Literature Search Results And Characteristics
Our searches of four databases yielded 6,378 articles. After 413 duplication records were removed, titles and abstracts of these records were screened for inclusion. Full texts of 46 records were read, and 33 studies met the inclusion criteria .
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the literature screening process and results.
Twenty PBT-related studies involved 48,765 patients with a median mean age of 66 years old. Median follow-up across all studies was 43.4 months . The included studies were published from 2010 to 2020. Most of the studies were from the USA , five from Japan , and one from Korea . For the trials from the USA, most of the studies set irradiation dose at 7082 GyE delivered in 544 fractions. For the five trials from Japan, the irradiation dose was usually set at 6380 GyE delivered in 2039 fractions. For one trial from Korea, they set irradiation dose at 3560 GyE delivered in 520 fractions. The basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Basic characteristics of included studies.
Proton Vs Photon Radiation
Proton radiation is different from other types of radiation, which rely on photons. Photon radiation comes in three types: intensity-modulated radiation therapy , radioactive seed radiation , and stereotactic body radiation therapy . Sometimes a combination of brachytherapy in conjunction with one of the other types of beam radiation is used.
All types of radiation are effective, resulting in the death of cancer cells. All can potentially cause side effects if the radiation touches adjacent normal organs, such as the bladder, rectum, and urethra.
What You Need To Know About The Prostate What Is The Success Rate Of Proton Therapy For Prostate Cancer
The main purpose of the prostate is to produce semen, a milky fluid that sperm swims in. During puberty, the body produces semen in a large number of cases, including enlarged prostate. This fluid causes the prostate to swell and cause a number of bladder-related symptoms. This is why the prostate is important to the body. It can be caused by many factors, including infection and inflammation.
A enlarged prostate can also cause blockages in the urethra. A blocked urethra can also damage the kidneys. A patient suffering from an enlargement of the prostate may have pain in his lower abdomen and genitals. If pain is present, a digital rectal examination will reveal hard areas. A doctor may prescribe surgery or perform an endoscopic procedure. If the enlarged prostate is not completely removed, it will shrink.
While the size of an enlarged prostate will influence the extent of urinary symptoms, men may experience a range of urinary symptoms. Some men have minimal or no symptoms at all. Some men will have a very enlarged prostate, whereas others will have a mild enlargement. Generally, the symptoms can stabilize over time. Some men may have an enlarged prostate but not notice it. If they have an enlarged colon, their physician can perform a TURP procedure.
Read Also: What Is A Prostate Biopsy
Advantages Of Proton Therapy For Prostate Cancer
Proton therapy has proven to show remarkable promise and advantages over conventional therapy-especially in the treatment of prostate cancer. Proton radiation therapys accuracy and the control it gives physicians in terms of adapting treatment make it a non-invasive and low-risk option for prostate cancer treatment.
Technical Delivery Of Proton Therapy
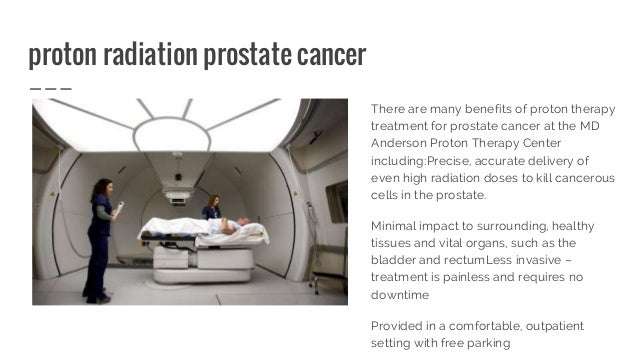
A minimum standard of treatment delivery must be followed to ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of proton therapy for prostate cancer. The goals of delivery should be to overcome 3 fundamental radiation therapy challenges: to minimize uncertainty regarding the precise location of the target during beam exposure, to maximize target coverage, and to minimize radiation exposure to organs at risk.
Although intrafraction and interfraction variability must be accounted for with both proton- and photon-based treatment planning, there is a proton-specific uncertainty called range uncertainty, which refers to the effect on the proton beam range that the slight variations in prostate position may have on the composition of tissues in the beam path. Range uncertainty is based on modeling studies and includes the addition of a margin to the proximal and distal edge of the target.
