node is not at all involved
N1 the closest lymph node is involved
N2 the regional lymph node is involved
N3 remote lymph nodes are also involved
MX the occurrence of remote metastases cannot be determined
M0 No occurrence of remote metastases
M1- remote metastases are present
Also Read: Pancoast Tumor Cancer
Read Also: Survival Rate For Stage 4 Prostate Cancer
What You Need To Know About The Prostate Neoplasm Of Uncertain Behavior Of Prostate
A enlarged prostate can also cause blockages in the urethra. A blocked urethra can also damage the kidneys. A patient suffering from an enlargement of the prostate may have pain in his lower abdomen and genitals. If pain is present, a digital rectal examination will reveal hard areas. A doctor may prescribe surgery or perform an endoscopic procedure. If the enlarged prostate is not completely removed, it will shrink.
While the size of an enlarged prostate will influence the extent of urinary symptoms, men may experience a range of urinary symptoms. Some men have minimal or no symptoms at all. Some men will have a very enlarged prostate, whereas others will have a mild enlargement. Generally, the symptoms can stabilize over time. Some men may have an enlarged prostate but not notice it. If they have an enlarged colon, their physician can perform a TURP procedure.
What Can I Expect If I Have Malignant Neoplasm
If youve been diagnosed with malignant neoplasm, your healthcare provider will work with you to determine an appropriate course of action. Treatment options will depend on several factors, including what type of cancer you have, whether its spread, your health history and your personal preferences.
Is malignant neoplasm curable?
Many types of malignant neoplasms can be cured or managed successfully with proper treatment. The sooner a tumor is detected, the more effectively it can be treated. So, early diagnosis is key.
Don’t Miss: Localized Prostate Cancer Survival Rate
Prostate Cancer Screening And Chemoprevention
Prostate cancer screening is a subject of substantial ongoing controversy in the United States and elsewhere. Some organizations, such as the AUA, generally support at least offering screening to men with good life expectancy , whereas others are neutral and some, such as the US Preventive Services Task Force , are relatively hostile to screening .
The European Randomized Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer randomized 162,387 men in seven countries to PSA screening at 2- or 4-year intervals, with biopsy thresholds ranging from 2.5 to 4.0 ng/mL. This was a larger study than PLCO, with longer follow-up and much less contamination among control patients. The study demonstrated that screening was associated with a 20% relative reduction in prostate cancerspecific mortality at 9 years median follow-up. A follow-up analysis found that with adjustment for compliance with screening, the reduction in mortality rose to 31%. The hazard curves in the ERSPC study only began to diverge approximately 7 years into the trial thus, with longer follow-up, the observed benefit to screening will likely be further magnified . In a subanalysis of patients from one of the ERSPC study centers with particularly high compliance and long follow-up, the mortality reduction was nearly 50% .
Early Stage Prostate Cancer
If the cancer is small and localized, a doctor may recommend:
Watchful waiting or monitoring
The doctor may check PSA blood levels regularly but take no immediate action.
Prostate cancer grows slowly, and the risk of side effects may outweigh the need for immediate treatment.
Surgery
A surgeon may carry out a prostatectomy. They can remove the prostate gland using either laparoscopic or open surgery.
Radiation therapy
Options include:
Brachytherapy: A doctor will implant radioactive seeds into the prostate to deliver targeted radiation treatment.
Conformal radiation therapy: This targets a specific area, minimizing the risk to healthy tissue. Another type, called intensity modulated radiation therapy, uses beams with variable intensity.
Treatment will depend on various factors. A doctor will discuss the best option for the individual.
Read Also: Cialis For Prostatitis
Recommended Reading: Where In The Body Is The Prostate
