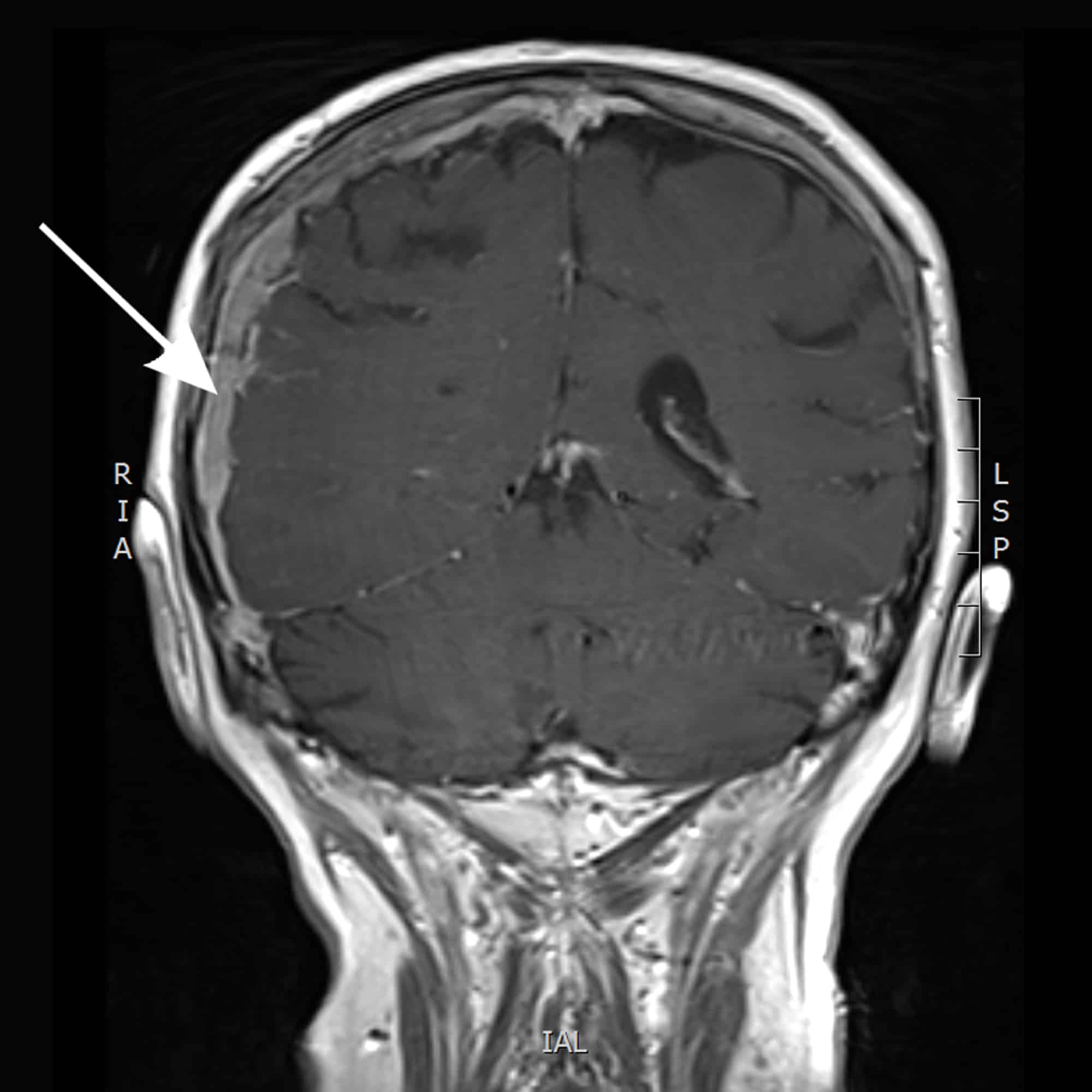
How Do Doctors Find Metastatic Prostate Cancer
When you are diagnosed with prostate cancer, your doctor will order tests such as:
These tests may focus on your skeleton and in your belly and pelvic areas. That way doctors can check for signs that the cancer has spread.
If you have symptoms such as bone pain and broken bones for no reason, your doctor may order a bone scan. It can show if you have signs of cancer spreading to your bones.
Your doctor will also ask for blood tests, including a check of PSA levels, to look for other signs that the cancer is spreading.
PSA is a protein made by the prostate gland. A rise in PSA is one of the first signs your cancer may be growing. But PSA levels can also be high without there being cancer, such as if you have an enlarged prostate, a prostate infection, trauma to the perineum, or sexual activity.
