Side View Of The Prostate
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is just in front of the rectum. The urethra runs through the center of the prostate, from the bladder to the penis, letting urine flow out of the body.
The prostate secretes fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. During ejaculation, the prostate squeezes this fluid into the urethra, and itâs expelled with sperm as semen.
The vasa deferentia bring sperm from the testes to the seminal vesicles. The seminal vesicles contribute fluid to semen during ejaculation.
> > > All Natural Technique Fixes Enlarged Prostate Watch Here< <
Surgical procedures to remove the diseased prostate are usually necessary. Surgical procedures are not always necessary. If the disease is caused by bacterial infections, a doctor can treat the symptoms using alpha-blockers or surgery. Physical therapy, relaxation exercises, and warm baths are all recommended. A physician may also prescribe antibiotics to cure the infection. A bacterial infection can also cause a recurrence of the condition.
An enlarged prostate can be uncomfortable for both men and women. Some of the symptoms of an enlarged male reproductive organ include a weakened urine stream, urgent need to urinate, and urinary tract infections. BPH can also cause damage to the kidneys. A sudden inability to urinate can be life-threatening, as it can lead to bladder and kidney damage. Unfortunately, most men with enlarged prostrates put up with the symptoms for years before they seek treatment. However, many of the men with symptoms finally decide to go to a doctor for proper gynecological evaluation and to begin enlarged prostatic therapy.
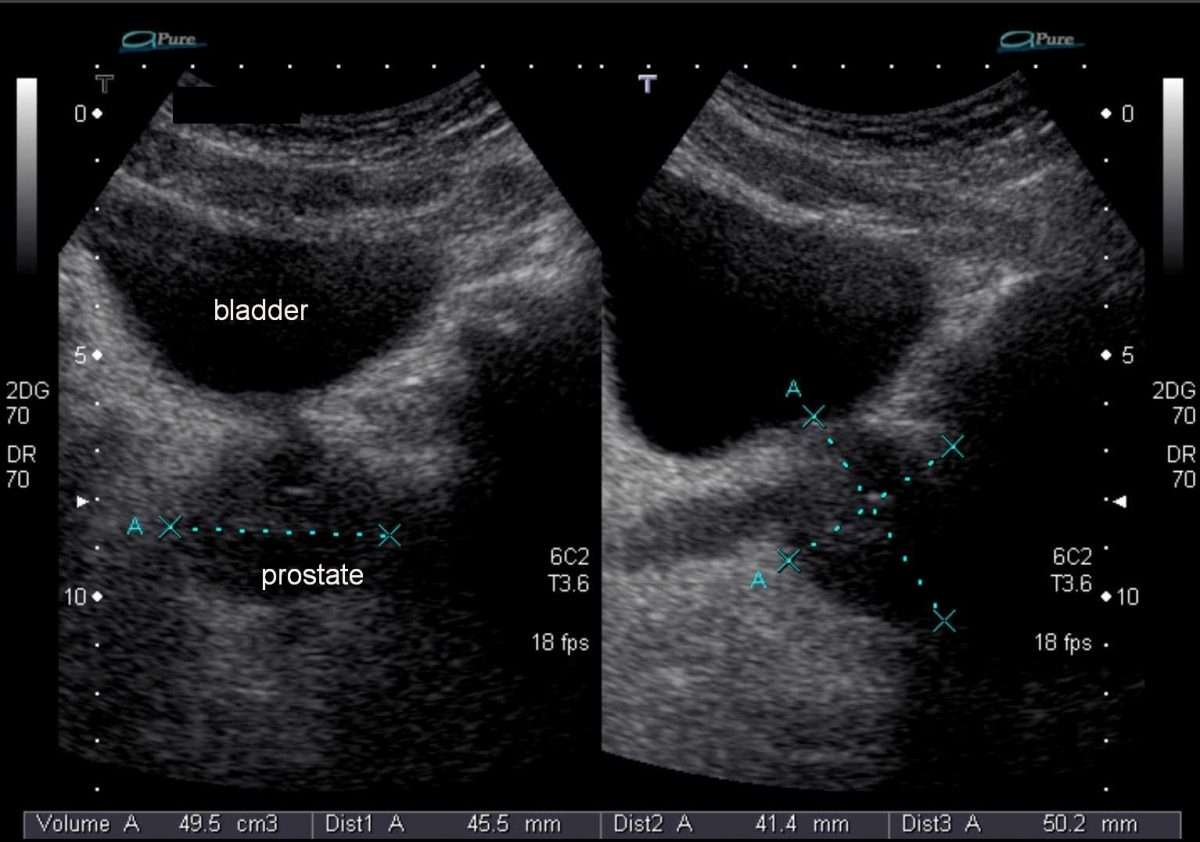
Relationship Between Measured And Estimated Prostate Volumes
The estimated volume from TRUS imaging assumes an ellipsoid geometrical shape of the prostate using the formula . In order to identify the best coefficient for this series of 153 fresh prostate specimens, we used the measured prostate weight converted to measured prostate volume by using 1.02g/cc as the density, as defined above. Thus, the mean measured volume of our cohort was 48.1cc .
