What Is Stage 4 Prostate Cancer
The fourth stage of prostate cancerdefines a tumor that has progressed to other regions of the body, such as the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones, or bladder. The 5-year survival rate for these tumors is 29 percent.
Keep in mind that each case is unique, and figures like these are merely suggestions. As advances in prostate cancer treatment become more common, your odds of surviving this disease improve.
In general, prostate cancer has a very good survival rate one of the greatest of any cancer type. Because prostate cancer is frequently a slow-moving disease, the majority of men diagnosed with it will die from an unrelated reason.
Stage 4 prostate cancer means the cancer has spread to lymph nodes or to other parts of the body. It is further divided into two substages:
- Prostate Cancer Stage 4A Stage 4A: The cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes but may or may not have spread to nearby tissues.
- Prostate Cancer Stage 4B Stage 4B: The cancer has spread to another area of the body, such as the bones or distant lymph nodes.
What Is The Life Expectancy For Stage 4 Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer life expectancy is determined using five-year survival rates. This is the percentage of people who may still be alive five years after being diagnosed.
The five-year survival rate for men with localized prostate cancer, where there is no evidence of cancer spreading outside the prostate, and regional prostate cancer, when cancer has migrated outside the prostate to adjacent structures or lymph nodes exclusively, is approximately 100 percent.
When prostate cancer reaches stage 4 and has spread to other organs such as the lungs, liver, or bones, the five-year survival rate falls below 30%. At stage 4, prostate cancer is unlikely to be cured, although with effective therapy, many people can live for several years. The patients life expectancy is determined by the precise characteristics of his cancer.
However, thanks to routine screening procedures, prostate cancer is often discovered early, before it has spread to other organs, and it is usually not fatal. When diagnosed early, there are several treatment options available, as well as a good likelihood of a cure.
What Are The Treatment Options For Aggressive Prostate Cancer
The majority of people with prostate cancer nearly 80% are diagnosed early and cured by their treatment, most often radiation or surgery.
But one in five of those diagnosed with prostate cancer has a more aggressive form of the disease. Even before the individual has received any treatment or experienced a recurrence, doctors can identify whether the cancer is likely to be more dangerous and aggressive.
Prostate cancer is determined to be high risk if it is distinguished by any of the following characteristics:
Physicians perform biopsies or take X-rays to determine a cancers grade and stage. The stage is based on the size of the primary tumor or the extent it has spread in the body. The grade describes the appearance of the cancer cells and tissue under a microscope: the more abnormal they are, the higher the grade.
What are the main treatment options for people with aggressive or high-risk prostate cancer and can the sequencing, or order in which different treatments are given, make a difference in overall effectiveness of these therapies?
Why Roswell Park for Prostate Cancer?
Find out what makes Roswell Park unique in treating prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: Can Low Grade Prostate Cancer Become Aggressive
Impact Of Age On Treatment
The rising number of men diagnosed with prostate cancer is a result of increasing life expectancy as well as the current practice of screening by prostate-specific antigen blood tests.10 Besides PSA and Gleason score, age is considered a key prognostic factor in treatment decision making. Although organ-confined disease can be cured by radical prostatectomy and full-dose local radiation therapy, treatment options for advanced- stage disease remain palliative. They include active surveillance, or watchful waiting, early versus delayed hormonal therapy to control disease progression, and continuous or intermittent androgen deprivation. Observational studies of older men with early stage disease have suggested conservative management as a viable option.11,12
Chodak and associates12 evaluated 828 men who were managed expectantly in a series of nonrandomized trials. Median follow-up was approximately 6.5 years. Patients with poorly differentiated cancers had a 10-fold increased risk of death from prostate cancer as compared with men showing highly differentiated prostate cancer. A 5-year disease-specific survival of only 34% was found in men with poorly differentiated prostate cancer. In contrast a 5-year disease-specific survival of 87% was described in men with well-or moderately differentiated cancers.