You May Like: What Happens When A Man Loses His Prostate
Safety And Efficacy Of Proton Therapy
Many people with locally advanced cancers are treated with a combination of chemotherapy and either traditional or proton radiation. For patients getting chemotherapy and radiation at the same time, finding ways to limit side effects without making the treatment less effective is a high priority, Dr. Baumann said.
He and his colleagues analyzed data from nearly 1,500 adults with 11 different types of cancer. All participants had received simultaneous chemotherapy plus radiation at the University of Pennsylvania Health System between 2011 and 2016 and had been followed to track side effects and cancer outcomes, including survival. Almost 400 had received proton therapy and the rest received traditional radiation.
Those who received proton therapy experienced far fewer serious side effects than those who received traditional radiation, the researchers found. Within 90 days of starting treatment, 45 patients in the proton therapy group and 301 patients in the traditional radiation group experienced a severe side effectthat is, an effect severe enough to warrant hospitalization.
In addition, proton therapy didnt affect peoples abilities to perform routine activities like housework as much as traditional radiation. Over the course of treatment, performance status scores were half as likely to decline for patients treated with proton therapy as for those who received traditional radiation.
When Is Proton Therapy Appropriate
Proton therapy is not effective at treating certain cancers, such as those that have spread widely. Since the radiation focuses on a targeted area, it is impractical to use this treatment for cancers that have metastasized to more than a few places. Most importantly, proton therapy is most often used for cancers requiring radiation that are near extremely sensitive organs and tissues. In fact, proton therapy is used predominantly to treat the following types of cancer:
Treatment of these cancers using traditional radiation have a higher potential risk for both immediate and permanent damage to nearby tissues and cellular death.
Read Also: Does Prostate Cancer Have A Cure
Also Check: What Is A High Psa Level For Prostate Cancer
Precision Of Proton Therapy
Proton therapy is precise, and therefore better able to avoid surrounding organs. The radiation dose deposited by protons increases gradually until it peaks suddenly, called the Bragg Peak, and then falls to zero. Radiation oncologists can control where the Bragg Peak occurs, pinpointing it to peak exactly within the prostate.
The images below show the amount and location of radiation that the body receives during treatment with proton therapy and X-rays/IMRT . Proton therapy limits the radiation delivered outside the prostate.
Potential Disadvantages Of Proton Therapy
Depending on techniques compared, there may be disadvantages in dose distribution with proton therapy compared with IMRT. For example, Trofimov et al found that IMRT provided better conformality of the high-dose volume to the target than double-scattered proton therapy did. The average conformality index was 2.73 with IMRT and 3.11 with the double-scattered proton therapy plans . Similarly, in a comparison of IMRT to double-scattered proton therapy, Underwood et al found that IMRT provided better high-dose conformality than proton therapy did when evaluating prescription isodose lines. In addition, IMRT provided lower volumes of both rectum- and bladder-receiving doses in the range of V50 to V70 compared with double-scattered proton therapy. This shortfall of double-scattered proton therapy can be eliminated by using IMPT, which is a more refined delivery method of proton particles using PBS. Trofimov et al found that IMPT provided a better conformality index than IMRT did when delivering high-dose radiation therapy to the prostate.
Read Also: Best Thing For Healthy Prostate
Also Check: Can Abdominal Ultrasound Detect Prostate Cancer
Active Surveillance For Prostate Cancer
Also known as watchful waiting, active surveillance is a non-treatment option that involves continued monitoring of prostate cancer. More frequent checkups are often required to keep an eye on any changes through PSA blood tests, Digital Rectal Exams and ultrasounds. Biopsies may also be done to assess the aggressiveness of the cancer and its risk of growing and spreading. Studies have found that, after 15 years on active surveillance, less than 1% of men developed a metastatic disease. Additionally, over 30% of men have prostate cancers so slow-growing that non-treatment may be a better option.