Measured prostate volumes along with TRUS-obtained prostate dimensions were then used to calculate a new coefficient from the rearranged algebraic formula: Coefficient=V/L x H x W, where L, H and W were all obtained by TRUS, and V is the measured prostatic volume of fresh prostates, obtained just after surgery, as mentioned above. This calculation was performed for each of the 153 prostates, which led to a calculated mean coefficient of 0.66.
Linear regression plots were created in order to compare the newfound coefficient of 0.66 with the ellipsoid coefficient of 0.52. Figure a shows that plotting estimated prostate volumes against measured prostate volumes using 0.66 as a coefficient yielded an equation of y=0.892x+8.8829 with an R2 value of 0.42 . By performing the same analysis using 0.52 as the coefficient, the equation generated was y=0.5652x+13.028 with R2=0.32 .
Fig. 1Fig. 2Fig. 3
Recommended Reading: Does Prostate Cancer Come Back
Also Check: How Deep Is The Prostate
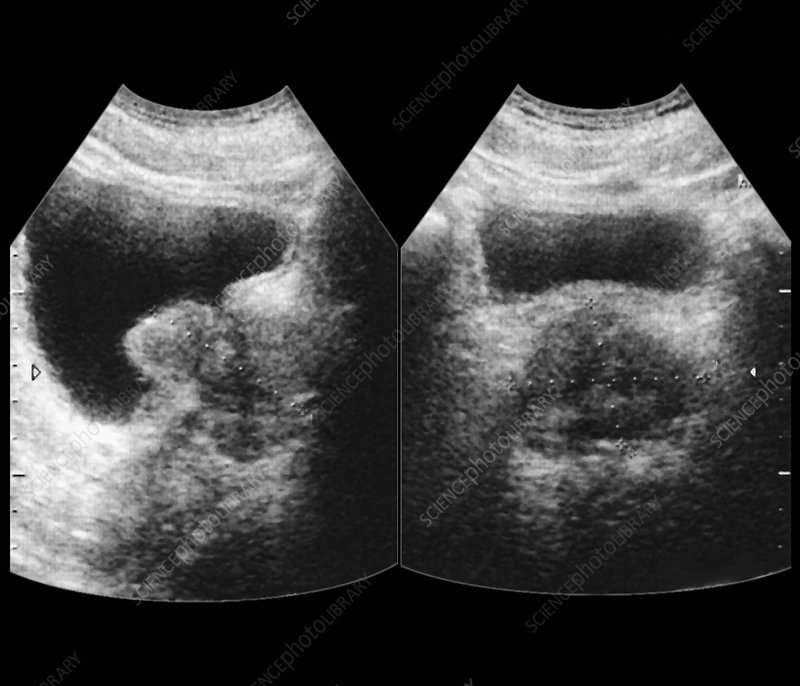
How Is Trus Performed
The patient traditionally lies on his left side, which is considered a more relaxing position as well as allowing for easier insertion of the rectal probe. After the probe is inserted into the rectum, the tester adjusts the console on the ultrasound machine to a baseline for the echoes of normal prostate tissue, which will serve as the standard by which other tissue will be classified. Imaging usually starts at the base of the bladder, as the probe is rotated to provide a full picture of the prostate.