Treatment Of Metastatic Stage Iv Or D2 Prostate Cancer
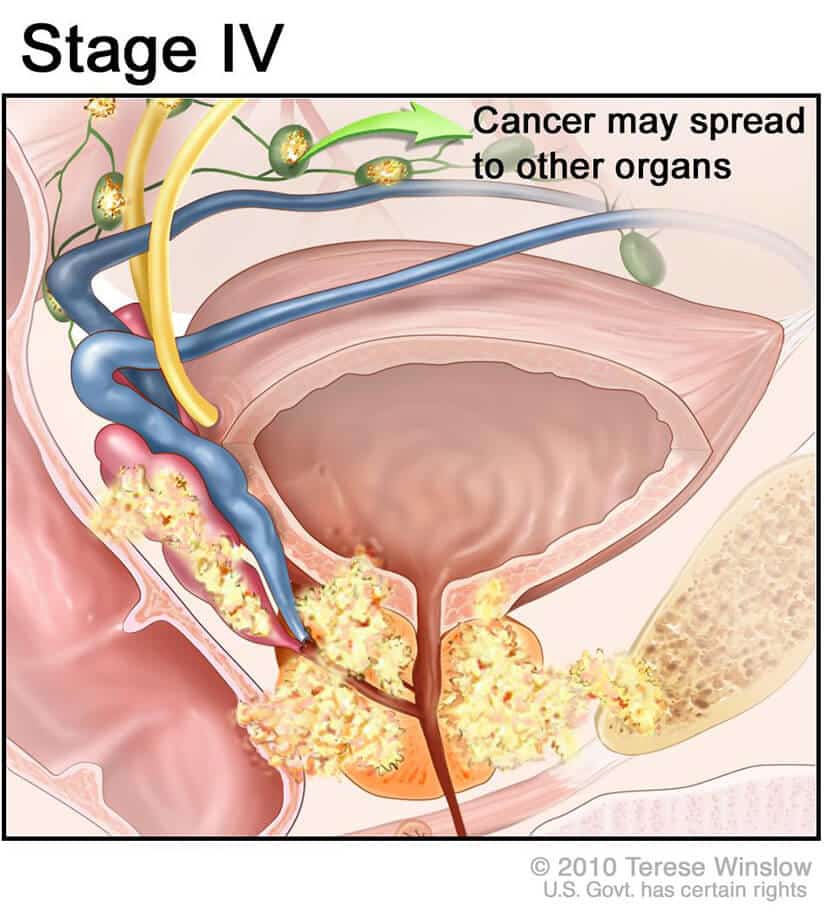
Prostate cancer that has spread to distant organs and bones is treatable, but not curable with current standard therapies. Hormone therapy has been the standard treatment of metastatic prostate cancer for many years. Metastatic prostate cancer can be controlled with hormone therapy for many years and new treatment options continue to become available.
Don’t Miss: Which Is Better For Prostate Cancer Radiation Or Surgery
How To Make The Right Treatment Decision
Current expert guidelines for treatment of localized prostate carcinoma recommend potentially curative therapy for patients whose life expectancy is at least 10 years., Patients with limited life expectancy are more likely to die from health conditions other than prostate cancer. Men with a life expectancy of more than 10 years are more likely to die from progressive prostate cancer. This 10-year rule enjoys broad acceptance among urologists and radiation oncologists.,
Conservative management proved to be an acceptable treatment option for men with low-grade Gleason scores, clinically localized disease, and life expectancies of less than 10 years. Increasing age was described as a risk factor for receiving inadequate treatment for prostate cancer. Thus, older men have been shown to receive potentially curative therapy less often than younger men., Radical prostatectomy is preferred treatment in men younger than 70 years, whereas radiation therapy is applied predominantly in patients older than 70 years. Conservative therapy such as watchful waiting or androgen deprivation by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogs is preferentially applied in men older than 80 years. Watchful waiting or hormonal therapy is used to treat 82% of men older than 80 years.