Who Is At Risk For Advanced Prostate Cancer
The exact cause of prostate cancer isnt clear. Your risk of developing this particular cancer increases after you reach age 50.
Certain groups are more likely to develop aggressive forms of prostate cancer, including African-American men and men who carry certain inherited genetic mutations such as BRCA1, BRCA2, and HOXB13.
Most men with prostate cancer dont always have a family history of the disease. But having a father or brother with prostate cancer more than
You probably wont need all of these tests. Your doctor will choose the tests based on your symptoms and physical exam.
If any of the images reveal abnormalities, it doesnt necessarily mean that you have cancer. Additional testing may be necessary. If they find a mass, your doctor will probably order a biopsy.
For a biopsy, your doctor will use a needle to remove samples from the suspicious area. A pathologist will then analyze the removed cells under a microscope to see if theyre cancerous. The pathologist can also determine if you have an aggressive form of prostate cancer.
What Happens After Treatment
If you’ve been treated, especially if a surgeon removed your prostate, your PSA levels should start to go down. Doctors usually wait several weeks after surgery before checking PSA levels.
A rise in PSA after treatment may suggest the cancer is back or spreading. In that case, your doctor may order the same tests used to diagnose the original cancer, including a CT scan, MRI, or bone scan. The radiotracer Axumin could be used along with a PET scan to help detect and localize any recurrent cancer.
Though very rare, it’s possible to have metastatic prostate cancer without a higher-than-normal PSA level.
Go to all of your follow-up doctor appointments. At these checkups, let your doctor know about any symptoms youâre having, especially ones like bone pain or blood in your pee. You could keep track of your symptoms by writing them down in a journal or diary.
At home, follow some healthy habits to feel your best:
Eat a balanced diet. It can boost your energy and your immune system. Fill your plate with fruits and vegetables and high-fiber foods. Cut back on fattening foods, sugar, and processed foods and meats.
Let your doctor know if youâre having trouble staying at a healthy weight or if youâre losing your appetite.
Get exercise if your doctor OKs it. It can be good for your body and mind. It can also help you stay at a healthy weight, keep up your strength, and help manage medication side effects.
Show Sources
You May Like: How Soon After Prostate Surgery Can You Fly
How Do Brain Metastases Affect My Body
Different parts of your brain control different body functions, so the impact brain metastases have on your body depends on where your primary cancer ended up when it traveled to your brain. About 85% of brain metastases develop in your cerebrum, which is the top and largest part of your brain, with 15% developing in your cerebellum, the lower part of your brain.
Your cerebrum has four lobes or sections. Each section manages different body functions. For example, if you have a metastatic brain tumor in your frontal lobe, it could affect your behavior, reasoning and thinking. If you have metastatic brain tumors in the left frontal lobe, it could affect your speech.
Clonality Of Single Nucleotide Variants
Clonal prevalence analysis was conducted using the hierarchical Bayesian model PyClone, and the ABSOLUTE V2.0 algorithm in the case of samples used in analysis of clonal evolution. PyClone estimates the cellular prevalence of mutations in deeply sequenced samples, using allelic counts, and infers clonal structure by clustering these mutations into groups with co-varying cellular frequency. PyClone was run using a two-pass approach, whereby mutations whose cellular prevalence estimate had standard deviation > 0.3 were removed before a second pass analysis was run. A cellular prevalence of > 80% was used as a threshold for clonality. ABSOLUTE infers CCF from the reads supporting the reference/alternative allele, in conjunction with segmented copy-number data from WES, and was run after patching as described here: . Solutions from ABSOLUTE were manually curated to assure the solution matched the ploidy estimate generated by FACETS.
Also Check: What Is Stage 3 Prostate Cancer
What If You Have Metastatic Castration
This means you have a type of metastatic prostate cancer thatâs able to grow and spread after you had hormone therapy to lower your testosterone levels.
Still, most people with mCRPC stay on androgen deprivation therapy because it might still be effective against some prostate cancer cells.
Your doctor may recommend adding other treatments like:
- Treatments to ease symptoms like pain
You could also find out if a clinical trial might be right for you.
Some people with mCRPC simply choose to try active surveillance or watchful waiting.
What You Need To Know
- Metastatic brain cancer is caused by cancer cells spreading to the brain from a different part of the body.
- The most common types of cancer that can spread to the brain are cancers of the lung, breast, skin , colon, kidney and thyroid gland.
- Metastatic brain tumors are five times more common than primary brain tumors .
- Metastatic brain tumors can grow rapidly, crowding or destroying nearby brain tissue. Sometimes a patient may have multiple metastatic tumors in different areas of the brain.