Often Recommended for:
Possible Side Effects of Active Surveillance:
- No treatment-related side effects
Pros & Cons of Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer
Pros:
- No surgery or hospital stays
- New technologies continue to improve imaging and testing
Cons:
- Frequent checkups for testing and biopsies
- May face a greater risk of prostate cancer growing and spreading
- Stage of your prostate cancer may advance
- May limit future treatment options and chances of curing the cancer
- Diagnosis can create stress and anxiety
Benefits Of Proton Prostate Cancer Treatment
Proton therapy improves the quality of life for prostate cancer patients and survivors by offering a number of compelling benefits:
- It is non-invasive and therefore painless
- It is more accurate than other kinds of radiation
- Full or higher doses of radiation can be used for treatment without damaging healthy tissues and organs
- Treatment is provided in an outpatient setting
- Proton radiation therapy does not require recovery time
- The treatment has little to no impact on a patients energy level
- Proton therapy poses minimal risk of impotency
- The treatment has lower risk of side effects compared with conventional treatment.
Read Also: Which Laboratory Test Is Done To Screen For Prostate Cancer
Proton Therapy Faqs For Prostate Cancer
Proton Therapy FAQs for Prostate Cancer
The outlook for patients diagnosed with prostate cancer has improved in recent years. Through advancements in technology, imaging, and treatment delivery, researchers have found ways to better characterize tumors and tailor treatments to each patient. No longer are there one size fits all treatment solutions. The multidisciplinary prostate cancer treatment team can discuss care strategies that might include surgery, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and various forms of radiation.
Radiation is a powerful tool in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is a curative alternative to surgery or may be indicated after surgery to treat patients with high risk features or biochemically recurrent prostate cancer in the adjuvant or salvage setting. It can also used to treat oligometastases sites of spread or considered to retreat areas of previous disease.
Why Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer?
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells and surrounding tissues using high-energy photons or particles. Radiation therapy may be used:
- To eradicate early-stage cancers confined to the prostate gland
- As a treatment to prolong survival for men with advanced or recurrent prostate cancer
- Alone or in combination with other treatments, such as androgen deprivation , in more advanced cancers that may have spread beyond the prostate
- As a way to slow cancer growth and palliate pain or bleeding in cases of advanced cancer
References:
Proton Therapy Success Stories
Its one thing to hear about the success rate of proton therapy treatment for prostate cancer. Its another thing to hear the success stories straight from the mouths of survivors.
Walter Knight, an Army pilot, biker, and all around adventurer, was diagnosed with prostate cancer only six weeks after being prescribed testosterone for his anemia.
There are unending volumes in thousands of books that attempt to describe the kaleidoscope of feelings and emotions that follow a diagnosis of metastatic cancer, said Knight in his journal entitled the Proton Chronicles. Im sure that like many, I attempted to rationalize or even justify the situation, but when faced with real mortality, your life and that of your family is forever altered.
After considering surgery and consulting multiple online forums, Knight finally decided on proton therapy to treat his cancer. Over the course of 20 hypofractionated treatments, Knight continued to bike on his favorite trails and play hockey in the local ice rink.
Its really kind of difficult to get your head around the whole situation, said Knight about his proton treatment. This is happening at the cellular level and its absolutely painless.
Earl Malpass, a mission pilot and pastor, also received proton therapy after being diagnosed with prostate cancer. Malpass, whos lived in Alaska for over 15 years with his wife, Lynn, chose to seek medical care in other states after receiving his diagnosis.
Don’t Miss: Can You Still Have An Erection After Prostate Removal
How Proton Therapy Effectively Treats Prostate Cancer
Proton therapy treats prostate cancer with high doses of radiation that are more accurate, and potentially more effective, than traditional radiation. Our targeted proton beams focus most of their destructive energy at the tumor site, therefore causing less damage to healthy surrounding tissue as they enter the body. Because of this, proton therapy patients dont have to worry about many of the side effects and additional healthy tissue damage that is commonly associated with X-ray therapy.
an effective cancer treatment alternative
Types Of Prostate Cancer Treated At The New York Proton Center
The New York Proton Center treats the following prostate cancers and genitourinary cancers with proton therapy.
Localized prostate cancer, which includes stage 1, stage 2, and stage 3 cancer, that has not grown into nearby tissues or more distant body parts. There are three types:
- Very-low-risk and low-risk prostate cancer, each of which are unlikely to grow or spread for a long time, if at all.