Read Also: Does Cialis Shrink The Prostate
Cancer Cells Under A Microscope
If you have had a biopsy,the biopsied tissue is sent to a laboratory where a doctor called a pathologist will look at the cells in the tissue under a microscope. When healthy cells become cancerous, their appearance begins to change. The more changed the cells look, the more dangerous the cancer is likely to be.
The results from a prostate biopsy are usually given in the form of the Gleason score. On the simplest level, this scoring system assigns a number to describe how abnormal the cells appear under a microscope. Grade 1 and 2 are thought of as normal prostate cells. Grades 3 5 are thought of as cancer cells, with grade 5 being the most abnormal.
The doctor will take more than one sample when you have a biopsy. This is because there may be more than one grade of cancer in the tumour. The pathologist works out an overall Gleason score by adding together the two most common Gleason grades.
For example, if the most common grade of the samples is grade 3 and the second most common is grade 4 then the overall Gleason score is 7. Some doctors write the two scores separately, for example 3 + 4, instead of 7.
The grade can only ever give a doctor an idea of how a cancer might behave. It cannot definitely predict what will happen. Most cancers will behave as expected, but not all.
Don’t Miss: Prostate Cancer Robotic Surgery Side Effects
Good Prostate Cancer Care
Your MDT will be able to recommend what they feel are the best treatment options, but ultimately the decision is yours.
You should be able to talk with a named specialist nurse about treatment options and possible side effects to help you make a decision.
You should also be told about any clinical trials you may be eligible for.
If you have side effects from treatment, you should be referred to specialist services to help stop or ease these side effects.
Stage Iv Of Prostate Cancer:
Stage IV of prostate cancer is a very advanced stage, with the cancer spreading to the lymph nodes and distant organs like the liver, bones or lungs. It is categorized into the following stages:
Stage IVA:
In this stage, the cancer has spread to the nearby tissues and lymph nodes, but not to any distant organs. It is staged as Any T, N1, M0, Any Grade Group and any PSA levels.
Stage IVB:
These cancers have spread beyond the prostate to the nearby tissues, distant lymph nodes and other organs. It is staged as Any T, any N, M1, Any Grade Group with any levels of PSA.
Recommended Reading: Can You Check Your Prostate Yourself
Treatment Choices For Prostate Cancer That Has Spread
If your prostate cancer has spread to other parts of your body, it cannot be cured. But it can be controlled by lowering the level of testosterone in your body with hormone therapy. You can have hormone therapy as
- Tablets you take each day
- Injections each month or every 3 months or 6 months.
- Tablets for a few months, then a break, followed by more tablets, and so on
Another way of reducing testosterone levels is removing the testicles. This is called surgical castration or orchidectomy. It quickly lowers the testosterone levels and can control the cancer very well.
Orchidectomy or hormone therapy can control the cancer for a few years in many men. When the cancer starts to develop again, your doctors may suggest treatment with chemotherapy or steroids. These can control or shrink the cancer for some time. Chemotherapy can work well at controlling advanced prostate cancer in some men.
If your cancer has spread to your bones and is causing you pain, your specialist may suggest radiotherapy to the affected areas of bone. Radiotherapy for bone pain can work very well to strengthen the bone and relieve pain. The damaged bone begins to repair itself after radiotherapy treatment. Bisphosphonate treatment can also reduce bone pain and help to reduce the risk of bone fracture.
For more information on Thrombosis which may occur during / after chemo click here
If Treatment Does Not Work
Recovery from cancer is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or terminal.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for some people, advanced cancer may be difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment, including a hospital bed, can make staying at home a workable option for many families. Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss. Learn more about grief and loss.
