Coping With Prostate Cancer
The diagnosis of cancer can cause great anxiety to the individual and his family and friends. At times, one may have troubles coping with the diagnosis, the disease, and its treatment. Searching online for information may prove overwhelming also and may not be the best resource. Ask your physician or local hospital about local resources. Often, there are local prostate cancer support groups which may help you cope with your feelings and provide local resources for more knowledge.
You may consider contacting one or more of the following organizations:
- US Prostate Cancer Foundation,
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ,
- American Cancer Society, and
- Patient Advocates for Advanced Cancer Treatment.
The Internet has provided access to a number of sites focusing on prostate cancer treatment and outcomes. The National Cancer Institute and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network have patient information, as well as the American Urological Association.
What Is Advanced Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer spreads beyond the prostate or returns after treatment, it is often called advanced prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is often grouped into four stages, with stages III and IV being more advanced prostate cancer.
- Early Stage | Stages I & II: The tumor has not spread beyond the prostate.
- Locally Advanced | Stage III: Cancer has spread outside the prostate but only to nearby tissues.
- Advanced | Stage IV: Cancer has spread outside the prostate to other parts such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver or lungs.
When an early stage prostate cancer is found, it may be treated or placed on surveillance . Advanced prostate cancer is not curable, but there are many ways to treat it. Treatment can help slow advanced prostate cancer progression.
There are several types of advanced prostate cancer, including:
Biochemical Recurrence
With biochemical recurrence, the prostate-specific antigen level has risen after treatment using surgery or radiation, with no other sign of cancer.
Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Non-Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer that no longer responds to hormone treatment and is only found in the prostate. This is found by a rise in the PSA level, while the testosterone level stays low. Imaging tests do not show signs the cancer has spread.
Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Lymph nodes outside the pelvis
- Bones
- Other organs, such as liver or lungs
Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
Help Getting Through Cancer Treatment
People with cancer need support and information, no matter what stage of illness they may be in. Knowing all of your options and finding the resources you need will help you make informed decisions about your care.
Whether you are thinking about treatment, getting treatment, or not being treated at all, you can still get supportive care to help with pain or other symptoms. Communicating with your cancer care team is important so you understand your diagnosis, what treatment is recommended, and ways to maintain or improve your quality of life.
Different types of programs and support services may be helpful, and can be an important part of your care. These might include nursing or social work services, financial aid, nutritional advice, rehab, or spiritual help.
The American Cancer Society also has programs and services including rides to treatment, lodging, and more to help you get through treatment. Call our National Cancer Information Center at 1-800-227-2345 and speak with one of our trained specialists.
Also Check: Can You Have Your Prostate Removed
Treatment Options For Advanced Prostate Cancer
Its rare for prostate cancer to metastasize, or spread to other parts of the body. In about 90 percent of all cases, this type of prostate cancer is diagnosed in its early stages, when the disease is confined to the prostate. However, when the disease metastasizes, prostate cancer cells tend to spread to the brain, bones, lungs and liver. Metastatic prostate cancer cells may also be found in lymph nodes outside the pelvis.