Read Also: Fast Growing Prostate Cancer Symptoms
Chemotherapy For Metastatic Brain Tumors
Because traditional chemotherapy cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, newer treatments called targeted therapy are used as the primary type of chemotherapy for treating metastatic brain tumors.
These drugs identify and attack cancer cells with minimal harm to normal cells while preventing the growth and spread of cancer cells. Targeted therapy can be administered after surgery or in conjunction with radiation therapy to destroy remaining cancer cells.
Targeted therapies used to treat metastatic brain tumors include:
- Trastuzumab for breast cancer that has spread to the brain
- Erlotinib for the most common type of lung cancer that has spread to the brain
Palliative Care At Johns Hopkins
Palliative care is specialized medical care that helps patients facing serious illnesses and their families by adding an extra layer of support.
Palliative care teams can help with the symptoms and the stress of living with a serious illness, including controlling pain, providing support for the mental and emotional effects of an illness, and managing other symptoms.
Read Also: Can You Feel Prostate Cancer
What Are Bone Metastases With Prostate Cancer
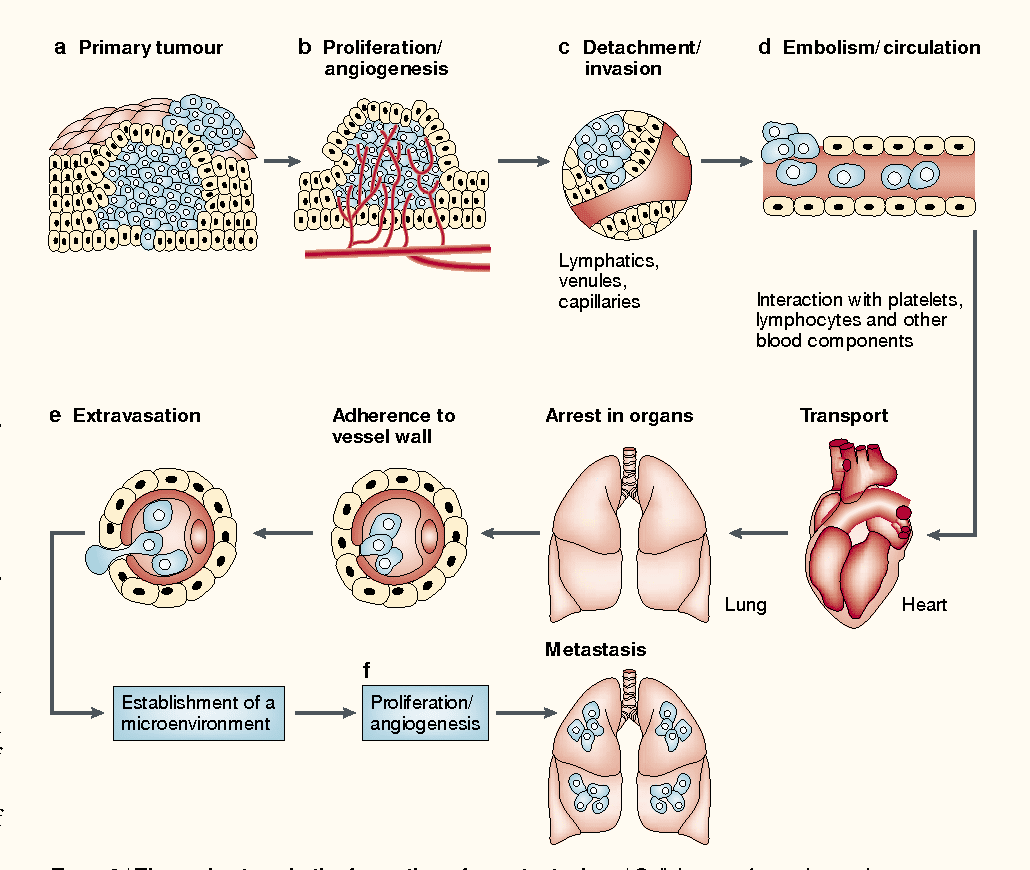
The ACS describes bone metastases as areas of bone containing cancer cells that have spread from another place in the body. In the case of prostate cancer, the cells have spread beyond the prostate gland. Since the cancer cells originated in the prostate gland, the cancer is referred to as metastatic prostate cancer.
The cancer cells spread to the bones by breaking away from the prostate gland and escaping attack from your immune system as they travel to your bones.
These cancer cells then grow new tumors in your bones. Cancer can spread to any bone in the body, but the spine is most often affected. Other areas cancer cells commonly travel to, according to the ACS, include the pelvis, upper legs and arms, and the ribs.