Recommended Reading: Real Health Prostate Complete Walmart
Stage Iv Prostate Cancer Prognosis
Prostate cancers detected at the distant stage have an average five-year survival rate of 28 percent, which is much lower than local and regional cancers of the prostate. This average survival rate represents stage IV prostate cancers that have metastasized beyond nearby areas to lymph nodes, organs or bones in other parts of the body.
How We Treat Prostate Cancer
The prognosis for metastatic prostate cancer can be discouraging, but some treatment centerslike the Johns Hopkins Precision Medicine Center of Excellence for Prostate Cancerspecialize in innovative, individualized therapy with the potential to improve outcomes.
Recommended Reading: Early Warnings Of Prostate Cancer
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
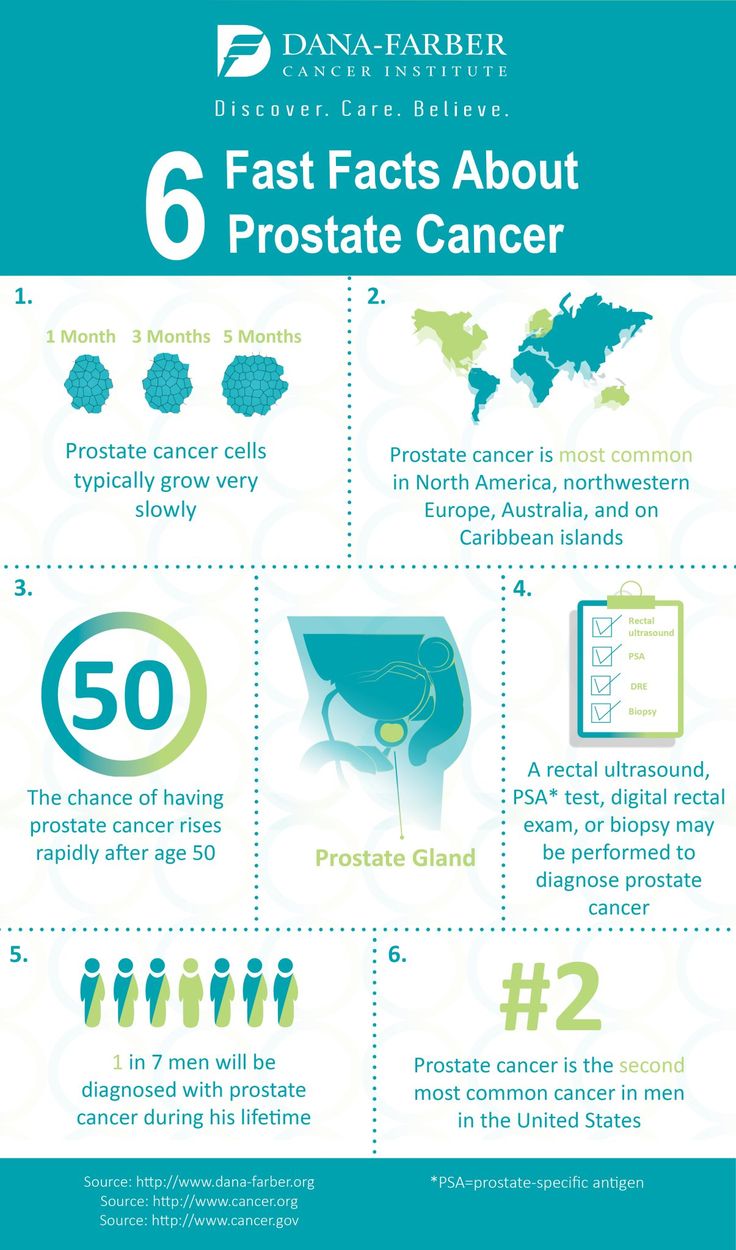
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages, with stages III and IV being more advanced prostate cancer.
- Early Stage | Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate.
- Locally Advanced | Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate but only to nearby tissues.