In some cases, the treatment options for advanced prostate cancer may be considered palliative, used to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment options include:
How Is Stage I Prostate Cancer Treated
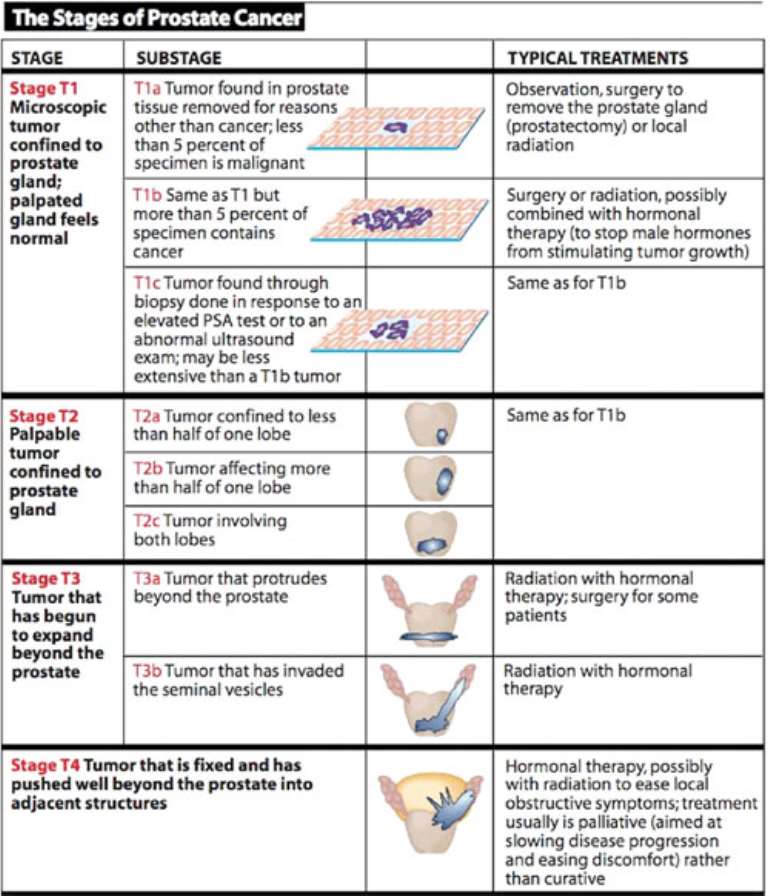
As the cancer is small and is confined to the prostate gland and the growth and spread may be slow and it may never show symptoms. The course of action depends on the age of the patient and their overall health and if they can withstand the treatment. The following are the treatment methods generally preferred for stage I prostate cancer treatment:
Active surveillance:
Because this cancer type grows very slowly, men may often not require any treatment immediately if not throughout their lifetime. Active surveillance is a method of monitoring the cancer closely regularly. PSA blood test, DRE , prostate biopsies may be done once in six months or so. If the results show signs of the cancer spreading, the treatment options are reviewed to eliminate the cancer.
Radiation therapy:
This treatment uses high beams of x-rays to kill the malignant cells. The radiation is aimed at the cancer cells to kill them, restrict their growth and to shrink tumours. The two main types of radiation therapy used in the treatment of prostate cancer:
Radical prostatectomy:
Also Check: Does Frequent Sex Help Prevent Prostate Cancer
If Your Prostate Cancer Comes Back
If your cancer goes into remission but later returns, follow-up treatments will depend on where the cancer is located and which treatments youâve already tried.
- If the cancer is contained in your prostate, surgery or a second attempt at radiation is suggested. If you’ve had a radical prostatectomy, radiation therapy is a good option. If you had radiation, radical prostatectomy might be the best approach. Cryosurgery might also be an option.
- If the cancer has spread to other parts of your body, hormone therapy might be the most effective treatment. External or IV radiation therapy or bisphosphonate drugs can relieve your bone pain.
Show Sources
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis and treatment options depend on the following:
- The stage of the cancer .
- The patients age.
- Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred .
Treatment options also may depend on the following:
- Whether the patient has other health problems.
- The expected side effects of treatment.
- Past treatment for prostate cancer.
- The wishes of the patient.
Most men diagnosed with prostate cancer do not die of it.
Recommended Reading: How Far Is The Prostate Gland
Choosing A Treatment Option
Treatment Options for Localized or Locally Advanced Prostate CancerA man diagnosed with localized or locally advanced prostate cancer has 3 major treatment options: Active Surveillance, surgery, and radiation therapy. For patients whose cancer appears more aggressive, combination treatment may be recommended. For …
Treatment Option Overview For Prostate Cancer
In This Section
Local treatment modalities are associated with prolonged disease-free survival for many patients with localized prostate cancer but are rarely curative in patients with locally extensive tumors. Because of clinical understaging using current diagnostic techniques, even when the cancer appears clinically localized to the prostate gland, some patients develop disseminated tumors after local therapy with surgery or radiation.
