Why Is An Mri Scan Used To Diagnose Prostate Cancer
While the PSA blood test and a DRE can indicate a problem, we really need to see what is happening in your prostate. MRI scans provide a relatively easy way to produce quality images of practically any organ in the body and identify potential cancer cells.
Multi-parametric MRI scanners are often used because they can produce more detailed images of areas like the prostate gland. The options open to hospitals are to do the prostate biopsy first and test in the lab for cancer and then run an MRI scan or the other way around.
The benefit of undertaking the MRI scan first is that it can identify what area of the prostate to take the biopsy sample from, thereby reducing the need to take samples from all over the prostate. An MRI scan has little to no side effects or risks associated with it.
Results can be analysed quickly by experienced radiologists that specialise in prostate cancer.
In The Case Where Aggressive Cancer Is Present A Prostate Mri Can Help Prevent A Missed Diagnosis
When a doctor performs a biopsy, multiple tissue samples are taken at random. While this method technically has the capability to find cancer, it can easily miss the cancerous parts of the prostate. In such cases, a repeat test may be ordered. This means another uncomfortable and expensive procedure, and also doubles a patients already high exposure to infection.
Getting a prostate MRI before a biopsy allows radiologists to identify exact areas in the prostate that are suspicious for cancer so that they can be marked as the best targets for a needle biopsy. Advanced technology can then fuse MRI images with real-time ultrasound to help guide the prostate needle biopsies to the specific areas of concern. This increases the accuracy of diagnoses, reduces the risk of infection from the procedure, and helps accelerate treatment planning for positive patients.
As mentioned above, prostate MRIs are complex images. Getting a second opinion by a subspecialist before undergoing biopsy can further improve the accuracy of the procedure, as well as the overall diagnosis. Benign prostatic hyperplasia , enlarged prostate, and bacterial prostatitis can often be mistaken as prostate cancer. A second opinion can help rule out these conditions before proceeding with treatment.
How accurate is MRI in diagnosing prostate cancer?
CONNECT WITH A SPECIALIST
How Is The Procedure Performed
MRI exams may be done on an outpatient basis.
The technologist will position you on the moveable exam table. They may use straps and bolsters to help you stay still and maintain your position.
The technologist may place devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves around or next to the area of the body under examination.
MRI exams generally include multiple runs , some of which may last several minutes. Each run will create a different set of noises.
Your exam may use an endorectal coil. If so, a nurse or doctor will place a disposable cover over the coil. They will lubricate the assembly and insert the coil a short distance into your rectum. After insertion, the doctor inflates the circular balloon that sits around the coil and holds it in place during the exam. When the exam is complete, the doctor deflates the balloon and removes the coil.
If your exam uses a contrast material, a doctor, nurse, or technologist will insert an intravenous catheter into a vein in your hand or arm. They will use this IV to inject the contrast material.
You will be placed into the magnet of the MRI unit. The technologist will perform the exam while working at a computer outside of the room. You will be able to talk to the technologist via an intercom.
If your exam uses a contrast material, the technologist will inject it into the intravenous line after an initial series of scans. They will take more images during or following the injection.
Recommended Reading: Is Fish Good For Prostate
What Does The Mri Scan Report Look Like
Once you have had your MRI scan, a qualified and highly experienced radiologist will look at the images and then complete a report that is sent to your doctor. Rather than the standard text report that you normally see, Prime Health has worked with an expert team of urologists to produce a report that gives a full and comprehensive outline of the scan results and what they do and do not mean.
What this usually covers includes:
- The descriptive text of the scan. This will include aspects such as the appearance of cancer and its staging and whether the patient will require a biopsy to follow up on the MRI test. Its essentially a concise written report that covers all you need to know.
- In line with current reporting guidelines, we provide a grid of scoring 1 to 5 for the risk of cancer as well as a clear diagram highlighting the position of the tumour and its size.
- Using the state of the art multi parametric MRI, we can produce high quality images in 3 axes and estimate elements such as PSA density , spincter length and prostate volume to a high degree of accuracy.
- In addition to this, the report contains up to 6 different images from the scan which can be compared with previous scans .
The aim of our process is to make referral and scanning as fast, efficient and seamless as possible. This means you get your appointment quickly and the results soon after.
What Are Some Common Uses Of Prostate Mri
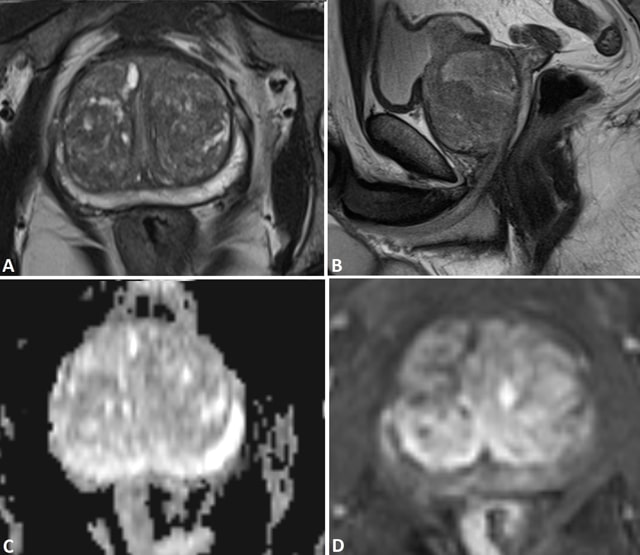
Your doctor uses MRI to evaluate prostate cancer and see if it is limited to the prostate. MRI provides information on how water molecules and blood flow through the prostate. This helps determine whether cancer is present and, if so, whether it is aggressive and if it has spread.