- Advanced | Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . Advanced prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to treat it. Treatment can help slow advanced prostate cancer progression.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
With biochemical recurrence, the prostate-specific antigen level has risen after treatment using surgery or radiation, with no other sign of cancer.
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone treatment and is only found in the prostate. This is found by a rise in the PSA level, while the testosterone level stays low. Imaging tests do not show signs the cancer has spread.
Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Lymph nodes outside the pelvis
- Other organs, such as liver or lungs
Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
Don’t Miss: What Does The Prostate Do In The Male Body
First Line Treatment For Advanced Prostate Cancer
The established first line approach is to control the progression of the disease by reducing levels of testosterone in the body. This is because testosterone increases the speed at which prostate cancer cells reproduce.
There are two different ways to lower testosterone levels. Hormone therapy lowers the levels of testosterone in the body by taking tablets or having injections. It is sometimes referred to as medical castration. The surgical option involves removing the testicles, known as surgical castration or orchidectomy, although this is now rarely used.
Another approach is called anti-androgen treatment. Androgens have to bind to a protein in the cell called an androgen receptor to work. Anti-androgens are drugs that bind to these receptors so the androgens cant, effectively blocking them. The main side-effects are gynaecomastia breast enlargement and breast pain, although a single radiotherapy dose to the breasts can help this side-effect.
Combining anti-androgens with testosterone reduction is known as Maximum Androgen Blockade and may be used if hormone treatment alone is not working sufficiently.
Treating with chemotherapy at the same time as the start of hormone deprivation was found to increase survival by 13 months in all patients and 17 months in men with high-volume disease.
Side Effects Of Chemotherapy
Side effects of chemotherapy are common and may include:
- Digestive issues such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea
While on chemotherapy, patients are also susceptible to infections because their white blood cell counts are lower. Other common side effects include bruising or bleeding due to fewer blood platelets and fatigue due to the lowered red blood cell count.
Its also possible to experience a severe allergic reaction to some of the drugs used to treat prostate cancer, especially Taxotere® and Jevtana® . The patients care team may recommend medicines before each session to help prevent a reaction.
The prostate chemotherapy drug mitoxantrone may cause leukemia later in life, but this is rare. The prostate chemotherapy drug Emcyt® may increase the risk for blood clots.
During chemotherapy, doctors may also offer supportive care services to help ease side effects. For example, naturopathic providers may suggest supplements to reduce nausea. Also, a mind-body therapist may recommend techniques to help the patient relax and feel less anxious during prostate cancer chemotherapy treatments.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Best Over The Counter Prostate Medicine
The Role Of Bone Morphogenetic Protein
Bone morphogenetic protein belongs to the TGF- superfamily, which functionally stimulates the replication and differentiation of normal cells in the osteoblast lineage. It also plays a crucial role during the process of mesoderm induction, neural tissue differentiation, and morphogenesis of various tissues . Interestingly, BMPs are not only synthesized by osteoblasts but also secreted by prostate cancers. The unusual expression of BMPs in prostate cancer has been implicated in the progression of the disease.
Taken together, BMP expressions are detectable in either normal prostate tissue or prostate cancer cells. The pattern of BMP expression has a close relationship with the progression of prostate cancer and contributes to the onset of bone lesions. It is clear that BMPs play a role in the vicious cycle of metastatic bone formation from prostate cancer. BMPs produced by prostate cancer will induce osteoblastic activities and promote osteoblastic lesions. On the other hand, BMPs synthesized by osteoblasts subsequently enhance the growth of prostate cancer cells allowing further production of BMPs from prostate cancer.
Research Into Hormone Therapy
Prostate cancer depends on the male hormone testosterone for its growth. Hormone therapies block or lower the levels of testosterone. You might have it to lower the risk of your cancer coming back after treatment or to shrink or slow the growth of prostate cancer.
Researchers are looking into:
- the best time to have hormone therapy
- having hormone therapy in combination with other treatments
Read Also: Can You Check For Prostate Cancer Yourself