What Is The Treatment For Advanced Prostate Cancer
No matter where prostate cancer spreads, its still treated as prostate cancer. Its harder to treat when it reaches an advanced stage.
Treatment for advanced prostate cancer involves targeted and systemic therapies. Most men need a combination of treatments and they may have to be adjusted from time to time.
Read Also: What Is The Normal Level For Prostate
Metastatic Brain Tumor Surgery
Surgery provides fast relief of mass effect pressure inside the skull resulting from a growing metastatic tumor and swelling of the brain. Some patients may find improvement of symptoms as early as within hours of surgery if mass effect is what is causing your symptoms.
The goal of surgery is to minimize the amount of space the tumor takes up by debulking, which means removing as much of the tumor as possible while maintaining neurological function.
In general, doctors recommend surgery for metastatic brain cancer when:
- There is a clear link between the symptoms and the tumors location.
- The primary cancer is treatable and under control.
- The tumor can be safely removed.
The most common type of surgery to remove metastatic brain tumors is called a craniotomy, which can be performed through a variety of approaches, including the keyhole craniotomy.
Learn more about brain tumor surgery and recovery.
Intradural Extramedullary Spinal Cord Metastasis Of The Prostate: A Case Presentation And Review Of The Literature
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 10 May 2016
- Amparo Wolf
- Affiliation:Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences, Division of Neurosurgery, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada.
- Ryan Johnstone
- Affiliation:Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences, Division of Neurosurgery, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada.
- Fawaz Siddiqi
- Affiliation:Department of Clinical Neurological Sciences, Division of Neurosurgery, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada.
You May Like: What Can You Do To Help Prevent Prostate Cancer
What Are The Chances Of Getting Metastatic Prostate Cancer
About 50% of men diagnosed with local prostate cancer will get metastatic cancer during their lifetime. Finding cancer early and treating it can lower that rate.
A small percentage of men aren’t diagnosed with prostate cancer until it has become metastatic. Doctors can find out if it’s metastatic cancer when they take a small sample of the tissue and study the cells.
Types Of Imaging Studies
If your doctor suspects your cancer might be spreading, they will likely order more imaging tests. A common imaging workup may include a bone scan and a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. An MRI might be done as well. Some research centers are also using magnetic MRIs or PET scans to further refine the staging of prostate cancer.
Prostate Cancer Doctor Discussion Guide
Get our printable guide for your next doctors appointment to help you ask the right questions.
Dont Miss: How Do Doctors Check Prostate Cancer
Read Also: What Kind Of Doctor Checks For Prostate Cancer
Incidence Of Intracranial Metastasis In Patients With Prostate Cancer
This review identified a total of 5644 imaging examinations, inclusive of the brain, performed on 4341 unique prostate cancer patients. A total of eight prostate cancer patients were identified as having an intracranial metastasis from prostate cancer, yielding an incidence of 0.18%. Of the 5644 imaging examinations reviewed, the majority were 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT scans followed by FDG PET/CT and brain MRI scans. Although 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT scans are the standard method used at our center for prostate cancer staging/restaging, it is not uncommon for patients to undergo FDG PET/CT instead, reasons for this are typically either because of the presence of a prostate cancer variant with limited PSMA expression or because the patient has concurrent primary cancers and the FDG PET/CT scan is performed to monitor both cancers. Brain MRIs are largely performed to investigate spinal cord and cranial disease, new neurological symptoms, or new lesion/s observed on other imaging modalities.
Can I Survive Advanced Prostate Cancer Whats The Prognosis
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of death from cancer in men, according to the National Cancer Institute. While theres no cure, men can live with it for years if they get the right treatment. Each man with advanced prostate cancer is different, of course. You and your cancer have unique qualities that your doctor takes into consideration when planning the best treatment strategy for you.
According to Harvard Medical School, the prognosis for men with advanced prostate cancer is improving because of newer medications that help them get past a resistance to androgen-deprivation therapy that typically develops after a few years of treatment. With these medications, many men are living longer, and a number of men diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer are dying with the cancer, not from it.
Promptly treating prostate cancer bone metastases with the newest medication can help change a mans prognosis dramatically, Tagawa says. There are men who do well for decades, he says. Some men can even stop treatment, go on to live many years, and actually die of something unrelated.
Tagawa says that cancer specialists who use sophisticated imaging technologies, like positron-emission tomography scans, have gotten very good at finding even tiny bone metastases, which is valuable in diagnosing and removing early stage metastases.