Sometimes, MRI of the prostate is needed to evaluate other prostate issues, including:
- infection or abscess.
- an enlarged prostate
- congenital abnormalities
- complications after pelvic surgery
MRI can tell the difference between diseased tissue and normal tissue better than x-ray, CT and ultrasound.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have Erection After Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer In Patients Without Prior Treatment
The MRI features of prostate cancer might vary significantly based on location, prior treatment, and volume and grade of cancer .3 Generally speaking, high-grade cancers have more typical MR features than low-grade cancers.35 In 2012, in order to provide guidelines for Mp-MRI, a prostate imaging reporting and data system scoring system for structured reporting was introduced by the European Society of Urogenital Radiology.5 The system is beneficial in that it indicates the likelihood of a suspicious lesion on Mp-MRI being prostate cancer and thereby enhances the clinical relevance of Mp-MRI.
What You Need To Know About The Prostate What Do Cancerous Lesions In The Back From Prostate Cancer Look Like On Mri
A enlarged prostate can also cause blockages in the urethra. A blocked urethra can also damage the kidneys. A patient suffering from an enlargement of the prostate may have pain in his lower abdomen and genitals. If pain is present, a digital rectal examination will reveal hard areas. A doctor may prescribe surgery or perform an endoscopic procedure. If the enlarged prostate is not completely removed, it will shrink.
While the size of an enlarged prostate will influence the extent of urinary symptoms, men may experience a range of urinary symptoms. Some men have minimal or no symptoms at all. Some men will have a very enlarged prostate, whereas others will have a mild enlargement. Generally, the symptoms can stabilize over time. Some men may have an enlarged prostate but not notice it. If they have an enlarged colon, their physician can perform a TURP procedure.
Read Also: Da Vinci Robotic Surgery Prostate Cancer Video
Will The Mri Be Done With An Endorectal Coil Or An External Pelvic Coil
Some radiology practices use an endorectal coil a probe-like device covered with latex which is inserted into the rectum and helps provide high-quality images of the prostate. With a newer, high-quality MRI system, endorectal coils are not necessary and an external pelvic coil can be used instead, eliminating patient discomfort while maintaining high quality images.
The Initial Causes What Do Cancerous Lesions In The Back From Prostate Cancer Look Like On Mri
One of the first symptoms of prostate issues is pain or tenderness in the groin or lower back. This can be the result of a noncancerous condition called enlarged prostatic tissue, or it could be an infection of the bladder. In either case, its important to see a doctor as soon as possible. If youre suffering from prostate pain, you may want to consider reducing your caffeine intake.
Another symptom of a potentially enlarged prostate is difficulty starting a stream of urine, leaking, or dribbling. These symptoms are not serious, but theyre still alarming. Most men put up with an enlarged prostate for years before seeking medical attention, but they typically seek treatment as soon as they notice symptoms. Even if you dont have symptoms, its worth getting checked to determine if you have any prostate issues.
If you experience nightly bathroom runs, you may be experiencing an enlarged prostate. You may be having difficulty starting a stream of urine, or you may even be dribbling or leaking during the day. These problems arent life-threatening, but can become a nuisance. You should not ignore these signs and seek treatment as soon as you notice them. If you feel any of these symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Don’t Miss: Can An Enlarged Prostate Cause Gas
What Should You Do If You Are Worried About The Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Its best to speak to your doctor about screening tests which you can have.
This is especially if you are of African background, over the age of 45 years and have a relative who has prostate cancer.
You may also be worried about symptoms that suggest cancer in the prostate gland.
These may be:
- Passing urine more often and with urgency that means being unable to hold your urine before you get to a toilet.
- Pain when passing urine
- A change to your urinary flow such as weakness of the flow.
- Dribbling when passing urine.
- Difficulty in starting to pass urine even when you feel pressed known as strain.
- There may also be a difficulty holding your urine.
- Pain in the lower back, hips, legs etc.
Multiparametric Mri Scan For Prostate Cancer
MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging. It is a type of scan that creates pictures using magnetism and radio waves. MRI scans produce pictures from angles all around the body and shows up soft tissues very clearly.
A multiparametric MRI is a special type of MRI scan that produces a more detailed picture of your prostate gland than a standard MRI scan does. You usually have a mpMRI scan if doctors suspect that you have prostate cancer.