What Does The Equipment Look Like
Ultrasound machines consist of a computer console, video monitor and an attached transducer. The transducer is a small hand-held device that resembles a microphone. Some exams may use different transducers during a single exam. The transducer sends out inaudible, high-frequency sound waves into the body and listens for the returning echoes. The same principles apply to sonar used by boats and submarines.
The technologist applies a small amount of gel to the area under examination and places the transducer there. The gel allows sound waves to travel back and forth between the transducer and the area under examination. The ultrasound image is immediately visible on a video monitor. The computer creates the image based on the loudness , pitch , and time it takes for the ultrasound signal to return to the transducer. It also considers what type of body structure and/or tissue the sound is traveling through.
For ultrasound procedures such as transrectal exams that require insertion of an imaging probe, also called a transducer, the device is covered and lubricated with a gel.
You May Like: What Is The Main Function Of The Prostate Gland
What Happens During A Prostate/rectal Ultrasound
You may have a prostate/rectal ultrasound done as an outpatient or during ahospital stay. The way the test is done may vary depending on yourcondition and your healthcare provider’s practices.
Generally, a prostate/rectal ultrasound follows this process:
You will need to remove any clothing, jewelry, or other objects that may get in the way of the procedure.
If asked to remove clothing, you will be given a gown to wear.
You will lie on an exam table on your left side with your knees bent up to your chest.
The healthcare provider may do a digital rectal exam before the ultrasound.
The provider puts a clear gel on the transducer and puts the probe into the rectum. You may feel a fullness of the rectum at this time.
The provider will turn the transducer slightly several times to see different parts of the prostate gland and other structures.
If blood flow is being looked at, you may hear a whoosh, whoosh sound when the Doppler probe is used.
Once the test is done, the provider will wipe off the gel.
A prostate/rectal ultrasound may be uncomfortable and you will need toremain still during the test. The gel will also feel cool and wet. Thetechnologist will use all possible comfort measures and do the scan asquickly as possible to minimize any discomfort.
How Is The Psa Test Used In Men Who Have Been Treated For Prostate Cancer
The PSA test is often used to monitor patients who have a history of prostate cancer to see if their cancer has recurred . If a mans PSA level begins to rise after prostate cancer treatment, it may be the first sign of a recurrence. Such a biochemical relapse typically appears months or years before other clinical signs and symptoms of prostate cancer recurrence.
However, a single elevated PSA measurement in a patient who has a history of prostate cancer does not always mean that the cancer has come back. A man who has been treated for prostate cancer should discuss an elevated PSA level with his doctor. The doctor may recommend repeating the PSA test or performing other tests to check for evidence of a recurrence. The doctor may look for a trend of rising PSA level over time rather than a single elevated PSA level.
Also Check: How To Shrink Prostate Gland
Read Also: What Is Laparoscopic Prostate Surgery
Prostate Volume And Bph Prevalence Among Tsimane
Prostate volumes ranged from 4 to 67 cc, with a median volume of 16.5 cc. Prostate volume increased with age equivalent to 0.109 cc/y, controlling for height . The prevalence of anatomical BPH was positively associated with age, with the odds of BPH increasing each year by approximately 3.4% controlling for height.
Prostate volume by age. Cross population comparison of prostate volumes with a 95% confidence interval for Tsimane men. The dashed line indicates prostate size for Tsimane men if their height was scaled up to that of adult U.S. males.
What Happens After A Prostate Ultrasound
Once the test is done, you can take off the gown and put your clothes back on. Your rectum may feel tender for a few days, but you wont need to follow any specific aftercare instructions. Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic to prevent infection.
In some cases, your doctor or technician may ask you to wait in the facility until your results are available. Youll usually need to wait a few days for a radiologist to look at the images and diagnose any conditions, however. Depending on where the test was done, you may wait up to two weeks for results.
Your doctor will schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss your test results. If you have any abnormalities or conditions that are visible on the images, your doctor will point out these areas. Excess tissue, prostate enlargement, or cancerous tumors will appear on the ultrasound images as bright white areas that represent the dense tissue.