- Intermediate-risk prostate cancer, which may grow or spread in a few years.
- High-risk prostate, which has the highest likelihood of spreading and, even after treatment, recurring.
Prostate cancer will sometimes grow quickly and spread to lymph nodes, pea-sized pieces of tissue that filter a waste product called lymph. When this happens, a larger area needs to be targeted for treatment that includes the prostate gland and the lymph nodes. Proton therapy is particularly beneficial when treating large areas in the pelvis.
Data suggest that men who have undergone prostatectomy for prostate cancer may benefit from follow-up treatment with proton therapy, depending on several factors:
- Gleason score
- Seminal vesicle and lymph nodes involvement
- PSA levels
Bladder cancers have a high correlation to prostate cancer. The types are named for the cells they affect, usually in the bladder wall.
Kidney cancer patients are at increased risk of prostate cancer.
Proton therapy can treat these recurrent tumors more safely than other methods, giving patients a better chance for a cure.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Massage The Prostate
What Is Cyberknife Versus Proton Therapy
CyberKnife is a brand name for one of several available radiosurgery devices called linear accelerators, which deliver stereotactic body radiation therapy or stereotactic radiosurgery . MSK uses a similar device, made by a company called Varian, that destroys tumors with extremely precise, very intense doses of radiation. Proton therapy delivers a beam of proton particles that stops at the tumor.
Who Are They Looking For
This study is looking for people who have been diagnosed with adenocarcinoma of the prostate within the last year. Only patients with early stage tumors will be accepted.
Patients with cancer spread beyond the prostate, who already underwent surgery, radiation therapy or chemotherapy cannot take part in this trial. Patients who received hormone therapy will also be excluded. Other conditions, such as autoimmune diseases , HIV infection, inflammatory bowel disease and previous hip replacement surgery also represent exclusion criteria.
Dont Miss: What Is Good To Take For Prostate Health
You May Like: Can Your Prostate Be Removed
Current Indications For Proton Therapy In The Management Of Prostate Cancer
Proton therapy is indicated in several clinical scenarios in the management of patients with prostate cancer in light of its potential to reduce the risk for acute and late toxicities related to dosimetric advantages compared with photon-based radiation therapy. The indications for proton therapy are listed in Table 1 and are summarized below.
Comparisons of and indications for intensity-modulated radiotherapyvolumetric modulated arc radiotherapy , double-scattering proton therapy , and intensity-modulated proton therapy .
Potential Advantages Of Proton Therapy
The relative advantages and disadvantages of proton therapy when compared with photon radiation have evolved over time as the radiation oncology community continues to refine the planning and delivery techniques for both modalities. The results of those comparisons depend on the delivery technique: intensity-modulated proton therapy or double-scattered proton therapy versus static intensity-modulated radiation therapy or volumetric arc photon therapy. The outcomes and costs are further modified by the facility-specific image guidance, motion management, and robust optimization. Nevertheless, some broad conclusions can be drawn concerning the advantages of protons over photons in radiation delivery.
Proton therapy has the potential to improve radiation dose homogeneity, especially within the PTV. Plan homogeneity is desirable with fractionated radiation therapy a homogenous plan avoids delivering hot spots, which are areas of unintentionally elevated dose either within the target volume or in the surrounding organs at risk. Trofimov et al showed that proton therapy reduced the maximum dose and the volume receiving more than 110% of the maximum dose when compared with IMRT among patients treated for prostate cancer.
Read Also: What Is The Scale For Prostate Cancer
How Do I Prepare For Proton Therapy
Proton therapy facilities are growing in number, but the treatment is still not available everywhere. Your doctor can let you know if theres a proton treatment center near you. If there is, there are a few things to think about in advance.
Treatment usually means going in five days a week for four to eight weeks, so youll want to clear your calendar. Although the actual treatment only takes a few minutes, you should probably block 45 minutes to an hour for the whole procedure.
Before you start treatment, youll have an initial consultation so the radiation team can get set up for future visits. Using a series of images and other data, theyll determine exactly how youll need to be positioned during therapy. It may involve the use of customized immobilization devices. This can be an involved procedure, but its necessary to ensure that protons are delivered precisely to improve your outlook.
No other preparation is necessary.