You May Like: Can You Get An Erection After Prostate Surgery
What Happens During A Prostate Mri
You will be asked to change into a hospital gown and lie on a table attached to the MRI machine. A small needle will be inserted into a vein in your arm or hand this will be used to give the following medications:
Some radiology practices use an endorectal coil as part of the scan. An endorectal coil is a latex balloon with a central tube that contains the coils. It helps to provide high-quality images of the prostate and surrounding area. It is inserted into the rectum and inflated before the scan. It stays in during the scan and is removed when the scan is finished.
What Happens During The Exam
You will be asked to wear a hospital gown during the MRI scan.
As the MRI scan begins, you will hear the equipment making a muffled thumping sound, which will last for several minutes. Other than the sound, you should notice no unusual sensations during the scanning.
Certain MRI exams require an injection of a dye . This helps identify certain anatomic structures on the scan images.
Before the exam, feel free to ask questions and tell the technician or doctor if you have any concerns.
People who get anxious when in tight spaces may benefit from talking to their doctor before the procedure. Some options include taking a prescription medication before the procedure to relieve anxiety or having the exam done in one of the newer and less confining MRI units, called an open MRI, when available.
Recommended Reading: What Are The 5 Warning Signs Of Prostate Cancer
Prostate Tb Abscess In A Patient With Bladder Tcc After Intravesical Instillation Of Bcg
Adjuvant intra-vesical immunotherapy with BCG for bladder transitional cell carcinoma can lead to a rare complication of tuberculous infection in the prostate via haematogenous spread and direct extension which can cause a prostate abscess .
The granulomatous reaction that occurs in prostate tissues following the topical instillations of BCG after resection of bladder cancer can present MRI features similar to prostate cancer . It appears as an ill-defined region with moderate contrast enhancement, diffusion restriction and very low ADC values due to the high cellular density. These are a well-recognised cause of false positive MRI. However, frank abscess formation related to BCG is rare with only a handful of cases described in the literature. History and biochemical correlation are important to consider this as a differential diagnosis and a biopsy may be needed to confirm .
Fig. 7
Prostate abscessa, b Axial T2W images show left lateral bladder wall thickening and heterogeneous but predominantly low T2 signal in the left prostate , respectively. c Post-contrast, the lesion demonstrates strong peripheral contrast enhancement and on DWI/ ADC in d, e, respectively, the central element of the left prostate lesion shows restricted diffusion with a very low ADC value
Hypertrophic Nodule In The Peripheral Zone
A hypertrophic nodule might appear in the peripheral zone as a low T2 signal focus mimicking prostate cancer. Such nodules might also demonstrate diffusion restriction, rapid contrast wash-in and wash-out , and elevated choline peaks resulting in a diagnostic challenge.10 However, the hypertrophic nodule is usually well defined and often does not extend to the capsule at T2WI . The nodule might have the same imaging features as the adjacent central gland since most of these nodules arise from the central gland. In addition, normal prostate tissue between the nodule and the capsule is often present .
Hypertrophic nodule in the left side of the midline of the peripheral zone mimicking prostate carcinoma in a patient with prostate-specific antigen to 9.1ngml1. Axial T2 weighted imaging shows a well-defined low signal lesion in the left side of the midline of the peripheral zone . The open arrow indicates a layer of normal prostate tissue between the lesion and capsule. Apparent diffusion coefficient map shows low ADC value of the lesion . Dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging shows contrast rapid wash-in and wash-out of the lesion . MRI-guided biopsy confirmed benign prostate tissue.
Don’t Miss: Effects Of Removing Prostate Gland
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope.
A biopsy is a procedure that can be used to diagnose prostate cancer. A biopsy is when a small piece of tissue is removed from the prostate and looked at under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells.
A Gleason score is determined when the biopsy tissue is looked at under the microscope. If there is a cancer, the score indicates how likely it is to spread. The score ranges from 2 to 10. The lower the score, the less likely it is that the cancer will spread.
A biopsy is the main tool for diagnosing prostate cancer, but a doctor can use other tools to help make sure the biopsy is made in the right place. For example, doctors may use transrectal ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging to help guide the biopsy. With transrectal ultrasound, a probe the size of a finger is inserted into the rectum and high-energy sound waves are bounced off the prostate to create a picture of the prostate called a sonogram. MRI uses magnets and radio waves to produce images on a computer. MRI does not use any radiation.
Symptoms Of Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer often shows few, or even no symptoms in early stages. Most men who are diagnosed with prostate cancer are in stages II or III. Early symptoms are mild, and often include:
- An increased PSA level . This test is usually included in a yearly physical for men ages 55 or older, or even earlier if a family history of prostate cancer exists.
- Increase in urinary frequency or the urge to urinate throughout the night.
- Difficulty stopping or starting urination.
- New onset of erectile dysfunction.
When the disease has progressed, symptoms often increase and can include:
- Nontraumatic pain in the bones that does not resolve normally.
- Swelling in the pelvis or legs.
- Numbness in the back, pelvis, or legs.
While each patient will vary with symptoms, men exhibiting any of the aforementioned symptoms should schedule an appointment with their provider immediately.
Also Check: Does Masturbation Help Your Prostate