Also Check: Is Riding A Bike Bad For Your Prostate
How Is A Prostate Ultrasound Done
When you get to the facility for the test, an ultrasound technician may ask you to take off your clothes and change into a gown. Then, the technician will ask you to lie down on your back or side on an examination table and bend your knees.
To perform a transrectal ultrasound , the technician covers a small imaging tool called a transducer with ultrasound gel to help the tool broadcast good images. Then, the technician slowly inserts the transducer into your rectum and moves it around gently to get images of your prostate from various angles. For a biopsy, the technician will slowly insert a needle alongside the transducer into your prostate to remove the tissue.
Your rectum might feel like its swelling while the transducers inside, and the gel can feel damp and cold. Let the technician know if youre uncomfortable during the procedure. Your technician may use local anesthesia or a sedative to help you feel you more comfortable.
How Do I Get Ready For A Prostate/rectal Ultrasound
-
Your healthcare provider will explain the procedure and you can ask questions. Make a list of questions and any concerns with your healthcare provider before the procedure. Consider bringing a family member or trusted friend to the medical appointment to help you remember your questions and concerns.
-
You may be asked to sign a consent form that gives your permission to do the procedure. Read the form carefully and ask questions if something is not clear.
-
You may be asked to stop taking blood-thinning medicines, such as aspirin, for a week or so before the test if it is being done as part of a biopsy.
-
You usually do not need to stop eating or drinking before the test. You also usually will not need medicine to help you relax .
-
You may be given a small enema before the test.
-
Follow any other instructions your provider gives you to get ready.
Read Also: How Do Prostate Problems Start
How Is Bph Diagnosed
After evaluating your medical history and giving you a complete physical, your doctor will perform a digital rectal examination.
Because the prostate gland is in front of the rectum, the doctor can feel if the back of the gland has any abnormalities during this examination. This enables the doctor to estimate the size of the prostate and to detect any hard areas that could be cancer.
Several studies may be done to help diagnose your condition:
- A urine test called a urinalysis
- A seven-question BPH Symptom Score Index survey to evaluate the severity of your symptoms
- A flow study to see if the urine stream is slow compared with normal flow
- A study to detect how much urine is left in the bladder after urination
Blood And Lymphatic Vessels
The prostate receives blood through the inferior vesical artery, internal pudendal artery, and middle rectal arteries. These vessels enter the prostate on its outer posterior surface where it meets the bladder, and travel forward to the apex of the prostate. Both the inferior vesical and the middle rectal arteries often arise together directly from the internal iliac arteries. On entering the bladder, the inferior vesical artery splits into a urethral branch, supplying the urethral prostate and a capsular branch, which travels around the capsule and has smaller branches which perforate into the prostate.
The veins of the prostate form a network the prostatic venous plexus, primarily around its front and outer surface. This network also receives blood from the deep dorsal vein of the penis, and is connected via branches to the vesical plexus and internal pudendal veins. Veins drain into the vesical and then internal iliac veins.
The lymphatic drainage of the prostate depends on the positioning of the area. Vessels surrounding the vas deferens, some of the vessels in the seminal vesicle, and a vessel from the posterior surface of the prostate drain into the external iliac lymph nodes. Some of the seminal vesicle vessels, prostatic vessels, and vessels from the anterior prostate drain into internal iliac lymph nodes. Vessels of the prostate itself also drain into the obturator and sacral lymph nodes.
-
Microscopic glands of the prostate
Don’t Miss: How To Reduce Prostate Inflamation
Hormones And Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The role of androgens in the development of prostate enlargement is evident, owing to the fact that BPH does not develop in men who have been castrated before puberty and therefore have greatly depleted levels of circulating androgens. Furthermore, in men with BPH, medical or surgical castration has been shown to lead to a reduction in prostate volume.5
For testosterone to have any effect on the prostate, it must be converted to dihydrotestosterone by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase.6 DHT has twice as great an effect on the prostate as testosterone.7
Although testosterone levels decline with age, the concentration of DHT remains constant in both younger and older men, even with a low serum level.5 Circulating DHT, by virtue of its low serum plasma concentration and tight binding to plasma proteins, is of diminished importance as a circulating androgen affecting prostate growth.8
Most of the research on BPH and its pharmaceutical treatment has focused on modulating DHT by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. Other intriguing and accumulating research has illustrated the effects of estrogen or, more importantly, the estrogen:testosterone ratio in aging men and its effects on BPH.