Treatment options for each stage of prostate cancer are presented in Table 6.
| Stage | Standard Treatment Options |
|---|---|
| EBRT = external-beam radiation therapy LH-RH = luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone PARP = poly polymerase TURP = transurethral resection of the prostate. | |
| Stage I Prostate Cancer | |
| PARP inhibitors for men with prostate cancer and BRCA1, BRCA2, and/or ATM mutations |
Recommended Reading: Can Prostate Issues Cause Erectile Dysfunction
What Are The Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Your healthcare provider uses the Gleason score and Grade Groups to stage prostate cancer based on its projected aggressiveness. To get this information, the pathologist:
- Assigns a grade to each type of cell in your sample. Cells are graded on a scale of three to five . Samples that test in the one to two range are considered normal tissue.
- Adds together the two most common grades to get your Gleason score .
- Uses the Gleason score to place you into a Grade Group ranging from one to five. A Gleason score of six puts you in Grade Group 1 . A score of nine or higher puts you in Grade Group five . Samples with a higher portion of more aggressive cells receive a higher Grade Group.
What Are Prostate Cancer Treatment Side Effects
Some prostate cancer treatments can affect the bladder, erectile nerves and sphincter muscle, which controls urination. Potential problems include:
- Incontinence: Some men experience urinary incontinence. You may leak urine when you cough or laugh, or you may feel an urgent need to use the bathroom even when your bladder isnt full. This problem can improve over the first six to 12 months without treatment.
- Erectile dysfunction : Surgery, radiation and other treatments can damage the erectile nerves and affect your ability to get or maintain an erection. Some men regain erectile function within a year or two . In the meantime, medications like sildenafil or tadalafil can help by increasing blood flow to the penis.
- Infertility: Treatments can affect your ability to produce or ejaculate sperm, resulting in male infertility. If you think you might want children in the future, you can preserve sperm in a sperm bank before you start treatments. After treatments, you may undergo sperm extraction. This procedure involves removing sperm directly from testicular tissue and implanting it into a womans uterus.
Don’t Miss: Ways To Get Prostate Cancer
Are Prostate Problems Always A Sign Of Prostate Cancer
Not all growths in the prostate are cancerous, and not all prostate problems indicate cancer. Other conditions that cause similar prostate cancer symptoms include:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia : At some point, almost every man will develop benign prostatic hyperplasia . This condition enlarges the prostate gland but doesnt increase cancer risk. The swollen gland squeezes the urethra and blocks the flow of semen and urine. Medications, and sometimes surgery, can help.
- Prostatitis: Men younger than 50 are more prone to prostatitis, inflammation and swelling of the prostate gland. Bacterial infections are often the cause. Treatments include antibiotics or other medications.
What Is The Difference Between Prostate Cancer And Advanced Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland begin to grow out of control. In the early stages of prostate cancer, the cancer cells are only present in the prostate and have not spread to nearby tissues.
Advanced prostate cancer, also known as stage 4 prostate cancer, occurs when cancer cells have spread to other areas of the body.
Don’t Miss: When Should You Get Your Prostate Checked
Survival For All Stages Of Prostate Cancer
Generally for men with prostate cancer in England:
- more than 95 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 1 year or more
- more than 85 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 5 years or more
- almost 80 out of 100 will survive their cancer for 10 years or more
Survival of prostate cancer is also reported in Scotland and Northern Ireland. But it is difficult to compare survival between these countries because of differences in the way the information is collected.
Cancer survival by stage at diagnosis for England, 2019Office for National Statistics
These statistics are for net survival. Net survival estimates the number of people who survive their cancer rather than calculating the number of people diagnosed with cancer who are still alive. In other words, it is the survival of cancer patients after taking into account the background mortality that they would have experienced if they had not had cancer.
Side Effects Of Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy may cause side effects associated with low testosterone, such as hot flashes, sweating, weight gain, reduced sexual desire and depression. Some men also may experience swollen breasts, depression, memory loss and heart problems. Eventually, the cancer may become resistant to hormone therapy. If hormone therapy stops working, doctors may switch treatments.
Don’t Miss: Can Biking Cause Prostate Problems
There Are Three Ways That Cancer Spreads In The Body
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if prostate cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually prostate cancer cells. The disease is metastatic prostate cancer, not bone cancer.