Don’t Miss: How To Stimulate Your Prostate
Demographic And Clinical Data Of The Pcbm Cohort
The cohort of 51 patients analyzed here , represents a substantial increase in the number of PCBM samples over existing studies. . The average age at the time of PCBM diagnosis among the 51 patients was 71years. 56% harbored multiple and 41% singular CNS metastasis. Metastases in brain parenchyma were present in 41% , dural metastases in 35% while in 24% of the patients the primarily metastatic location was either unknown or unclear by involvement of multiple anatomical structures. Additionally, 88% of the patients presented non-brain metastases with bone involvement in 91% of these. Androgen deprivation therapy or orchiectomy were conducted in 82% of the cases. From those, 26% underwent further therapy with next-generation ARSi , namely abiraterone and/or enzalutamide .
Solitary Brain Metastasis From Prostate Cancer: A Case Report
Tasneem Barakat, Arnav Agarwal, Rachel McDonald, Vithusha Ganesh, Sherlyn Vuong, Michael Borean, Edward Chow, Hany Soliman
Rapid Response Radiotherapy Program, Department of Radiation Oncology, Odette Cancer Centre, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada
Correspondence to:
Abstract: Brain metastases arising from prostate cancer are exceedingly rare and typically occur late in the course of the disease. Most patients have widespread metastatic disease before developing brain metastases from prostate cancer. We report the case of a 67-year-old male with prostate cancer presenting with an isolated symptomatic brain metastasis. Aggressive treatment of the metastatic site included tumor resection and adjuvant stereotactic radiation treatment to the surgical bed, resulting in a favorable outcome.
Keywords: Brain brain metastases metastatic cancer prostate cancer stereotactic radiosurgery radiotherapy
Submitted Mar 06, 2016. Accepted for publication Apr 16, 2016.
doi: 10.21037/apm.2016.04.02
Recommended Reading: When Do Guys Start Getting Prostate Exams
Patient And Disease Characteristics Associated With Brain Metastasis
Myint and Qasrawi reported an increased risk for BM in patients with CSPC and concurrent visceral metastases, with multivariate odds ratios for liver and lung metastasis of 2.85 and 4.6 , respectively . Other predictive factors described for prostate cancer BM included non-adenocarcinoma and rare histological types of prostate cancer, such as small-cell carcinoma . However, these latter studies lacked definite statistical confirmation of the suggested associations.
Neurologic Complications Of Prostate Cancer
RAMSIS BENJAMIN, M.D., M.P.H., Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California
Am Fam Physician. 2002 May 1 65:1834-1841.
This article exemplifies the AAFP 2002 Annual Clinical Focus on cancer: prevention, detection, management, support, and survival.
Neurologic complications continue to pose problems in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. From 15 to 30 percent of metastases are the result of prostate cancer cells traveling through Batsonâs plexus to the lumbar spine. Metastatic disease in the lumbar area can cause spinal cord compression. Metastasis to the dura and adjacent parenchyma occurs in 1 to 2 percent of patients with metastatic prostate cancer and is more common in those with tumors that do not respond to hormone-deprivation therapy. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, the most frequent form of brain metastasis in prostate cancer, has a grim prognosis. Because neurologic complications of metastatic prostate cancer require prompt treatment, early recognition is important. Physicians should consider metastasis in the differential diagnosis of new-onset low back pain or headache in men more than 50 years of age. Spinal cord compression requires immediate treatment with intravenously administered corticosteroids and pain relievers, as well as prompt referral to an oncologist for further treatment.
More Common Neurologic Complications in Patients with Metastatic Prostate Cancer*
? = unknown.
Recommended Reading: What Age Do You Start Screening For Prostate Cancer
Sequence Data Processing Pipeline And Single Nucleotide Variant Identification
Reads obtained were aligned to the reference human genome GRCh38 using Burrows-Wheeler Aligner . Local realignment, duplicate removal, and base quality adjustment were performed using the Genome Analysis Toolkit and Picard . Somatic single nucleotide variants and small insertions and deletions were detected using Mutect2 and Strelka2 v2.9.10. Only variants detected by both methods were reported. We filtered out SNVs and indels outside the target regions , those with a variant allelic fraction of < 5% and/or those supported by < 3 reads. We excluded variants for which the tumor VAF was < 5 times that of the paired non-tumor VAF, as well as those found at > 5% global minor allele frequency of dbSNP . We further excluded variants identified in at least two of a panel of 210 non-tumor samples, including the non-tumor samples included in the current study, captured and sequenced using the same protocols using the artifact detection mode of Mutect2 implemented in GATK. For samples for which we had no matched normal tissue, we also removed variants present at VAF of > 0.1% in the ExAC non-TCGA database of normal germline samples. All indels were manually inspected using the Integrative Genomics Viewer. Hotspot missense mutations were annotated using the published resources,.