Serum-creatinine concentration or clearance is useful before administration of intravenous contrast media, which might cause acute renal failure in patients with renal insufficiency , and for the adjustment of drug doses.
Table 6.4. Causes for an Increase or Decrease in Serum PSA Concentration
What Is Ultrasound Imaging Of The Prostate
Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. It is safe and painless. It produces pictures of the inside of the body using sound waves. Ultrasound imaging is also called sonography. It uses a small probe called a transducer and gel placed directly on the skin. High-frequency sound waves travel from the probe through the gel into the body. The probe collects the sounds that bounce back. A computer uses those sound waves to create an image. Ultrasound exams do not use radiation . Because ultrasound captures images in real-time, it can show the structure and movement of the body’s internal organs. The images can also show blood flowing through blood vessels.
Prostate ultrasound, also called transrectal ultrasound, provides images of a man’s prostate gland and surrounding tissue. The exam typically requires insertion of an ultrasound probe into the rectum of the patient. The probe sends and receives sound waves through the wall of the rectum into the prostate gland which is situated right in front of the rectum.
You May Like: Is Zinc Good For Prostate Problems
Example Of Confidence Interval For An Individual Patient Using T
Let us follow the prostate volume example as in the preceding section on the standard normal distribution, except that we shall use m and s from the small sample of Table DB1.1 rather than and . For the 10 volumes, m=32.7 ml and s=15.9 ml. Because we are dealing with only one sample, df=n1=9. We therefore need look only at the df=9 row in Table 6.2. The prostate volume 59 ml yields t=/15.9=1.65, which places it 1.65 standard deviations above the mean. This lies between the 1.38 which falls under =0.10 on the 9 df row and 1.83 which falls under =0.05. We can conclude that between 5% and 10% of patients will have volumes greater than this patient. Similarly, the 83-ml prostate yields t=3.16, which is between =0.01 and =0.005 less than 1% of patients will have volumes this large. We do not tabulate t for as many possible values as we do the standard normal, because a full table would be required for every possible df. We can calculate on a computer =0.067 for t=1.65 and =0.006 for t=3.16 if we need them.
R.H. Riffenburgh, in, 2012
What Are The Limitations Of Prostate Ultrasound Imaging
Men who have had the end of their bowel removed during prior surgery are not good candidates for ultrasound of the prostate gland because this type of ultrasound typically requires placing a probe into the rectum.
However, the radiologist may attempt to examine the prostate gland by placing a regular ultrasound imaging probe on the perineal skin of the patient .
Sometimes the gland can be examined by ultrasound this way, but the images may not be as detailed as with the transrectal probe. An MRI of the prostate gland is another alternative imaging option and may be done instead of or in-addition to an ultrasound.
Prostate MRI can sometimes be done without requiring anything to be placed into the rectum. It may be a good option for men who have had their rectum removed.
Also Check: Can You Ejaculate Without A Prostate
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of An Enlarged Prostate
An enlarged prostate is the most common cause of urinary problems in men as they get older. Possible symptoms include:
- a weak flow when you urinate
- a feeling that your bladder hasnt emptied properly
- difficulty starting to urinate
- dribbling urine after you finish urinating
- needing to urinate more often, especially at night
- a sudden urge to urinate you may sometimes leak before you get to the toilet.
You may not get all of these symptoms, and some men with an enlarged prostate dont get any symptoms at all. These symptoms can also be caused by other things, such as cold weather, anxiety, other health problems, lifestyle factors, and some medicines. Blood in your urine may be a symptom of an enlarged prostate. But this is rare and is usually caused by something else.
If you have any of the symptoms above, you should visit your GP to find out what may be causing them.
Read Also: What Age To Get Checked For Prostate Cancer