Denosumab, a monoclonal antibody, may be used to preventbone metastases.
Also Check: Does Ejaculation Help With Prostate Cancer
What Treatments Are Available
If you have advanced prostate cancer, treatment wont cure your cancer. But it can help keep it under control and manage any symptoms.
If youve just been diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer, you may be offered the following treatments:
- chemotherapy with hormone therapy
- clinical trials.
Research has found that having radiotherapy together with one of the main treatments listed above can help some men with advanced prostate cancer to live longer. But radiotherapy isnt suitable for all men with advanced prostate cancer.
If you live in Scotland, you may also be offered a type of hormone therapy called abiraterone acetate together with standard hormone therapy. In the rest of the UK, abiraterone is currently only given to men with advanced prostate cancer that has stopped responding to other types of hormone therapy. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence is currently deciding whether to make it available for men who have just been diagnosed with advanced prostate cancer.
Before you start treatment
Before you start any treatment, make sure you have all the information you need. Its important to think about how you would cope with the possible side effects. Speak to your doctor or nurse about this.
It can help to write down any questions you want to ask at your next appointment. It may also help to take someone with you, such as your partner, a family member or friend.
If you have any questions, speak to our Specialist Nurses.
Prognosis And Survival For Prostate Cancer
If you have prostate cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for prostate cancer.
Read Also: Michael Milken Prostate Cancer Diet
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed
Screenings are the most effective way to catch prostate cancer early. If you are at average cancer risk, youll probably have your first prostate screening at age 55. Your healthcare provider may start testing earlier if you have a family history of the disease or are Black. Screening is generally stopped after age 70, but may be continued in certain circumstances.
Screening tests for prostate cancer include:
- Digital rectal exam: Your provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum and feels the prostate gland, which sits in front of the rectum. Bumps or hard areas could indicate cancer.
- Prostate-specific antigen blood test: The prostate gland makes a protein called protein-specific antigen . Elevated PSA levels may indicate cancer. Levels also rise if you have BPH or prostatitis.
- Biopsy: A needle biopsy to sample tissue for cancer cells is the only sure way to diagnose prostate cancer. During an MRI-guided prostate biopsy, magnetic resonance imaging technology provides detailed images of the prostate.
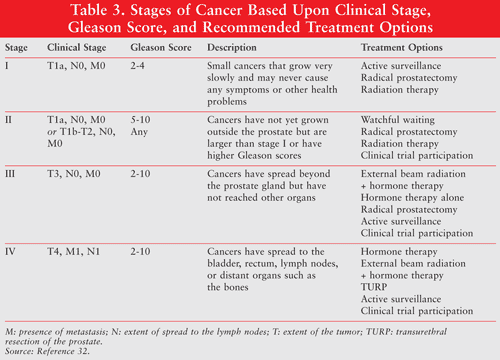
Prostate Cancer Treatment Options By Stage And Risk Group

The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland that produces seminal fluid, which transports sperm. Prostate cancer is one of the most common malignancies, but it responds well to treatment when discovered early. The treatment that you and your doctor decide is most appropriate will be based on several factors, including your age, life expectancy, personal preferences, and the stage of disease. Doctors use several criteria to determine the stage of prostate cancer. They include:
Has the cancer grown and spread? Tests will measure the size and location of the tumor, as well as whether it has spread to the lymph nodes or other tissues outside the prostate gland.
Gleason score. The Gleason score judges the appearance of cells in a sample of prostate tissue. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope and assigns a score from 6 to 10 . The Gleason score is widely used in diagnosing prostate cancer.
Prostate specific antigen. Known as the PSA test for short, this test measures levels of a protein that often rises in the blood when a man has prostate cancer. Many doctors recommend further testing for prostate cancer if a mans PSA rises above 4 ng/dL. Studies show that a man with a PSA level higher than 10 ng/dL has a greater than 50 percent chance of having prostate cancer.
Some doctors also categorize prostate cancer by risk group when making treatment recommendations. In this article, we will look at the different treatments used in each stage and risk group of prostate cancer.
Don’t Miss: How To Check My Prostate At Home
